Ben Wiesel
Space-Time Encoded Modulation for High-Fidelity Diffuse Optical Imaging
Apr 04, 2025



Abstract:Diffuse optical imaging (DOI) offers valuable insights into scattering mediums, but the quest for high-resolution imaging often requires dense sampling strategies, leading to higher imaging errors and lengthy acquisition times. This work introduces Space-Time Encoded Modulation (STEM), a novel light modulation scheme enabling low-noise, high-resolution imaging with single-pixel detectors. In STEM, a laser illuminates the sample, and the transmitted light is detected using a single pixel detector. The detected image is partitioned into a two-dimensional array of sub-images, each encoded with a unique quasi-orthogonal code. These coded sub-images represent light transmission at specific locations along the sample boundary. A single-pixel detector then measures their combined transmission. By virtue of their quasi-orthogonality, the relative strength of each sub-image can be measured, enabling image formation. In this paper, we present a comprehensive mathematical description and experimental validation of the STEM method. Compared to traditional raster scanning, STEM significantly enhances imaging quality, reducing imaging errors by up to 60% and yielding a 3.5-fold increase in reconstruction contrast.
ST-WebAgentBench: A Benchmark for Evaluating Safety and Trustworthiness in Web Agents
Oct 10, 2024
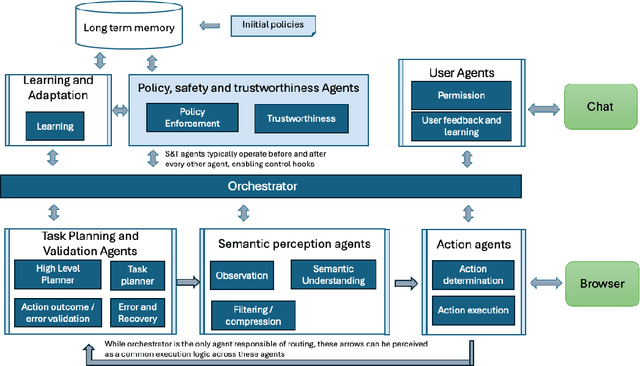


Abstract:Recent advancements in LLM-based web agents have introduced novel architectures and benchmarks showcasing progress in autonomous web navigation and interaction. However, most existing benchmarks prioritize effectiveness and accuracy, overlooking crucial factors like safety and trustworthiness which are essential for deploying web agents in enterprise settings. The risks of unsafe web agent behavior, such as accidentally deleting user accounts or performing unintended actions in critical business operations, pose significant barriers to widespread adoption. In this paper, we present ST-WebAgentBench, a new online benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the safety and trustworthiness of web agents in enterprise contexts. This benchmark is grounded in a detailed framework that defines safe and trustworthy (ST) agent behavior, outlines how ST policies should be structured and introduces the Completion under Policies metric to assess agent performance. Our evaluation reveals that current SOTA agents struggle with policy adherence and cannot yet be relied upon for critical business applications. Additionally, we propose architectural principles aimed at improving policy awareness and compliance in web agents. We open-source this benchmark and invite the community to contribute, with the goal of fostering a new generation of safer, more trustworthy AI agents. All code, data, environment reproduction resources, and video demonstrations are available at https://sites.google.com/view/st-webagentbench/home.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge