Asanka G Perera
UAV-GESTURE: A Dataset for UAV Control and Gesture Recognition
Jan 09, 2019
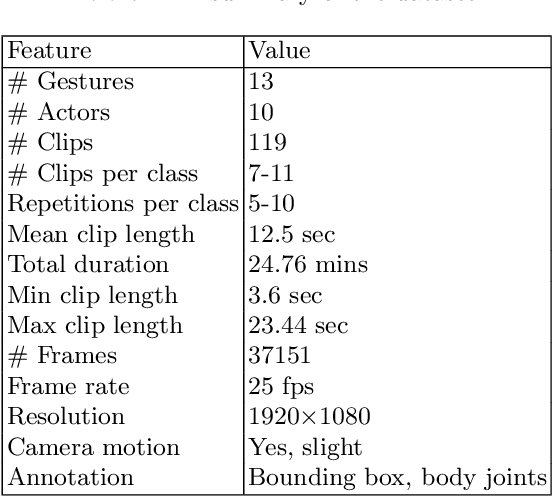


Abstract:Current UAV-recorded datasets are mostly limited to action recognition and object tracking, whereas the gesture signals datasets were mostly recorded in indoor spaces. Currently, there is no outdoor recorded public video dataset for UAV commanding signals. Gesture signals can be effectively used with UAVs by leveraging the UAVs visual sensors and operational simplicity. To fill this gap and enable research in wider application areas, we present a UAV gesture signals dataset recorded in an outdoor setting. We selected 13 gestures suitable for basic UAV navigation and command from general aircraft handling and helicopter handling signals. We provide 119 high-definition video clips consisting of 37151 frames. The overall baseline gesture recognition performance computed using Pose-based Convolutional Neural Network (P-CNN) is 91.9 %. All the frames are annotated with body joints and gesture classes in order to extend the dataset's applicability to a wider research area including gesture recognition, action recognition, human pose recognition and situation awareness.
Human Pose and Path Estimation from Aerial Video using Dynamic Classifier Selection
Dec 16, 2018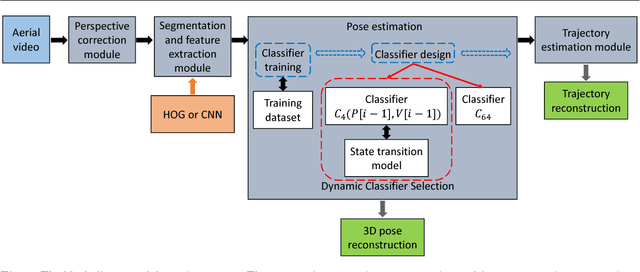

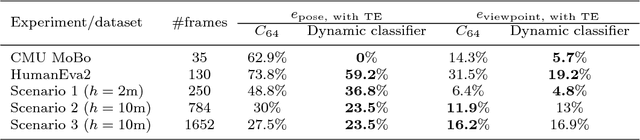

Abstract:We consider the problem of estimating human pose and trajectory by an aerial robot with a monocular camera in near real time. We present a preliminary solution whose distinguishing feature is a dynamic classifier selection architecture. In our solution, each video frame is corrected for perspective using projective transformation. Then, two alternative feature sets are used: (i) Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) of the silhouette, (ii) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) features of the RGB image. The features (HOG or CNN) are classified using a dynamic classifier. A class is defined as a pose-viewpoint pair, and a total of 64 classes are defined to represent a forward walking and turning gait sequence. Our solution provides three main advantages: (i) Classification is efficient due to dynamic selection (4-class vs. 64-class classification). (ii) Classification errors are confined to neighbors of the true view-points. (iii) The robust temporal relationship between poses is used to resolve the left-right ambiguities of human silhouettes. Experiments conducted on both fronto-parallel videos and aerial videos confirm our solution can achieve accurate pose and trajectory estimation for both scenarios. We found using HOG features provides higher accuracy than using CNN features. For example, applying the HOG-based variant of our scheme to the 'walking on a figure 8-shaped path' dataset (1652 frames) achieved estimation accuracies of 99.6% for viewpoints and 96.2% for number of poses.
* For associated dataset, see https://asankagp.github.io/aerialgaitdataset/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge