Aurelien Pelissier
Feature selection as Monte-Carlo Search in Growing Single Rooted Directed Acyclic Graph by Best Leaf Identification
Nov 19, 2018
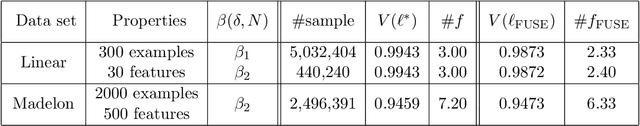
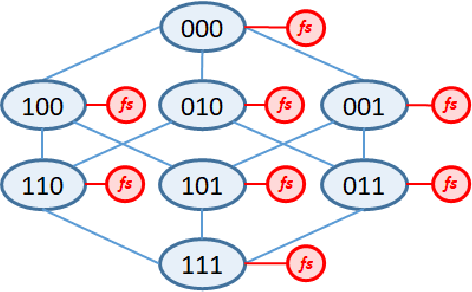
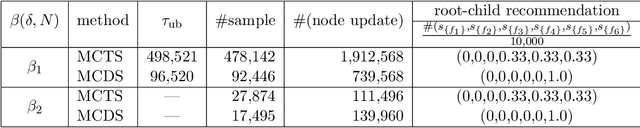
Abstract:Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS) has received considerable interest due to its spectacular success in the difficult problem of computer Go and also proved beneficial in a range of other domains. A major issue that has received little attention in the MCTS literature is the fact that, in most games, different actions can lead to the same state, that may lead to a high degree of redundancy in tree representation and unnecessary additional computational cost. We extend MCTS to single rooted directed acyclic graph (SR-DAG), and consider the Best Arm Identification (BAI) and the Best Leaf Identification (BLI) problem of an expanding SR-DAG of arbitrary depth. We propose algorithms that are (epsilon, delta)-correct in the fixed confidence setting, and prove an asymptotic upper bounds of sample complexity for our BAI algorithm. As a major application for our BLI algorithm, a novel approach for Feature Selection is proposed by representing the feature set space as a SR-DAG and repeatedly evaluating feature subsets until a candidate for the best leaf is returned, a proof of concept is shown on benchmark data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge