Anja Kroon
McGill University
Evaluation of Categorical Generative Models -- Bridging the Gap Between Real and Synthetic Data
Oct 28, 2022



Abstract:The machine learning community has mainly relied on real data to benchmark algorithms as it provides compelling evidence of model applicability. Evaluation on synthetic datasets can be a powerful tool to provide a better understanding of a model's strengths, weaknesses, and overall capabilities. Gaining these insights can be particularly important for generative modeling as the target quantity is completely unknown. Multiple issues related to the evaluation of generative models have been reported in the literature. We argue those problems can be avoided by an evaluation based on ground truth. General criticisms of synthetic experiments are that they are too simplified and not representative of practical scenarios. As such, our experimental setting is tailored to a realistic generative task. We focus on categorical data and introduce an appropriately scalable evaluation method. Our method involves tasking a generative model to learn a distribution in a high-dimensional setting. We then successively bin the large space to obtain smaller probability spaces where meaningful statistical tests can be applied. We consider increasingly large probability spaces, which correspond to increasingly difficult modeling tasks and compare the generative models based on the highest task difficulty they can reach before being detected as being too far from the ground truth. We validate our evaluation procedure with synthetic experiments on both synthetic generative models and current state-of-the-art categorical generative models.
Comparing Conventional Pitch Detection Algorithms with a Neural Network Approach
Jun 29, 2022
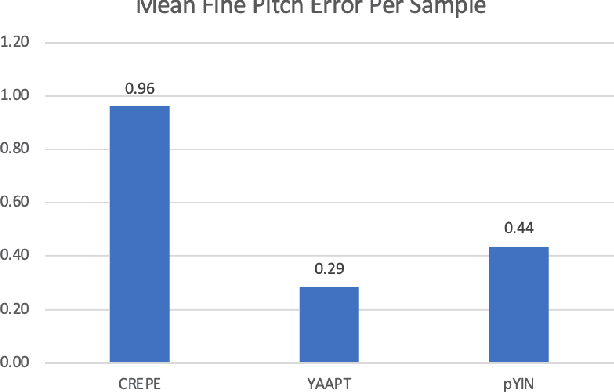
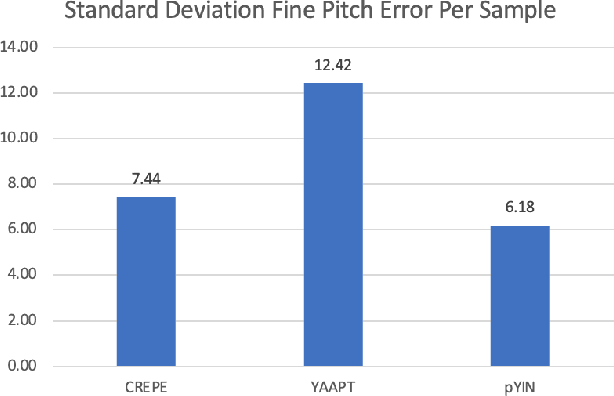
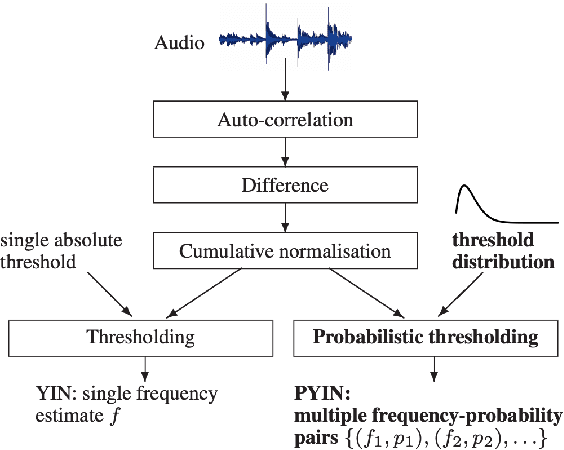
Abstract:Despite much research, traditional methods to pitch prediction are still not perfect. With the emergence of neural networks (NNs), researchers hope to create a NN-based pitch predictor that outperforms traditional methods. Three pitch detection algorithms (PDAs), pYIN, YAAPT, and CREPE are compared in this paper. pYIN and YAAPT are conventional approaches considering time domain and frequency domain processing. CREPE utilizes a data-trained deep convolutional neural network to estimate pitch. It involves 6 densely connected convolutional hidden layers and determines pitch probabilities for a given input signal. The performance of CREPE representing neural network pitch predictors is compared to more classical approaches represented by pYIN and YAAPT. The figure of merit (FOM) will include the amount of unvoiced-to-voiced errors, voiced-to-voiced errors, gross pitch errors, and fine pitch errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge