Arumoy Shome
Data vs. Model Machine Learning Fairness Testing: An Empirical Study
Jan 15, 2024Abstract:Although several fairness definitions and bias mitigation techniques exist in the literature, all existing solutions evaluate fairness of Machine Learning (ML) systems after the training stage. In this paper, we take the first steps towards evaluating a more holistic approach by testing for fairness both before and after model training. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed approach and position it within the ML development lifecycle, using an empirical analysis of the relationship between model dependent and independent fairness metrics. The study uses 2 fairness metrics, 4 ML algorithms, 5 real-world datasets and 1600 fairness evaluation cycles. We find a linear relationship between data and model fairness metrics when the distribution and the size of the training data changes. Our results indicate that testing for fairness prior to training can be a ``cheap'' and effective means of catching a biased data collection process early; detecting data drifts in production systems and minimising execution of full training cycles thus reducing development time and costs.
Data Smells in Public Datasets
Mar 25, 2022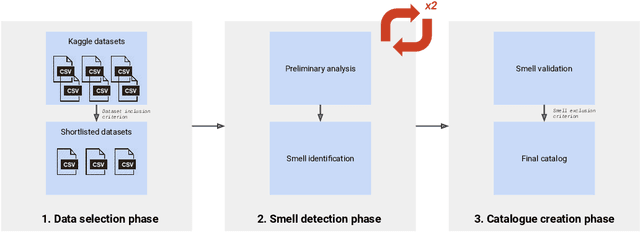
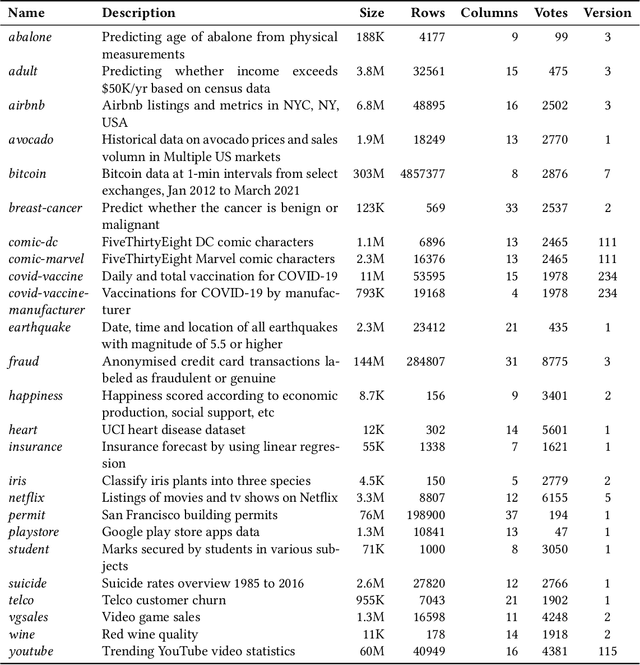
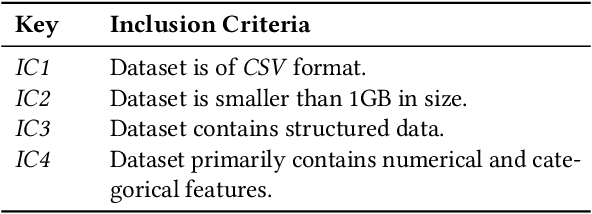
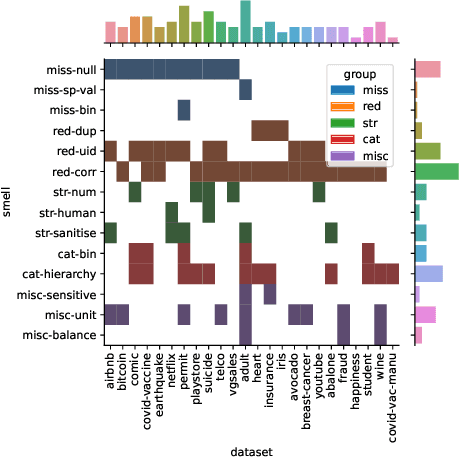
Abstract:The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in high-stakes domains such as healthcare, wildlife preservation, autonomous driving and criminal justice system calls for a data-centric approach to AI. Data scientists spend the majority of their time studying and wrangling the data, yet tools to aid them with data analysis are lacking. This study identifies the recurrent data quality issues in public datasets. Analogous to code smells, we introduce a novel catalogue of data smells that can be used to indicate early signs of problems or technical debt in machine learning systems. To understand the prevalence of data quality issues in datasets, we analyse 25 public datasets and identify 14 data smells.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge