Bethany Tunik
Automatic Assessment of Infant Face and Upper-Body Symmetry as Early Signs of Torticollis
Nov 07, 2022Abstract:We apply computer vision pose estimation techniques developed expressly for the data-scarce infant domain to the study of torticollis, a common condition in infants for which early identification and treatment is critical. Specifically, we use a combination of facial landmark and body joint estimation techniques designed for infants to estimate a range of geometric measures pertaining to face and upper body symmetry, drawn from an array of sources in the physical therapy and ophthalmology research literature in torticollis. We gauge performance with a range of metrics and show that the estimates of most these geometric measures are successful, yielding strong to very strong Spearman's $\rho$ correlation with ground truth values. Furthermore, we show that these estimates, derived from pose estimation neural networks designed for the infant domain, cleanly outperform estimates derived from more widely known networks designed for the adult domain
Computer Vision to the Rescue: Infant Postural Symmetry Estimation from Incongruent Annotations
Jul 19, 2022
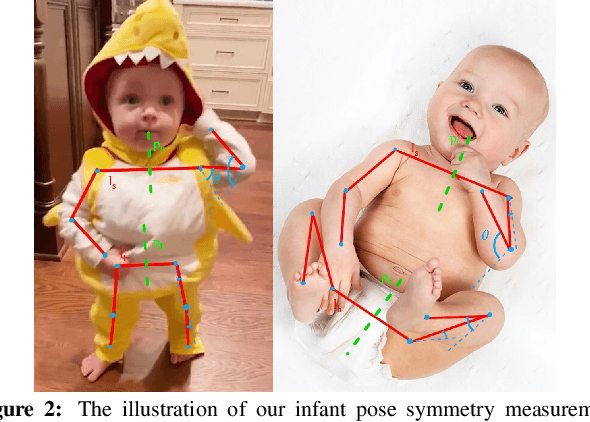

Abstract:Bilateral postural symmetry plays a key role as a potential risk marker for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and as a symptom of congenital muscular torticollis (CMT) in infants, but current methods of assessing symmetry require laborious clinical expert assessments. In this paper, we develop a computer vision based infant symmetry assessment system, leveraging 3D human pose estimation for infants. Evaluation and calibration of our system against ground truth assessments is complicated by our findings from a survey of human ratings of angle and symmetry, that such ratings exhibit low inter-rater reliability. To rectify this, we develop a Bayesian estimator of the ground truth derived from a probabilistic graphical model of fallible human raters. We show that the 3D infant pose estimation model can achieve 68% area under the receiver operating characteristic curve performance in predicting the Bayesian aggregate labels, compared to only 61% from a 2D infant pose estimation model and 60% from a 3D adult pose estimation model, highlighting the importance of 3D poses and infant domain knowledge in assessing infant body symmetry. Our survey analysis also suggests that human ratings are susceptible to higher levels of bias and inconsistency, and hence our final 3D pose-based symmetry assessment system is calibrated but not directly supervised by Bayesian aggregate human ratings, yielding higher levels of consistency and lower levels of inter-limb assessment bias.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge