Benjamin C Yang
Visual Tracking with Intermittent Visibility: Switched Control Design and Implementation
Nov 12, 2024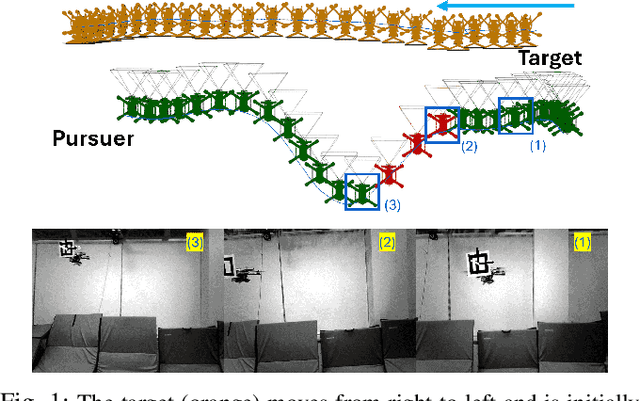
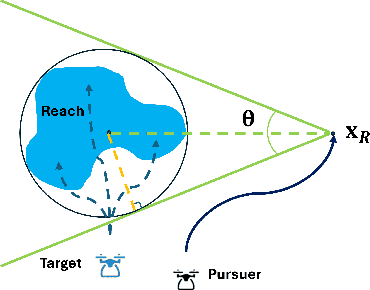
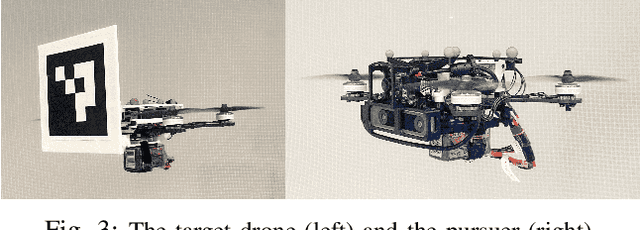
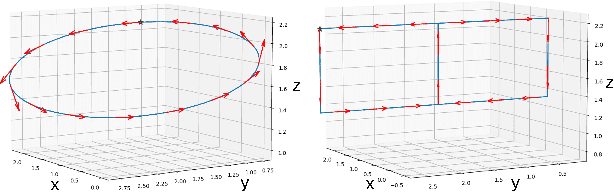
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of visual target tracking in scenarios where a pursuer may experience intermittent loss of visibility of the target. The design of a Switched Visual Tracker (SVT) is presented which aims to meet the competing requirements of maintaining both proximity and visibility. SVT alternates between a visual tracking mode for following the target, and a recovery mode for regaining visual contact when the target falls out of sight. We establish the stability of SVT by extending the average dwell time theorem from switched systems theory, which may be of independent interest. Our implementation of SVT on an Agilicious drone [1] illustrates its effectiveness on tracking various target trajectories: it reduces the average tracking error by up to 45% and significantly improves visibility duration compared to a baseline algorithm. The results show that our approach effectively handles intermittent vision loss, offering enhanced robustness and adaptability for real-world autonomous missions. Additionally, we demonstrate how the stability analysis provides valuable guidance for selecting parameters, such as tracking speed and recovery distance, to optimize the SVT's performance.
Refining Perception Contracts: Case Studies in Vision-based Safe Auto-landing
Nov 15, 2023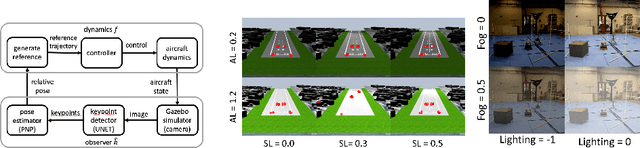
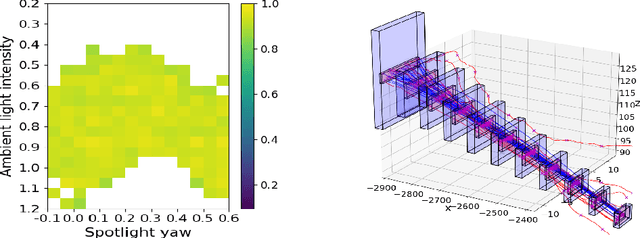
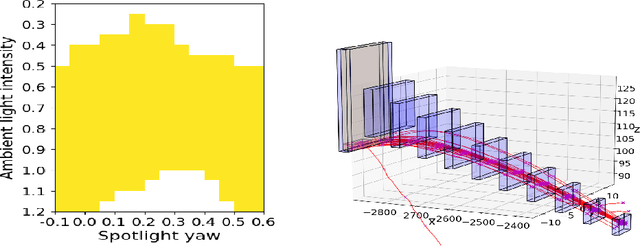
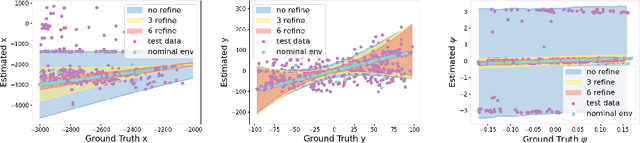
Abstract:Perception contracts provide a method for evaluating safety of control systems that use machine learning for perception. A perception contract is a specification for testing the ML components, and it gives a method for proving end-to-end system-level safety requirements. The feasibility of contract-based testing and assurance was established earlier in the context of straight lane keeping: a 3-dimensional system with relatively simple dynamics. This paper presents the analysis of two 6 and 12-dimensional flight control systems that use multi-stage, heterogeneous, ML-enabled perception. The paper advances methodology by introducing an algorithm for constructing data and requirement guided refinement of perception contracts (DaRePC). The resulting analysis provides testable contracts which establish the state and environment conditions under which an aircraft can safety touchdown on the runway and a drone can safely pass through a sequence of gates. It can also discover conditions (e.g., low-horizon sun) that can possibly violate the safety of the vision-based control system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge