Bastian Bunzeck
Dialogue Is Not Enough to Make a Communicative BabyLM (But Neither Is Developmentally Inspired Reinforcement Learning)
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:We investigate whether pre-training exclusively on dialogue data results in formally and functionally apt small language models. Based on this pre-trained llamalogue model, we employ a variety of fine-tuning strategies to enforce "more communicative" text generations by our models. Although our models underperform on most standard BabyLM benchmarks, they excel at dialogue continuation prediction in a minimal pair setting. While PPO fine-tuning has mixed to adversarial effects on our models, DPO fine-tuning further improves their performance on our custom dialogue benchmark.
Do Construction Distributions Shape Formal Language Learning In German BabyLMs?
Mar 14, 2025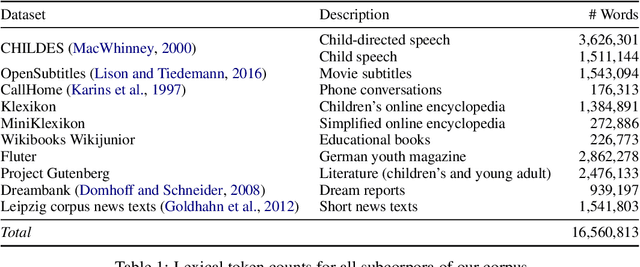
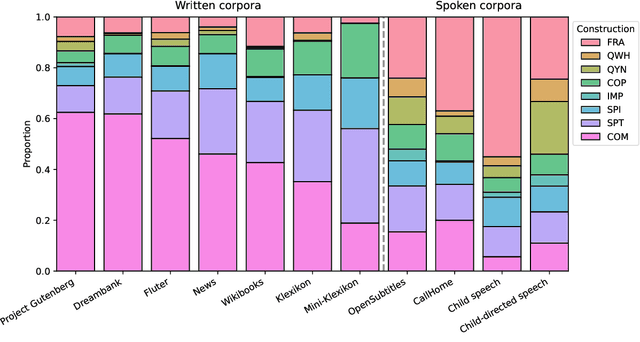
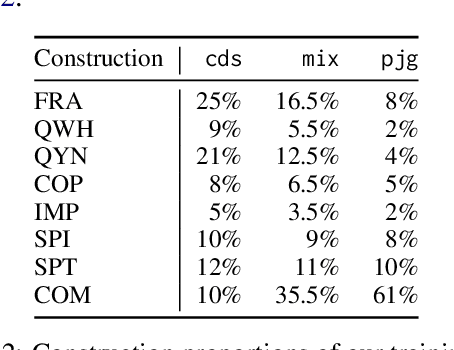
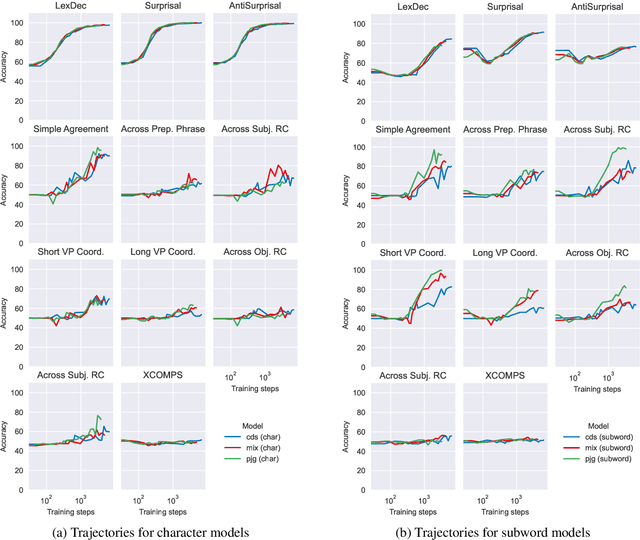
Abstract:We analyze the influence of utterance-level construction distributions in German child-directed speech on the resulting formal linguistic competence and the underlying learning trajectories for small language models trained on a novel collection of developmentally plausible language data for German. We find that trajectories are surprisingly robust for markedly different distributions of constructions in the training data, which have little effect on final accuracies and almost no effect on global learning trajectories. While syntax learning benefits from more complex utterances, lexical learning culminates in better scores with more fragmentary data. We argue that LMs trained on developmentally plausible data can contribute to debates on how rich or impoverished linguistic stimuli actually are.
Subword models struggle with word learning, but surprisal hides it
Feb 18, 2025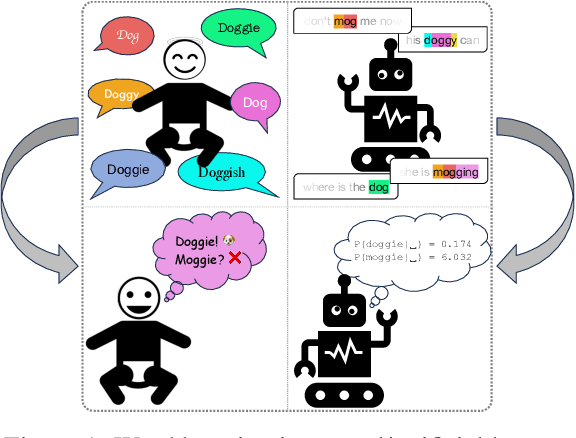
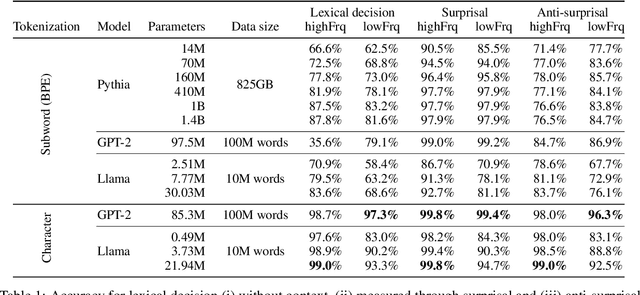
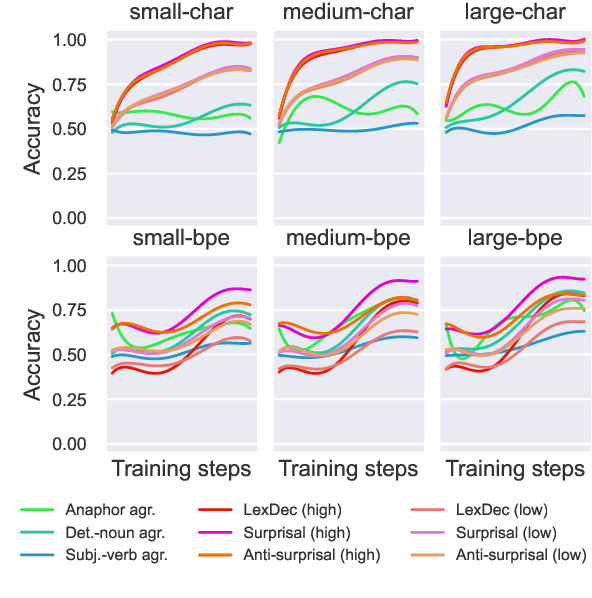
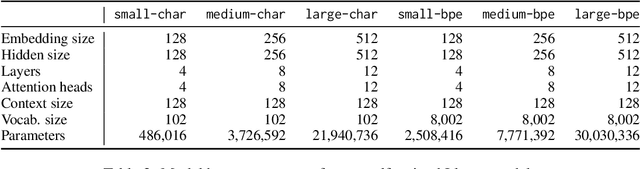
Abstract:We study word learning in subword and character language models with the psycholinguistic lexical decision task. While subword LMs struggle to discern words and non-words with high accuracy, character LMs solve this task easily and consistently. Furthermore, when comparing word learning and syntactic learning, both processes are separable in character LM where word learning predates syntactic learning, whereas these processes are simultaneous in subword LM. This raises questions about the adequacy of subword LMs for modeling language acquisition and positions character LMs as a viable alternative.
Small Language Models Like Small Vocabularies: Probing the Linguistic Abilities of Grapheme- and Phoneme-Based Baby Llamas
Oct 02, 2024

Abstract:Current language models use subword-based tokenization algorithms like Byte Pair Encoding, which put their validity as models of linguistic representations into question. In this paper, we explore the potential of tokenization-free, phoneme- and grapheme-based language models. We demonstrate that small models based on the Llama architecture can achieve strong linguistic performance on standard syntactic and novel lexical/phonetic benchmarks when trained with character-level vocabularies. We further show that phoneme-based models without any graphemic biases almost match grapheme-based models in standard tasks and novel evaluations. Our findings suggest a promising direction for creating more linguistically plausible language models that are better suited for computational studies of language acquisition and processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge