Antônio Theophilo
Reasoning for Complex Data through Ensemble-based Self-Supervised Learning
Feb 12, 2022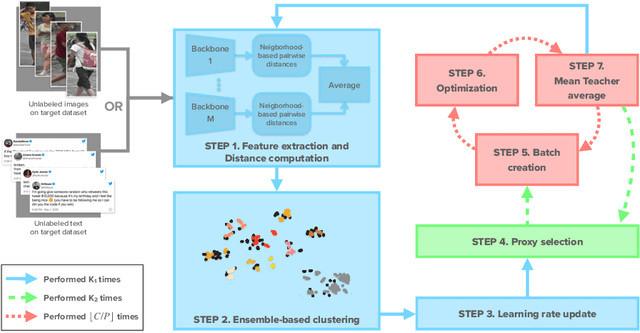
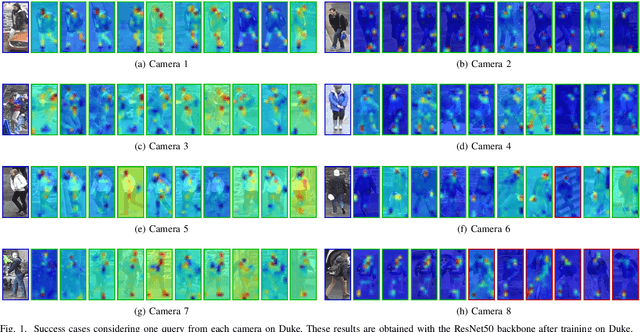
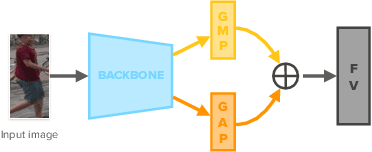
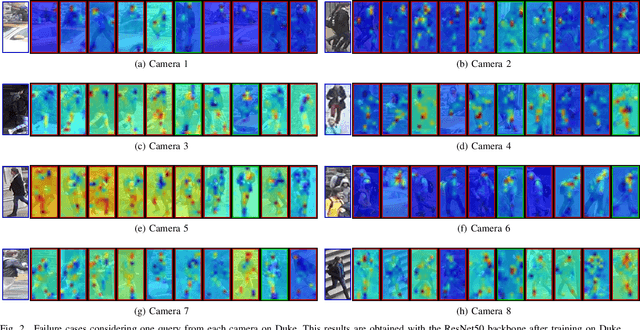
Abstract:Self-supervised learning deals with problems that have little or no available labeled data. Recent work has shown impressive results when underlying classes have significant semantic differences. One important dataset in which this technique thrives is ImageNet, as intra-class distances are substantially lower than inter-class distances. However, this is not the case for several critical tasks, and general self-supervised learning methods fail to learn discriminative features when classes have closer semantics, thus requiring more robust strategies. We propose a strategy to tackle this problem, and to enable learning from unlabeled data even when samples from different classes are not prominently diverse. We approach the problem by leveraging a novel ensemble-based clustering strategy where clusters derived from different configurations are combined to generate a better grouping for the data samples in a fully-unsupervised way. This strategy allows clusters with different densities and higher variability to emerge, which in turn reduces intra-class discrepancies, without requiring the burden of finding an optimal configuration per dataset. We also consider different Convolutional Neural Networks to compute distances between samples. We refine these distances by performing context analysis and group them to capture complementary information. We consider two applications to validate our pipeline: Person Re-Identification and Text Authorship Verification. These are challenging applications considering that classes are semantically close to each other and that training and test sets have disjoint identities. Our method is robust across different modalities and outperforms state-of-the-art results with a fully-unsupervised solution without any labeling or human intervention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge