Aysenur Bilgin
CWI
Is it a Fruit, an Apple or a Granny Smith? Predicting the Basic Level in a Concept Hierarchy
Oct 25, 2019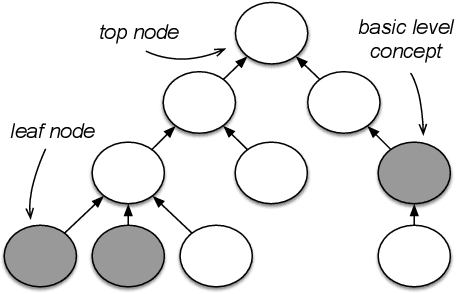
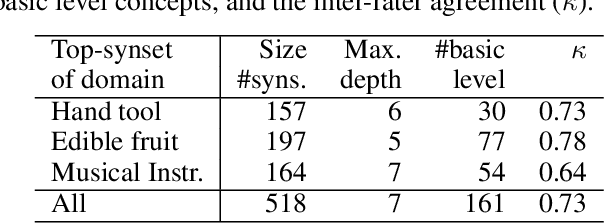
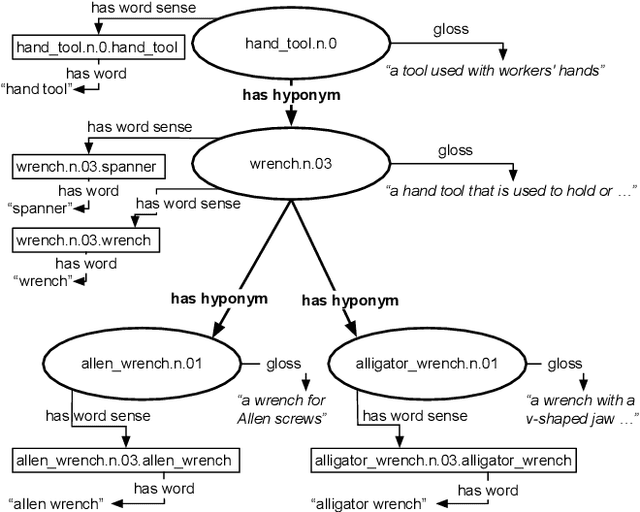
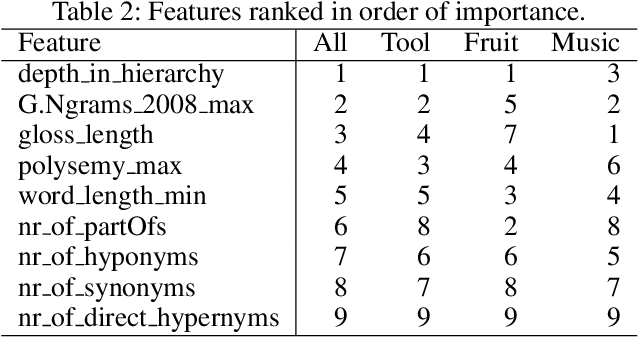
Abstract:The "basic level", according to experiments in cognitive psychology, is the level of abstraction in a hierarchy of concepts at which humans perform tasks quicker and with greater accuracy than at other levels. We argue that applications that use concept hierarchies - such as knowledge graphs, ontologies or taxonomies - could significantly improve their user interfaces if they `knew' which concepts are the basic level concepts. This paper examines to what extent the basic level can be learned from data. We test the utility of three types of concept features, that were inspired by the basic level theory: lexical features, structural features and frequency features. We evaluate our approach on WordNet, and create a training set of manually labelled examples that includes concepts from different domains. Our findings include that the basic level concepts can be accurately identified within one domain. Concepts that are difficult to label for humans are also harder to classify automatically. Our experiments provide insight into how classification performance across domains could be improved, which is necessary for identification of basic level concepts on a larger scale.
Utilizing a Transparency-driven Environment toward Trusted Automatic Genre Classification: A Case Study in Journalism History
Oct 01, 2018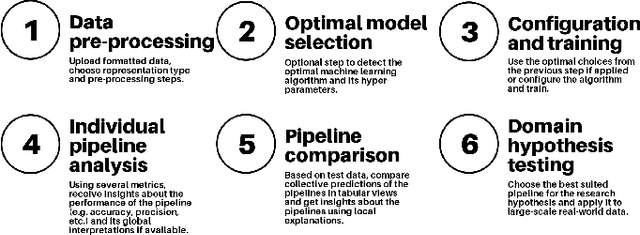
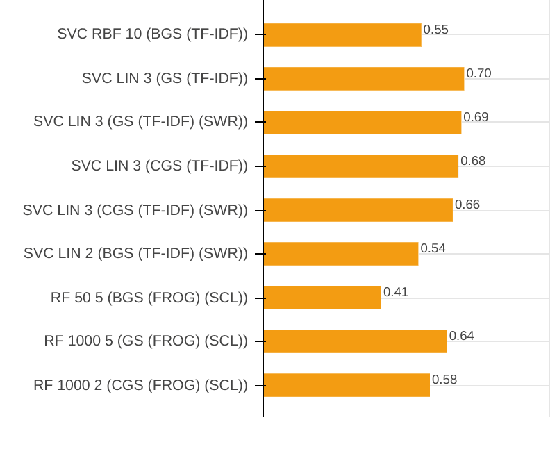
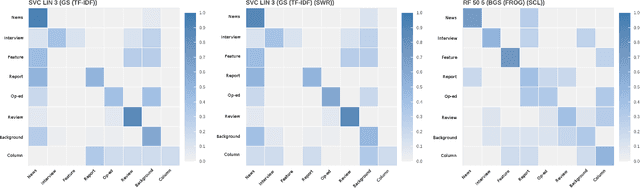
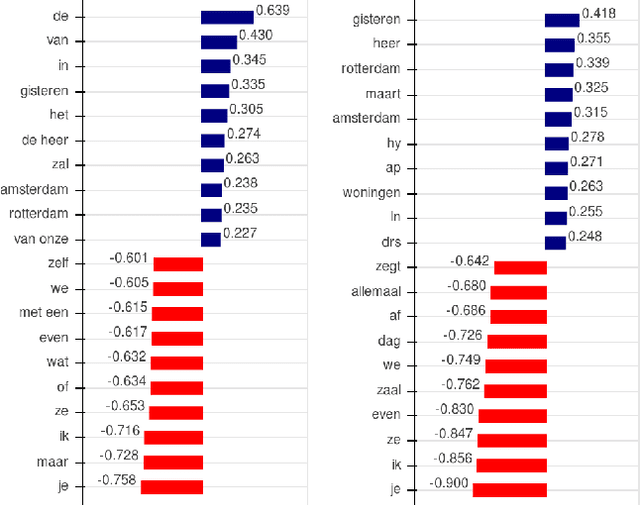
Abstract:With the growing abundance of unlabeled data in real-world tasks, researchers have to rely on the predictions given by black-boxed computational models. However, it is an often neglected fact that these models may be scoring high on accuracy for the wrong reasons. In this paper, we present a practical impact analysis of enabling model transparency by various presentation forms. For this purpose, we developed an environment that empowers non-computer scientists to become practicing data scientists in their own research field. We demonstrate the gradually increasing understanding of journalism historians through a real-world use case study on automatic genre classification of newspaper articles. This study is a first step towards trusted usage of machine learning pipelines in a responsible way.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge