Arastu Sharma
Can LLMs Compute with Reasons?
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) often struggle with complex mathematical tasks, prone to "hallucinating" incorrect answers due to their reliance on statistical patterns. This limitation is further amplified in average Small LangSLMs with limited context and training data. To address this challenge, we propose an "Inductive Learning" approach utilizing a distributed network of SLMs. This network leverages error-based learning and hint incorporation to refine the reasoning capabilities of SLMs. Our goal is to provide a framework that empowers SLMs to approach the level of logic-based applications achieved by high-parameter models, potentially benefiting any language model. Ultimately, this novel concept paves the way for bridging the logical gap between humans and LLMs across various fields.
Design of an Efficient, Ease-of-use and Affordable Artificial Intelligence based Nucleic Acid Amplification Diagnosis Technology for Tuberculosis and Multi-drug Resistant Tuberculosis
Apr 14, 2021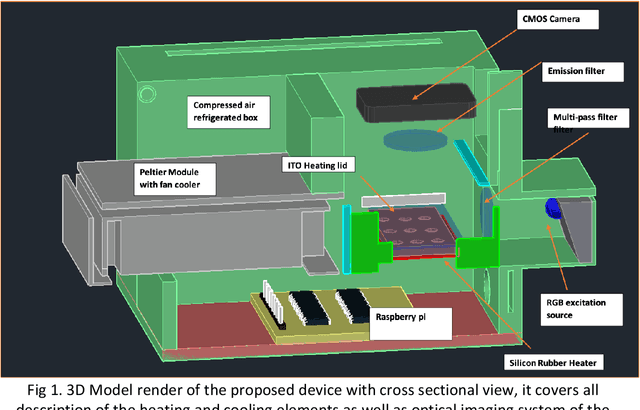
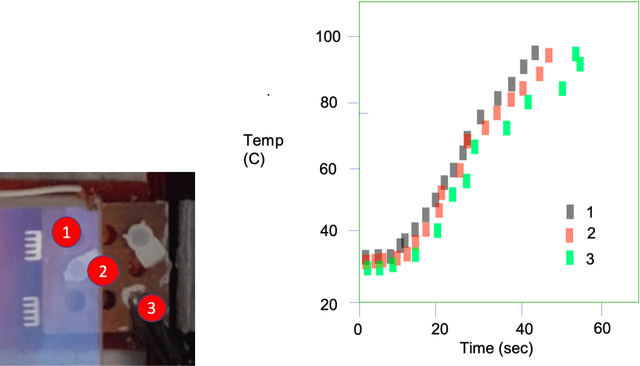
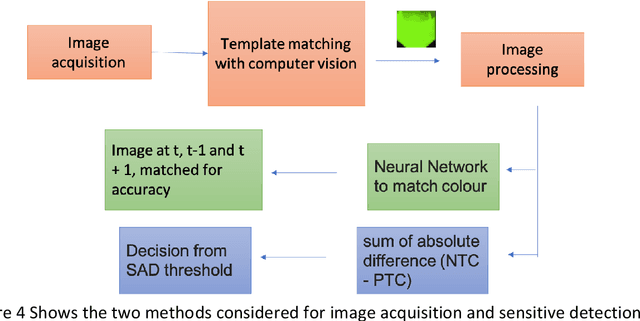
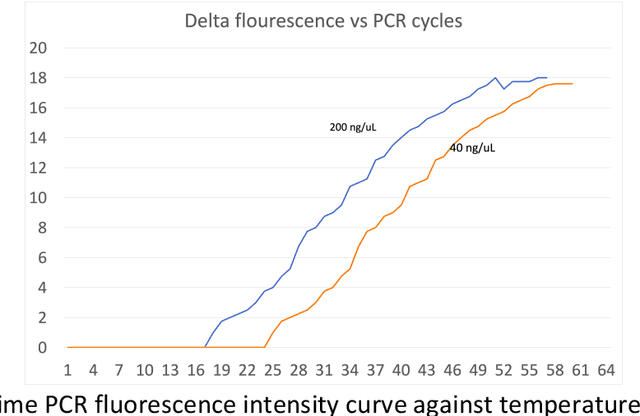
Abstract:Current technologies that facilitate diagnosis for simultaneous detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and its resistance to first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs (Isoniazid and Rifampicim) are designed for lab-based settings and are unaffordable for large scale testing implementations. The suitability of a TB diagnosis instrument, generally required in low-resource settings, to be implementable in point-of-care last mile public health centres depends on manufacturing cost, ease-of-use, automation and portability. This paper discusses a portable, low-cost, machine learning automated Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) device that employs the use of a smartphone-based fluorescence detection using novel image processing and chromaticity detection algorithms. To test the instrument, real time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) experiment on cDNA dilution spanning over two concentrations (40 ng/uL and 200 ng/uL) was performed and sensitive detection of multiplexed positive control assay was verified.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge