Ari Klein
Deep Neural Networks Ensemble for Detecting Medication Mentions in Tweets
Apr 10, 2019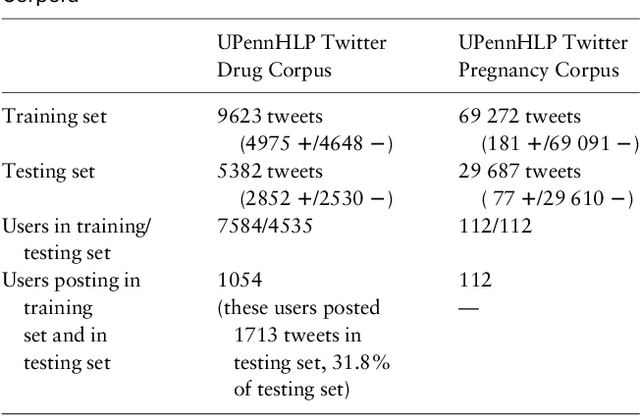


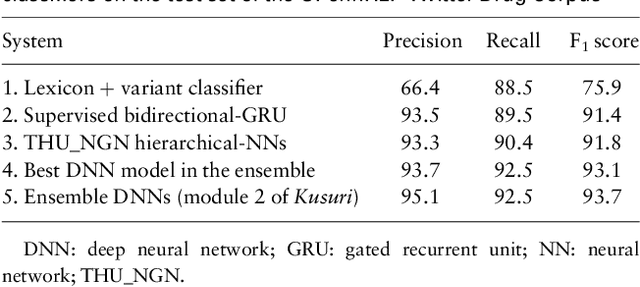
Abstract:Objective: After years of research, Twitter posts are now recognized as an important source of patient-generated data, providing unique insights into population health. A fundamental step to incorporating Twitter data in pharmacoepidemiological research is to automatically recognize medication mentions in tweets. Given that lexical searches for medication names may fail due to misspellings or ambiguity with common words, we propose a more advanced method to recognize them. Methods: We present Kusuri, an Ensemble Learning classifier, able to identify tweets mentioning drug products and dietary supplements. Kusuri ("medication" in Japanese) is composed of two modules. First, four different classifiers (lexicon-based, spelling-variant-based, pattern-based and one based on a weakly-trained neural network) are applied in parallel to discover tweets potentially containing medication names. Second, an ensemble of deep neural networks encoding morphological, semantical and long-range dependencies of important words in the tweets discovered is used to make the final decision. Results: On a balanced (50-50) corpus of 15,005 tweets, Kusuri demonstrated performances close to human annotators with 93.7% F1-score, the best score achieved thus far on this corpus. On a corpus made of all tweets posted by 113 Twitter users (98,959 tweets, with only 0.26% mentioning medications), Kusuri obtained 76.3% F1-score. There is not a prior drug extraction system that compares running on such an extremely unbalanced dataset. Conclusion: The system identifies tweets mentioning drug names with performance high enough to ensure its usefulness and ready to be integrated in larger natural language processing systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge