Anoop Toffy
Vehicle Driving Assistant
Feb 10, 2020



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles has been a common term in our day to day life with car manufacturers like Tesla shipping cars that are SAE Level 3. While these vehicles include a slew of features such as parking assistance and cruise control,they have mostly been tailored to foreign roads. Potholes, and the abundance of them, is something that is unique to our Indian roads. We believe that successful detection of potholes from visual images can be applied in a variety of scenarios. Moreover, the sheer variety in the color, shape and size of potholes makes this problem an apt candidate to be solved using modern machine learning and image processing techniques.
Semi-supervised and Active-learning Scenarios: Efficient Acoustic Model Refinement for a Low Resource Indian Language
Oct 02, 2018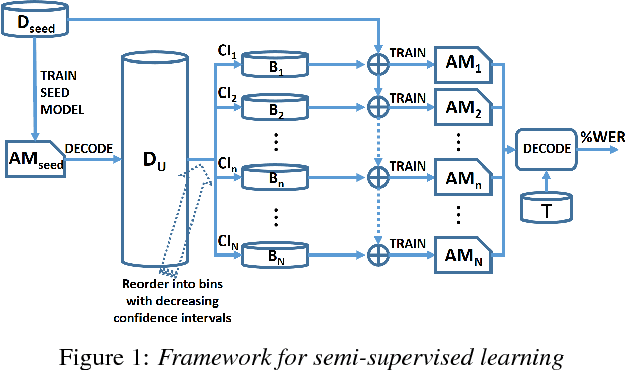
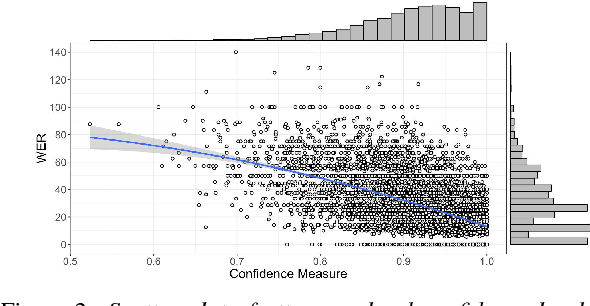
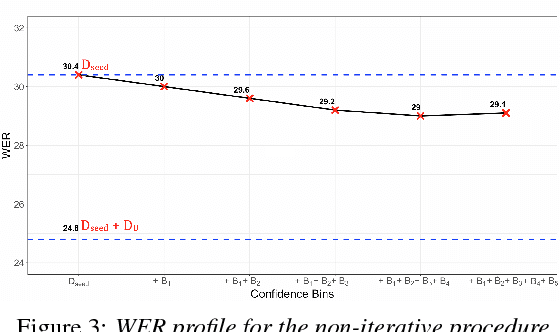
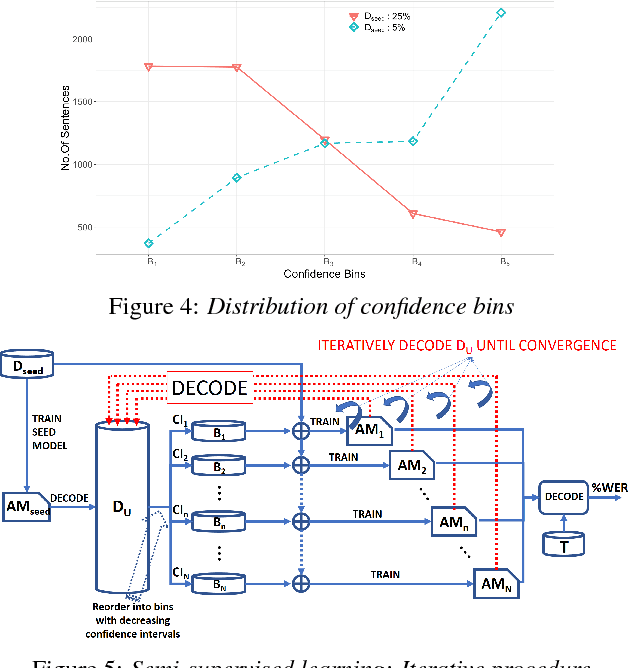
Abstract:We address the problem of efficient acoustic-model refinement (continuous retraining) using semi-supervised and active learning for a low resource Indian language, wherein the low resource constraints are having i) a small labeled corpus from which to train a baseline `seed' acoustic model and ii) a large training corpus without orthographic labeling or from which to perform a data selection for manual labeling at low costs. The proposed semi-supervised learning decodes the unlabeled large training corpus using the seed model and through various protocols, selects the decoded utterances with high reliability using confidence levels (that correlate to the WER of the decoded utterances) and iterative bootstrapping. The proposed active learning protocol uses confidence level based metric to select the decoded utterances from the large unlabeled corpus for further labeling. The semi-supervised learning protocols can offer a WER reduction, from a poorly trained seed model, by as much as 50% of the best WER-reduction realizable from the seed model's WER, if the large corpus were labeled and used for acoustic-model training. The active learning protocols allow that only 60% of the entire training corpus be manually labeled, to reach the same performance as the entire data.
Conditional WaveGAN
Sep 27, 2018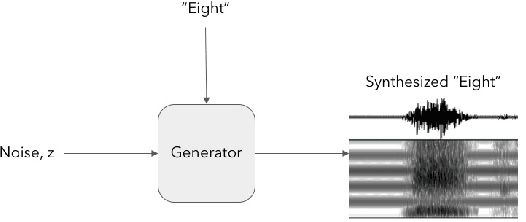
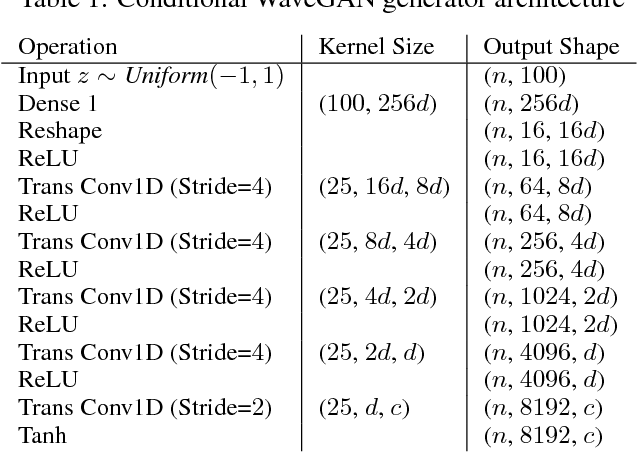
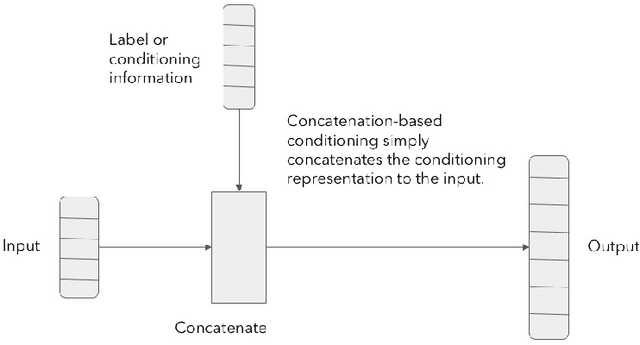
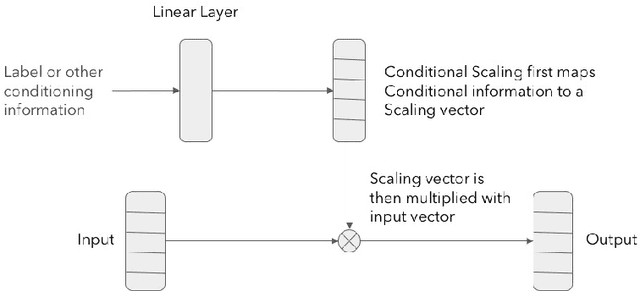
Abstract:Generative models are successfully used for image synthesis in the recent years. But when it comes to other modalities like audio, text etc little progress has been made. Recent works focus on generating audio from a generative model in an unsupervised setting. We explore the possibility of using generative models conditioned on class labels. Concatenation based conditioning and conditional scaling were explored in this work with various hyper-parameter tuning methods. In this paper we introduce Conditional WaveGANs (cWaveGAN). Find our implementation at https://github.com/acheketa/cwavegan
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge