Bailin Pan
Collective Certified Robustness against Graph Injection Attacks
Mar 03, 2024Abstract:We investigate certified robustness for GNNs under graph injection attacks. Existing research only provides sample-wise certificates by verifying each node independently, leading to very limited certifying performance. In this paper, we present the first collective certificate, which certifies a set of target nodes simultaneously. To achieve it, we formulate the problem as a binary integer quadratic constrained linear programming (BQCLP). We further develop a customized linearization technique that allows us to relax the BQCLP into linear programming (LP) that can be efficiently solved. Through comprehensive experiments, we demonstrate that our collective certification scheme significantly improves certification performance with minimal computational overhead. For instance, by solving the LP within 1 minute on the Citeseer dataset, we achieve a significant increase in the certified ratio from 0.0% to 81.2% when the injected node number is 5% of the graph size. Our step marks a crucial step towards making provable defense more practical.
Node-aware Bi-smoothing: Certified Robustness against Graph Injection Attacks
Dec 07, 2023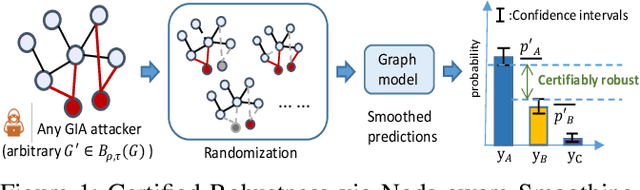
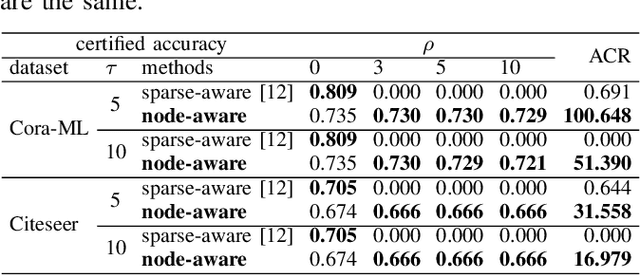
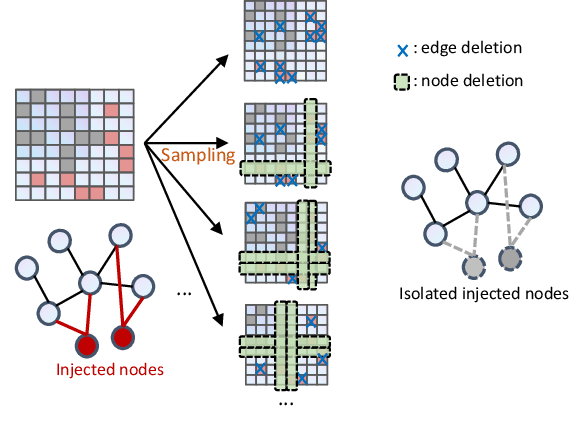
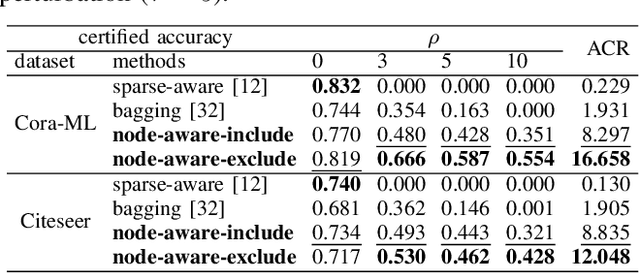
Abstract:Deep Graph Learning (DGL) has emerged as a crucial technique across various domains. However, recent studies have exposed vulnerabilities in DGL models, such as susceptibility to evasion and poisoning attacks. While empirical and provable robustness techniques have been developed to defend against graph modification attacks (GMAs), the problem of certified robustness against graph injection attacks (GIAs) remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce the node-aware bi-smoothing framework, which is the first certifiably robust approach for general node classification tasks against GIAs. Notably, the proposed node-aware bi-smoothing scheme is model-agnostic and is applicable for both evasion and poisoning attacks. Through rigorous theoretical analysis, we establish the certifiable conditions of our smoothing scheme. We also explore the practical implications of our node-aware bi-smoothing schemes in two contexts: as an empirical defense approach against real-world GIAs and in the context of recommendation systems. Furthermore, we extend two state-of-the-art certified robustness frameworks to address node injection attacks and compare our approach against them. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed certificates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge