Beomyeol Yu
Equivariant Reinforcement Learning Frameworks for Quadrotor Low-Level Control
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Improving sampling efficiency and generalization capability is critical for the successful data-driven control of quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that are inherently unstable. While various reinforcement learning (RL) approaches have been applied to autonomous quadrotor flight, they often require extensive training data, posing multiple challenges and safety risks in practice. To address these issues, we propose data-efficient, equivariant monolithic and modular RL frameworks for quadrotor low-level control. Specifically, by identifying the rotational and reflectional symmetries in quadrotor dynamics and encoding these symmetries into equivariant network models, we remove redundancies of learning in the state-action space. This approach enables the optimal control action learned in one configuration to automatically generalize into other configurations via symmetry, thereby enhancing data efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that our equivariant approaches significantly outperform their non-equivariant counterparts in terms of learning efficiency and flight performance.
Vision-in-the-loop Simulation for Deep Monocular Pose Estimation of UAV in Ocean Environment
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a vision-in-the-loop simulation environment for deep monocular pose estimation of a UAV operating in an ocean environment. Recently, a deep neural network with a transformer architecture has been successfully trained to estimate the pose of a UAV relative to the flight deck of a research vessel, overcoming several limitations of GPS-based approaches. However, validating the deep pose estimation scheme in an actual ocean environment poses significant challenges due to the limited availability of research vessels and the associated operational costs. To address these issues, we present a photo-realistic 3D virtual environment leveraging recent advancements in Gaussian splatting, a novel technique that represents 3D scenes by modeling image pixels as Gaussian distributions in 3D space, creating a lightweight and high-quality visual model from multiple viewpoints. This approach enables the creation of a virtual environment integrating multiple real-world images collected in situ. The resulting simulation enables the indoor testing of flight maneuvers while verifying all aspects of flight software, hardware, and the deep monocular pose estimation scheme. This approach provides a cost-effective solution for testing and validating the autonomous flight of shipboard UAVs, specifically focusing on vision-based control and estimation algorithms.
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for the Low-Level Control of a Quadrotor UAV
Nov 10, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents multi-agent reinforcement learning frameworks for the low-level control of a quadrotor UAV. While single-agent reinforcement learning has been successfully applied to quadrotors, training a single monolithic network is often data-intensive and time-consuming. To address this, we decompose the quadrotor dynamics into the translational dynamics and the yawing dynamics, and assign a reinforcement learning agent to each part for efficient training and performance improvements. The proposed multi-agent framework for quadrotor low-level control that leverages the underlying structures of the quadrotor dynamics is a unique contribution. Further, we introduce regularization terms to mitigate steady-state errors and to avoid aggressive control inputs. Through benchmark studies with sim-to-sim transfer, it is illustrated that the proposed multi-agent reinforcement learning substantially improves the convergence rate of the training and the stability of the controlled dynamics.
Equivariant Reinforcement Learning for Quadrotor UAV
Jun 02, 2022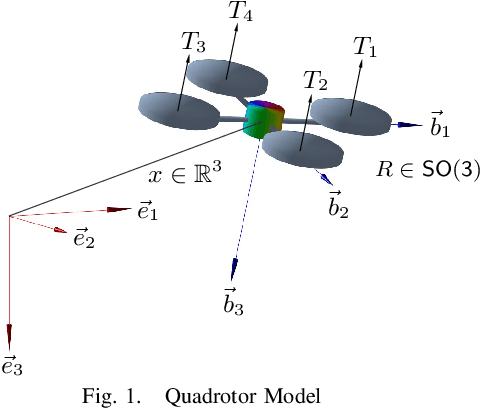
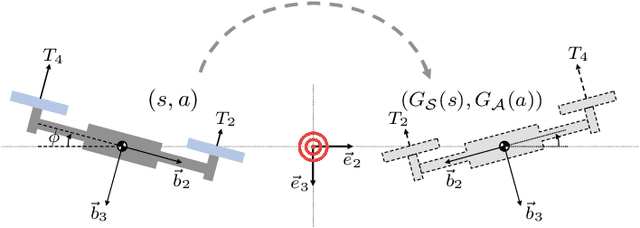
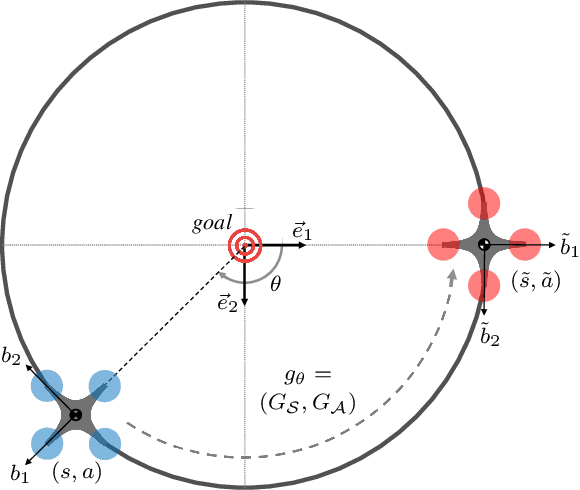
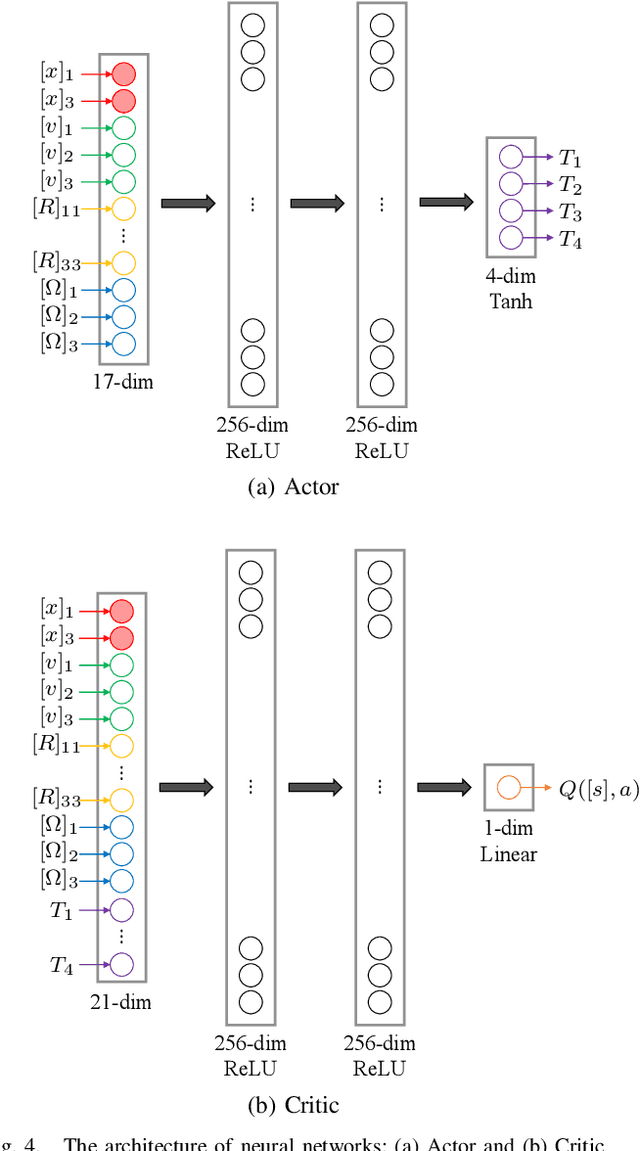
Abstract:This paper presents an equivariant reinforcement learning framework for quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicles. Successful training of reinforcement learning often requires numerous interactions with the environments, which hinders its applicability especially when the available computational resources are limited, or when there is no reliable simulation model. We identified an equivariance property of the quadrotor dynamics such that the dimension of the state required in the training is reduced by one, thereby improving the sampling efficiency of reinforcement learning substantially. This is illustrated by numerical examples with popular reinforcement learning techniques of TD3 and SAC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge