Benoît Huet
Semantic and Visual Similarities for Efficient Knowledge Transfer in CNN Training
Sep 13, 2019
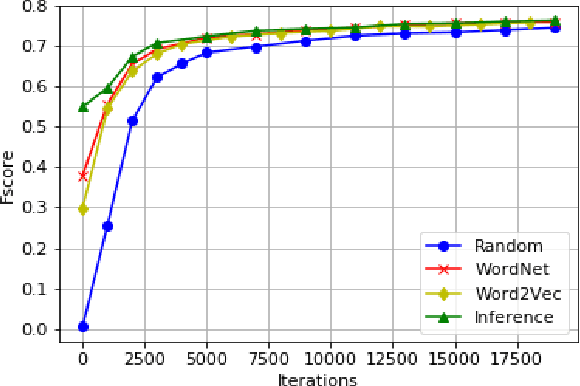
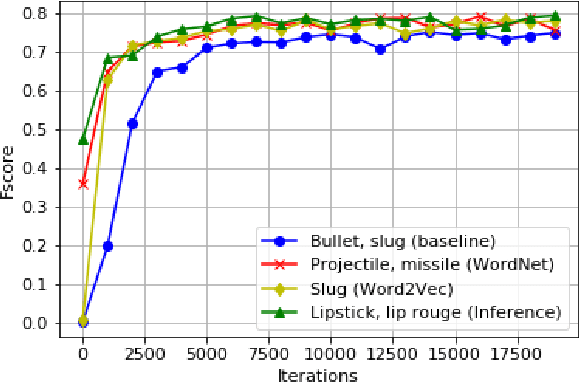
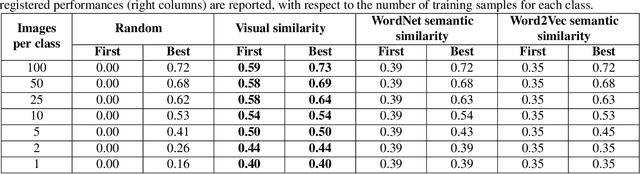
Abstract:In recent years, representation learning approaches have disrupted many multimedia computing tasks. Among those approaches, deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have notably reached human level expertise on some constrained image classification tasks. Nonetheless, training CNNs from scratch for new task or simply new data turns out to be complex and time-consuming. Recently, transfer learning has emerged as an effective methodology for adapting pre-trained CNNs to new data and classes, by only retraining the last classification layer. This paper focuses on improving this process, in order to better transfer knowledge between CNN architectures for faster trainings in the case of fine tuning for image classification. This is achieved by combining and transfering supplementary weights, based on similarity considerations between source and target classes. The study includes a comparison between semantic and content-based similarities, and highlights increased initial performances and training speed, along with superior long term performances when limited training samples are available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge