Armin Farhadi
UAV Trajectory Optimization via Improved Noisy Deep Q-Network
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:This paper proposes an Improved Noisy Deep Q-Network (Noisy DQN) to enhance the exploration and stability of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) when applying deep reinforcement learning in simulated environments. This method enhances the exploration ability by combining the residual NoisyLinear layer with an adaptive noise scheduling mechanism, while improving training stability through smooth loss and soft target network updates. Experiments show that the proposed model achieves faster convergence and up to $+40$ higher rewards compared to standard DQN and quickly reach to the minimum number of steps required for the task 28 in the 15 * 15 grid navigation environment set up. The results show that our comprehensive improvements to the network structure of NoisyNet, exploration control, and training stability contribute to enhancing the efficiency and reliability of deep Q-learning.
Resource Allocation in Uplink Multi STAR-RIS-aided NOMA System via Meta-Learning
Jan 13, 2024
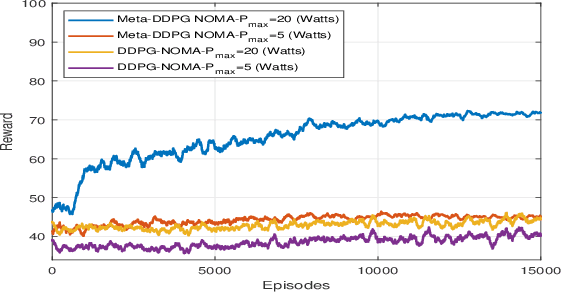

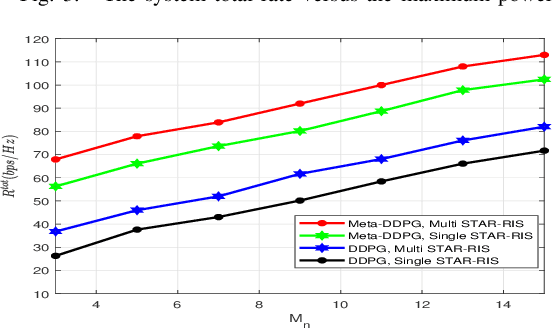
Abstract:Simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS) is a novel technology which enables the full-space coverage by splitting the incident signal into reflected and transmitted signals. In this letter, a multi STAR-RIS-aided system using non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) in an uplink transmission is considered, where the multi-order reflections among multiple STAR-RISs assist the transmission from the single-antenna users to the multi-antenna base station (BS). Specifically, the total sum rate maximization problem is solved by jointly optimizing the active beamforming, power allocation, transmission and reflection beamforming at the STAR-RIS, and user-STAR-RIS association indicator. To solve the non-convex optimization problem, a novel deep reinforcement learning algorithm is proposed which is the combination of meta-learning and deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG), namely Meta-DDPG. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed Meta-DDPG algorithm outperforms the conventional DDPG algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge