Ayaz Umer
SalNAS: Efficient Saliency-prediction Neural Architecture Search with self-knowledge distillation
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in deep convolutional neural networks have significantly improved the performance of saliency prediction. However, the manual configuration of the neural network architectures requires domain knowledge expertise and can still be time-consuming and error-prone. To solve this, we propose a new Neural Architecture Search (NAS) framework for saliency prediction with two contributions. Firstly, a supernet for saliency prediction is built with a weight-sharing network containing all candidate architectures, by integrating a dynamic convolution into the encoder-decoder in the supernet, termed SalNAS. Secondly, despite the fact that SalNAS is highly efficient (20.98 million parameters), it can suffer from the lack of generalization. To solve this, we propose a self-knowledge distillation approach, termed Self-KD, that trains the student SalNAS with the weighted average information between the ground truth and the prediction from the teacher model. The teacher model, while sharing the same architecture, contains the best-performing weights chosen by cross-validation. Self-KD can generalize well without the need to compute the gradient in the teacher model, enabling an efficient training system. By utilizing Self-KD, SalNAS outperforms other state-of-the-art saliency prediction models in most evaluation rubrics across seven benchmark datasets while being a lightweight model. The code will be available at https://github.com/chakkritte/SalNAS
* Published in Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence
Explainable Knowledge Distillation for On-device Chest X-Ray Classification
May 10, 2023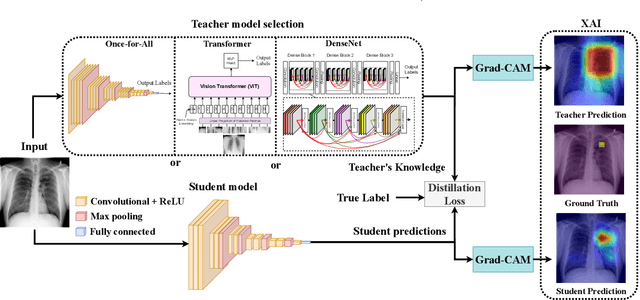
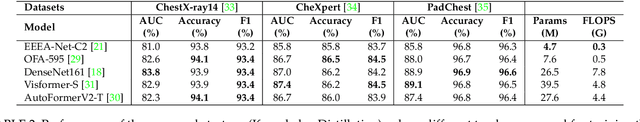
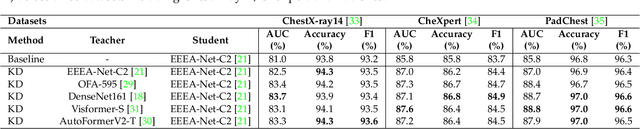
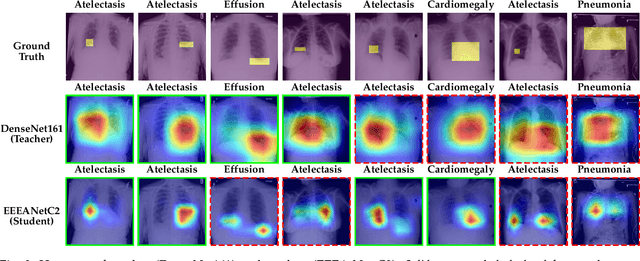
Abstract:Automated multi-label chest X-rays (CXR) image classification has achieved substantial progress in clinical diagnosis via utilizing sophisticated deep learning approaches. However, most deep models have high computational demands, which makes them less feasible for compact devices with low computational requirements. To overcome this problem, we propose a knowledge distillation (KD) strategy to create the compact deep learning model for the real-time multi-label CXR image classification. We study different alternatives of CNNs and Transforms as the teacher to distill the knowledge to a smaller student. Then, we employed explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) to provide the visual explanation for the model decision improved by the KD. Our results on three benchmark CXR datasets show that our KD strategy provides the improved performance on the compact student model, thus being the feasible choice for many limited hardware platforms. For instance, when using DenseNet161 as the teacher network, EEEA-Net-C2 achieved an AUC of 83.7%, 87.1%, and 88.7% on the ChestX-ray14, CheXpert, and PadChest datasets, respectively, with fewer parameters of 4.7 million and computational cost of 0.3 billion FLOPS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge