Arman Malekzadeh
PREDICT: Persian Reverse Dictionary
May 01, 2021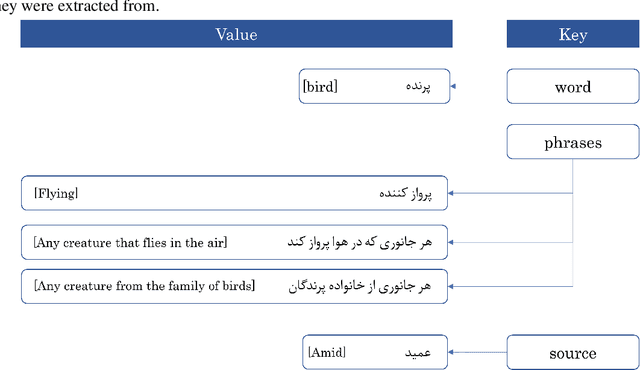
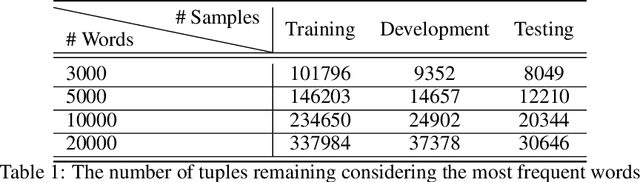
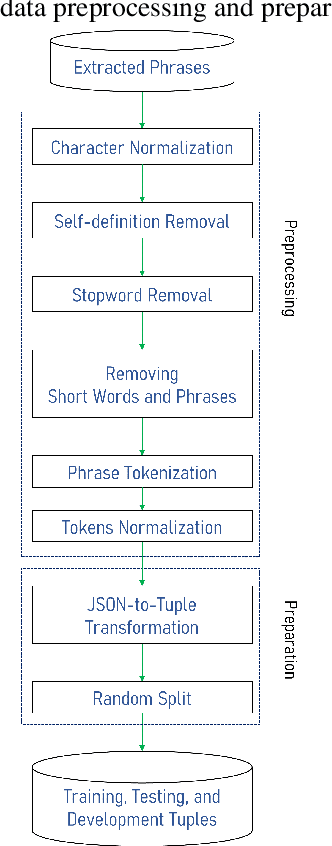
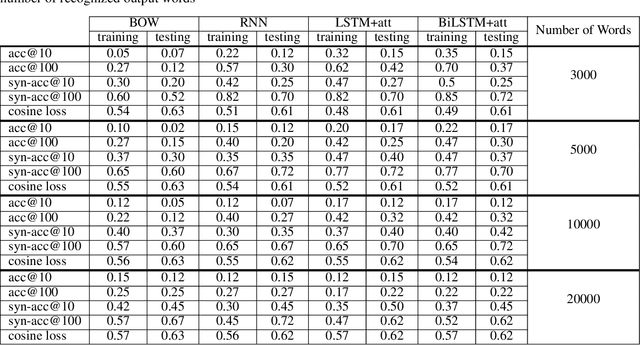
Abstract:Finding the appropriate words to convey concepts (i.e., lexical access) is essential for effective communication. Reverse dictionaries fulfill this need by helping individuals to find the word(s) which could relate to a specific concept or idea. To the best of our knowledge, this resource has not been available for the Persian language. In this paper, we compare four different architectures for implementing a Persian reverse dictionary (PREDICT). We evaluate our models using (phrase,word) tuples extracted from the only Persian dictionaries available online, namely Amid, Moein, and Dehkhoda where the phrase describes the word. Given the phrase, a model suggests the most relevant word(s) in terms of the ability to convey the concept. The model is considered to perform well if the correct word is one of its top suggestions. Our experiments show that a model consisting of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) units enhanced by an additive attention mechanism is enough to produce suggestions comparable to (or in some cases better than) the word in the original dictionary. The study also reveals that the model sometimes produces the synonyms of the word as its output which led us to introduce a new metric for the evaluation of reverse dictionaries called Synonym Accuracy accounting for the percentage of times the event of producing the word or a synonym of it occurs. The assessment of the best model using this new metric also indicates that at least 62% of the times, it produces an accurate result within the top 100 suggestions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge