Antoine Hébert
Can we Estimate Truck Accident Risk from Telemetric Data using Machine Learning?
Jul 17, 2020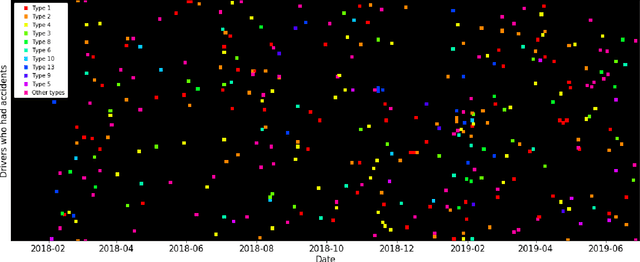


Abstract:Road accidents have a high societal cost that could be reduced through improved risk predictions using machine learning. This study investigates whether telemetric data collected on long-distance trucks can be used to predict the risk of accidents associated with a driver. We use a dataset provided by a truck transportation company containing the driving data of 1,141 drivers for 18 months. We evaluate two different machine learning approaches to perform this task. In the first approach, features are extracted from the time series data using the FRESH algorithm and then used to estimate the risk using Random Forests. In the second approach, we use a convolutional neural network to directly estimate the risk from the time-series data. We find that neither approach is able to successfully estimate the risk of accidents on this dataset, in spite of many methodological attempts. We discuss the difficulties of using telemetric data for the estimation of the risk of accidents that could explain this negative result.
High-Resolution Road Vehicle Collision Prediction for the City of Montreal
May 21, 2019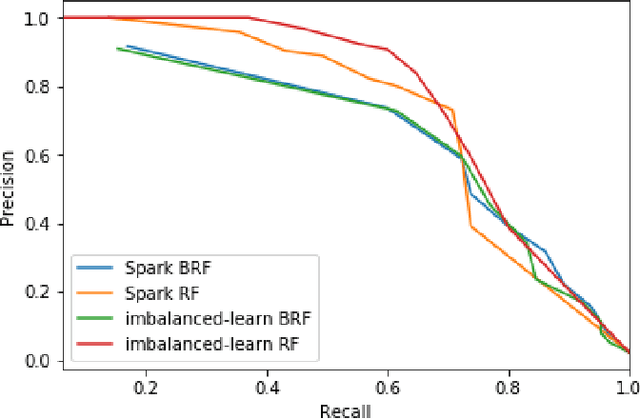
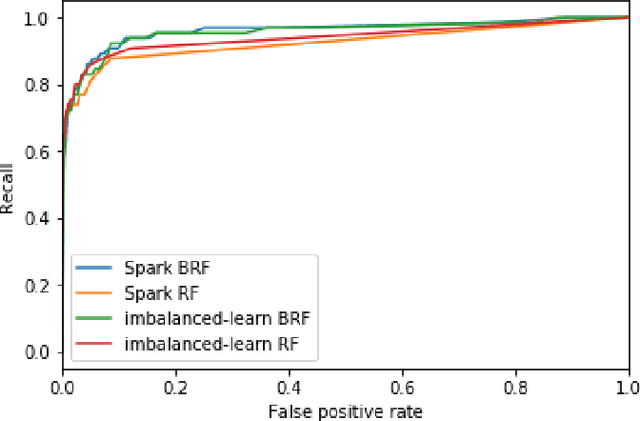
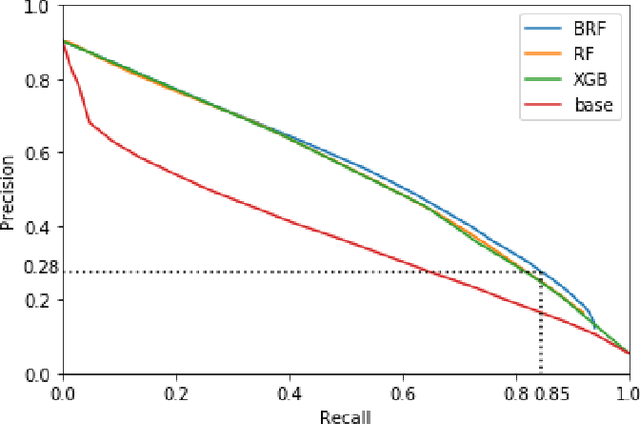

Abstract:Road accidents are an important issue of our modern societies, responsible for millions of deaths and injuries every year in the world. In Quebec only, road accidents are responsible for hundreds of deaths and tens of thousands of injuries. In this paper, we show how one can leverage open datasets of a city like Montreal, Canada, to create high-resolution accident prediction models, using state-of-the-art big data analytics. Compared to other studies in road accident prediction, we have a much higher prediction resolution, i.e., our models predict the occurrence of an accident within an hour, on road segments defined by intersections. Such models could be used in the context of road accident prevention, but also to identify key factors that can lead to a road accident, and consequently, help elaborate new policies. We tested various machine learning methods to deal with the severe class imbalance inherent to accident prediction problems. In particular, we implemented the Balanced Random Forest algorithm, a variant of the Random Forest machine learning algorithm in Apache Spark. Experimental results show that 85% of road vehicle collisions are detected by our model with a false positive rate of 13%. The examples identified as positive are likely to correspond to high-risk situations. In addition, we identify the most important predictors of vehicle collisions for the area of Montreal: the count of accidents on the same road segment during previous years, the temperature, the day of the year, the hour and the visibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge