Annajiat Alim Rasel
SonoVision: A Computer Vision Approach for Helping Visually Challenged Individuals Locate Objects with the Help of Sound Cues
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Locating objects for the visually impaired is a significant challenge and is something no one can get used to over time. However, this hinders their independence and could push them towards risky and dangerous scenarios. Hence, in the spirit of making the visually challenged more self-sufficient, we present SonoVision, a smart-phone application that helps them find everyday objects using sound cues through earphones/headphones. This simply means, if an object is on the right or left side of a user, the app makes a sinusoidal sound in a user's respective ear through ear/headphones. However, to indicate objects located directly in front, both the left and right earphones are rung simultaneously. These sound cues could easily help a visually impaired individual locate objects with the help of their smartphones and reduce the reliance on people in their surroundings, consequently making them more independent. This application is made with the flutter development platform and uses the Efficientdet-D2 model for object detection in the backend. We believe the app will significantly assist the visually impaired in a safe and user-friendly manner with its capacity to work completely offline. Our application can be accessed here https://github.com/MohammedZ666/SonoVision.git.
Introducing A Bangla Sentence - Gloss Pair Dataset for Bangla Sign Language Translation and Research
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Bangla Sign Language (BdSL) translation represents a low-resource NLP task due to the lack of large-scale datasets that address sentence-level translation. Correspondingly, existing research in this field has been limited to word and alphabet level detection. In this work, we introduce Bangla-SGP, a novel parallel dataset consisting of 1,000 human-annotated sentence-gloss pairs which was augmented with around 3,000 synthetically generated pairs using syntactic and morphological rules through a rule-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline. The gloss sequences of the spoken Bangla sentences are made up of individual glosses which are Bangla sign supported words and serve as an intermediate representation for a continuous sign. Our dataset consists of 1000 high quality Bangla sentences that are manually annotated into a gloss sequence by a professional signer. The augmentation process incorporates rule-based linguistic strategies and prompt engineering techniques that we have adopted by critically analyzing our human annotated sentence-gloss pairs and by working closely with our professional signer. Furthermore, we fine-tune several transformer-based models such as mBart50, Google mT5, GPT4.1-nano and evaluate their sentence-to-gloss translation performance using BLEU scores, based on these evaluation metrics we compare the model's gloss-translation consistency across our dataset and the RWTH-PHOENIX-2014T benchmark.
Virtual teaching assistant for undergraduate students using natural language processing & deep learning
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Online education's popularity has been continuously increasing over the past few years. Many universities were forced to switch to online education as a result of COVID-19. In many cases, even after more than two years of online instruction, colleges were unable to resume their traditional classroom programs. A growing number of institutions are considering blended learning with some parts in-person and the rest of the learning taking place online. Nevertheless, many online education systems are inefficient, and this results in a poor rate of student retention. In this paper, we are offering a primary dataset, the initial implementation of a virtual teaching assistant named VTA-bot, and its system architecture. Our primary implementation of the suggested system consists of a chatbot that can be queried about the content and topics of the fundamental python programming language course. Students in their first year of university will be benefited from this strategy, which aims to increase student participation and involvement in online education.
Optical Text Recognition in Nepali and Bengali: A Transformer-based Approach
Apr 03, 2024



Abstract:Efforts on the research and development of OCR systems for Low-Resource Languages are relatively new. Low-resource languages have little training data available for training Machine Translation systems or other systems. Even though a vast amount of text has been digitized and made available on the internet the text is still in PDF and Image format, which are not instantly accessible. This paper discusses text recognition for two scripts: Bengali and Nepali; there are about 300 and 40 million Bengali and Nepali speakers respectively. In this study, using encoder-decoder transformers, a model was developed, and its efficacy was assessed using a collection of optical text images, both handwritten and printed. The results signify that the suggested technique corresponds with current approaches and achieves high precision in recognizing text in Bengali and Nepali. This study can pave the way for the advanced and accessible study of linguistics in South East Asia.
A Survey: Credit Sentiment Score Prediction
Sep 30, 2022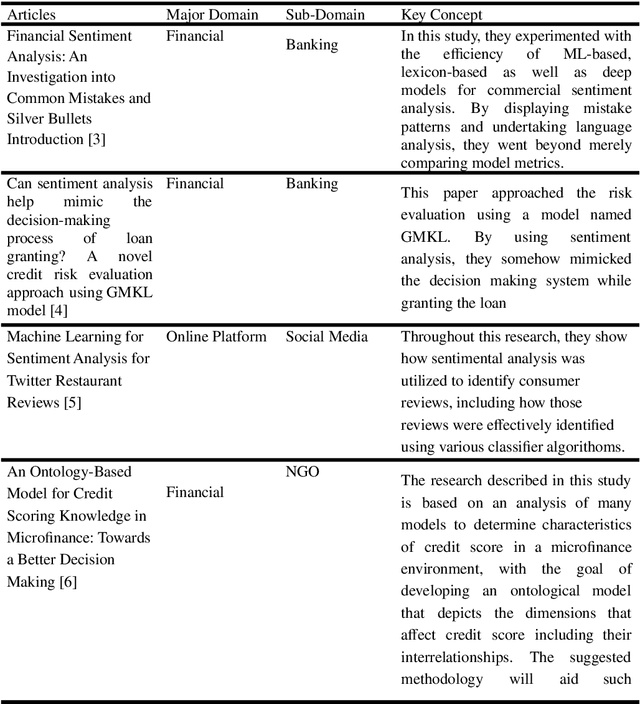
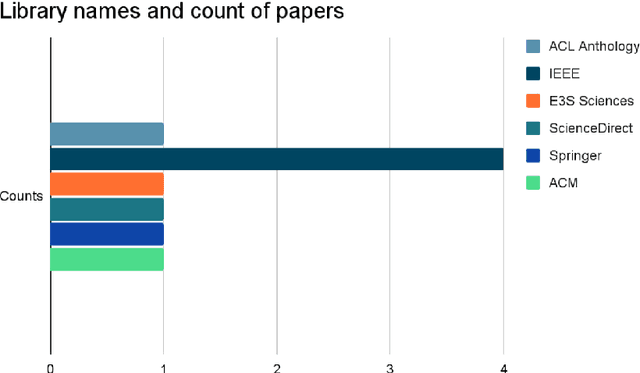
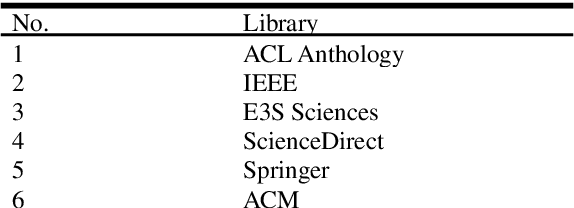
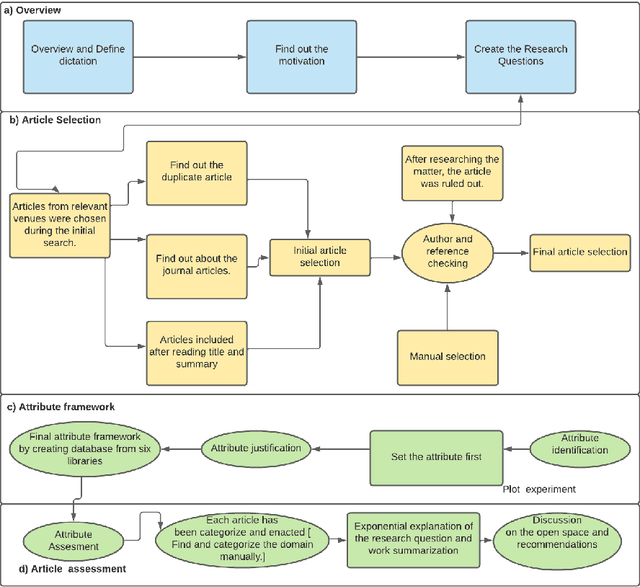
Abstract:Manual approvals are still used by banks and other NGOs to approve loans. It takes time and is prone to mistakes because it is controlled by a bank employee. Several fields of machine learning mining technologies have been utilized to enhance various areas of credit rating forecast. A major goal of this research is to look at current sentiment analysis techniques that are being used to generate creditworthiness.
Patients' Severity States Classification based on Electronic Health Record (EHR) Data using Multiple Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches
Sep 29, 2022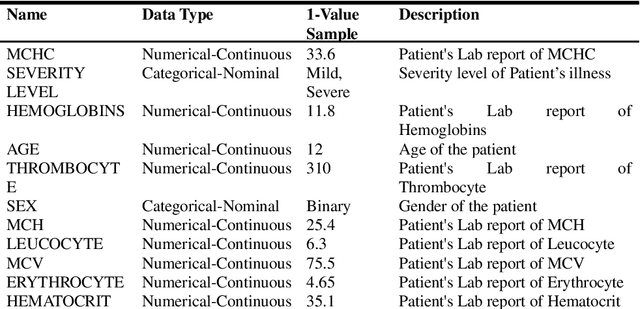
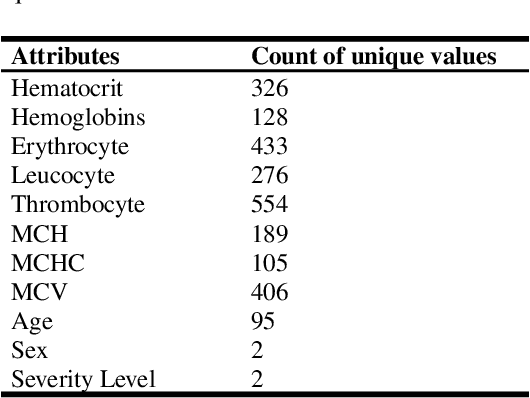
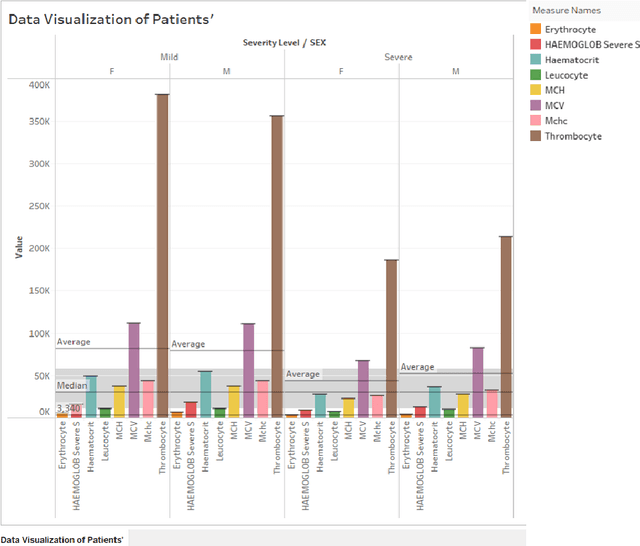
Abstract:This research presents an examination of categorizing the severity states of patients based on their electronic health records during a certain time range using multiple machine learning and deep learning approaches. The suggested method uses an EHR dataset collected from an open-source platform to categorize severity. Some tools were used in this research, such as openRefine was used to pre-process, RapidMiner was used for implementing three algorithms (Fast Large Margin, Generalized Linear Model, Multi-layer Feed-forward Neural Network) and Tableau was used to visualize the data, for implementation of algorithms we used Google Colab. Here we implemented several supervised and unsupervised algorithms along with semi-supervised and deep learning algorithms. The experimental results reveal that hyperparameter-tuned Random Forest outperformed all the other supervised machine learning algorithms with 76% accuracy as well as Generalized Linear algorithm achieved the highest precision score 78%, whereas the hyperparameter-tuned Hierarchical Clustering with 86% precision score and Gaussian Mixture Model with 61% accuracy outperformed other unsupervised approaches. Dimensionality Reduction improved results a lot for most unsupervised techniques. For implementing Deep Learning we employed a feed-forward neural network (multi-layer) and the Fast Large Margin approach for semi-supervised learning. The Fast Large Margin performed really well with a recall score of 84% and an F1 score of 78%. Finally, the Multi-layer Feed-forward Neural Network performed admirably with 75% accuracy, 75% precision, 87% recall, 81% F1 score.
Product Market Demand Analysis Using NLP in Banglish Text with Sentiment Analysis and Named Entity Recognition
Apr 04, 2022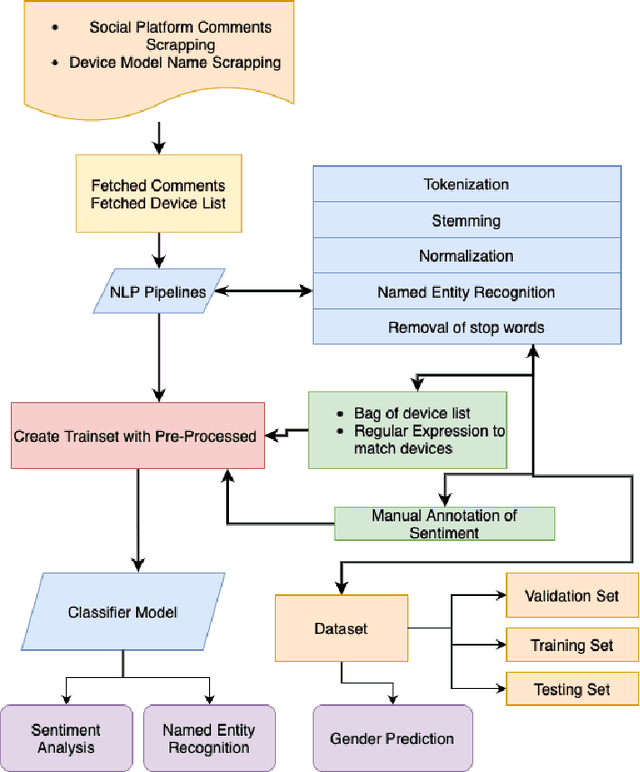
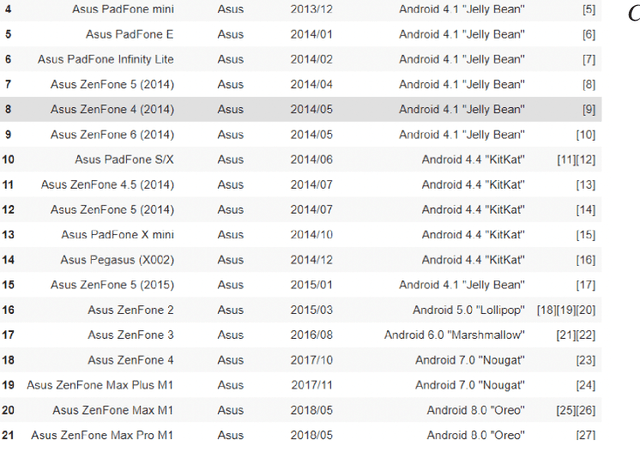
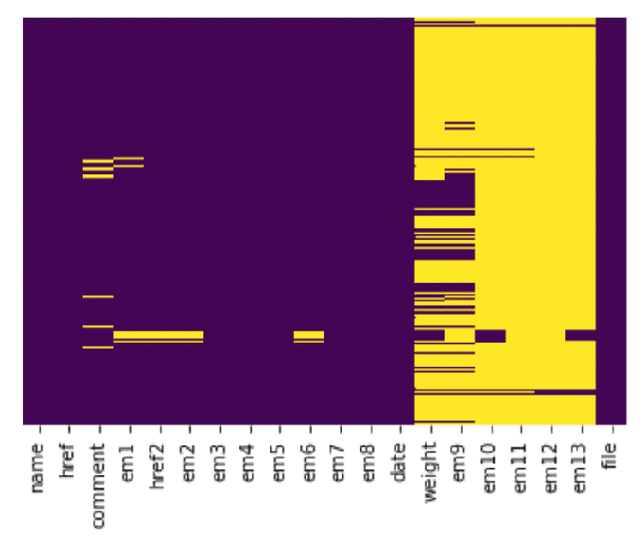

Abstract:Product market demand analysis plays a significant role for originating business strategies due to its noticeable impact on the competitive business field. Furthermore, there are roughly 228 million native Bengali speakers, the majority of whom use Banglish text to interact with one another on social media. Consumers are buying and evaluating items on social media with Banglish text as social media emerges as an online marketplace for entrepreneurs. People use social media to find preferred smartphone brands and models by sharing their positive and bad experiences with them. For this reason, our goal is to gather Banglish text data and use sentiment analysis and named entity identification to assess Bangladeshi market demand for smartphones in order to determine the most popular smartphones by gender. We scraped product related data from social media with instant data scrapers and crawled data from Wikipedia and other sites for product information with python web scrapers. Using Python's Pandas and Seaborn libraries, the raw data is filtered using NLP methods. To train our datasets for named entity recognition, we utilized Spacey's custom NER model, Amazon Comprehend Custom NER. A tensorflow sequential model was deployed with parameter tweaking for sentiment analysis. Meanwhile, we used the Google Cloud Translation API to estimate the gender of the reviewers using the BanglaLinga library. In this article, we use natural language processing (NLP) approaches and several machine learning models to identify the most in-demand items and services in the Bangladeshi market. Our model has an accuracy of 87.99% in Spacy Custom Named Entity recognition, 95.51% in Amazon Comprehend Custom NER, and 87.02% in the Sequential model for demand analysis. After Spacy's study, we were able to manage 80% of mistakes related to misspelled words using a mix of Levenshtein distance and ratio algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge