Berndt Müller
On Understanding the Influence of Controllable Factors with a Feature Attribution Algorithm: a Medical Case Study
Mar 23, 2022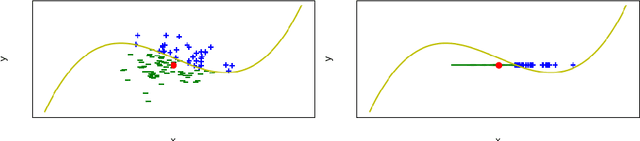


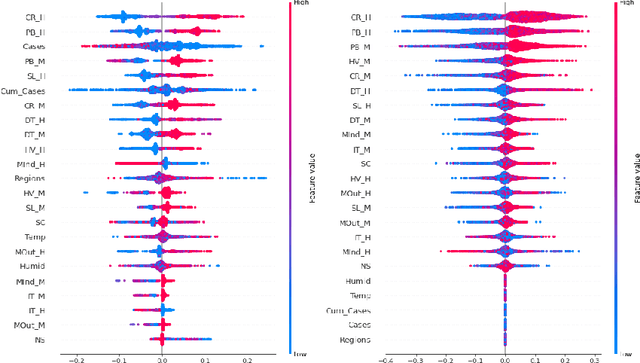
Abstract:Feature attribution XAI algorithms enable their users to gain insight into the underlying patterns of large datasets through their feature importance calculation. Existing feature attribution algorithms treat all features in a dataset homogeneously, which may lead to misinterpretation of consequences of changing feature values. In this work, we consider partitioning features into controllable and uncontrollable parts and propose the Controllable fActor Feature Attribution (CAFA) approach to compute the relative importance of controllable features. We carried out experiments applying CAFA to two existing datasets and our own COVID-19 non-pharmaceutical control measures dataset. Experimental results show that with CAFA, we are able to exclude influences from uncontrollable features in our explanation while keeping the full dataset for prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge