Barbara M. Klinkhammer
Unsupervisedly Training GANs for Segmenting Digital Pathology with Automatically Generated Annotations
Aug 01, 2018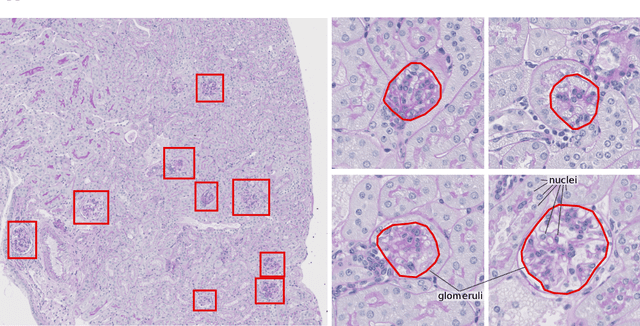
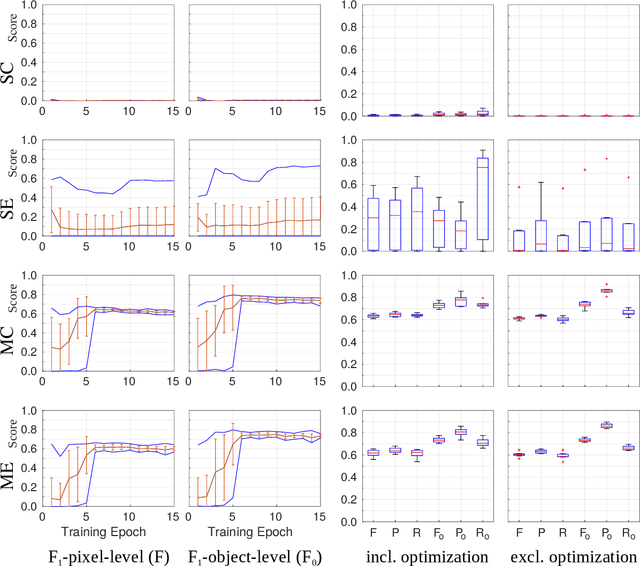
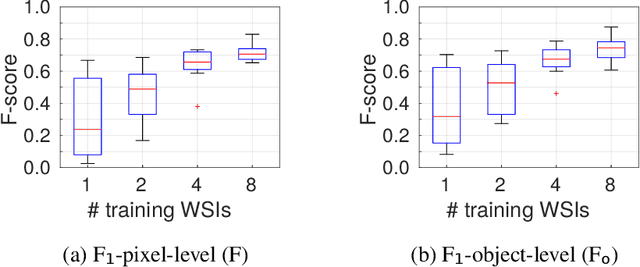
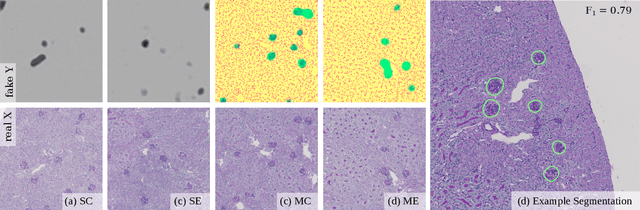
Abstract:Recently, generative adversarial networks exhibited excellent performances in semi-supervised image analysis scenarios. In this paper, we go even further by proposing a fully unsupervised approach for segmentation applications with prior knowledge of the objects' shapes. We propose and investigate different strategies to generate simulated label data and perform image-to-image translation between the image and the label domain using an adversarial model. Specifically, we assess the impact of the annotation model's accuracy as well as the effect of simulating additional low-level image features. For experimental evaluation, we consider the segmentation of the glomeruli, an application scenario from renal pathology. Experiments provide proof of concept and also confirm that the strategy for creating the simulated label data is of particular relevance considering the stability of GAN trainings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge