Audrey Mash
MT-LENS: An all-in-one Toolkit for Better Machine Translation Evaluation
Dec 16, 2024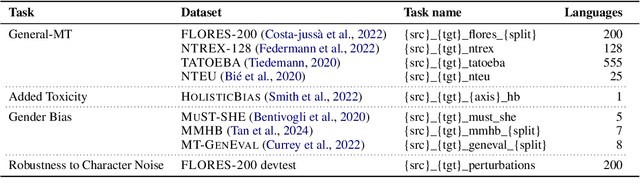
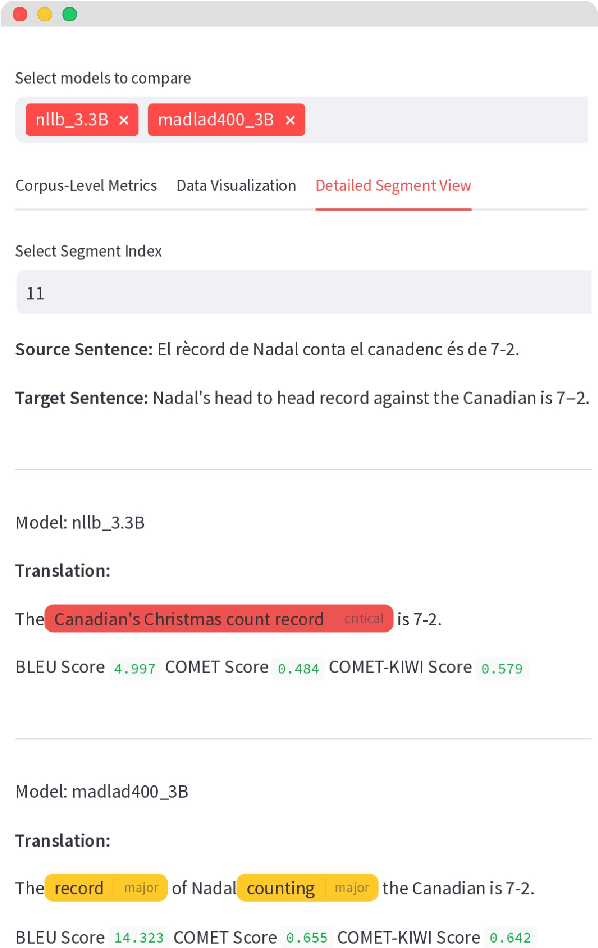
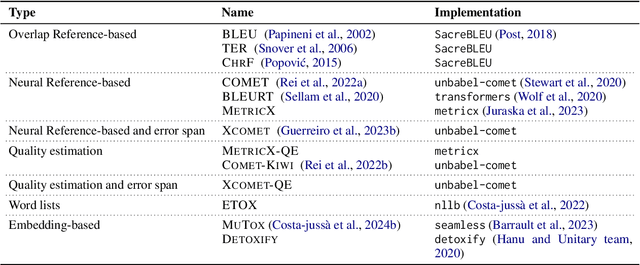
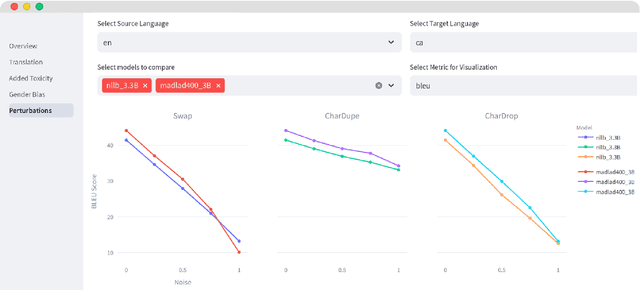
Abstract:We introduce MT-LENS, a framework designed to evaluate Machine Translation (MT) systems across a variety of tasks, including translation quality, gender bias detection, added toxicity, and robustness to misspellings. While several toolkits have become very popular for benchmarking the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), existing evaluation tools often lack the ability to thoroughly assess the diverse aspects of MT performance. MT-LENS addresses these limitations by extending the capabilities of LM-eval-harness for MT, supporting state-of-the-art datasets and a wide range of evaluation metrics. It also offers a user-friendly platform to compare systems and analyze translations with interactive visualizations. MT-LENS aims to broaden access to evaluation strategies that go beyond traditional translation quality evaluation, enabling researchers and engineers to better understand the performance of a NMT model and also easily measure system's biases.
The power of Prompts: Evaluating and Mitigating Gender Bias in MT with LLMs
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:This paper studies gender bias in machine translation through the lens of Large Language Models (LLMs). Four widely-used test sets are employed to benchmark various base LLMs, comparing their translation quality and gender bias against state-of-the-art Neural Machine Translation (NMT) models for English to Catalan (En $\rightarrow$ Ca) and English to Spanish (En $\rightarrow$ Es) translation directions. Our findings reveal pervasive gender bias across all models, with base LLMs exhibiting a higher degree of bias compared to NMT models. To combat this bias, we explore prompting engineering techniques applied to an instruction-tuned LLM. We identify a prompt structure that significantly reduces gender bias by up to 12% on the WinoMT evaluation dataset compared to more straightforward prompts. These results significantly reduce the gender bias accuracy gap between LLMs and traditional NMT systems.
Investigating the translation capabilities of Large Language Models trained on parallel data only
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional proficiency across a broad spectrum of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks, including Machine Translation. However, previous methods predominantly relied on iterative processes such as instruction fine-tuning or continual pre-training, leaving unexplored the challenges of training LLMs solely on parallel data. In this work, we introduce PLUME (Parallel Language Model), a collection of three 2B LLMs featuring varying vocabulary sizes (32k, 128k, and 256k) trained exclusively on Catalan-centric parallel examples. These models perform comparably to previous encoder-decoder architectures on 16 supervised translation directions and 56 zero-shot ones. Utilizing this set of models, we conduct a thorough investigation into the translation capabilities of LLMs, probing their performance, the impact of the different elements of the prompt, and their cross-lingual representation space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge