Anirudh Ravichandran
APEX-Agents
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We introduce the AI Productivity Index for Agents (APEX-Agents), a benchmark for assessing whether AI agents can execute long-horizon, cross-application tasks created by investment banking analysts, management consultants, and corporate lawyers. APEX-Agents requires agents to navigate realistic work environments with files and tools. We test eight agents for the leaderboard using Pass@1. Gemini 3 Flash (Thinking=High) achieves the highest score of 24.0%, followed by GPT-5.2 (Thinking=High), Claude Opus 4.5 (Thinking=High), and Gemini 3 Pro (Thinking=High). We open source the APEX-Agents benchmark (n=480) with all prompts, rubrics, gold outputs, files, and metadata. We also open-source Archipelago, our infrastructure for agent execution and evaluation.
DARD: A Multi-Agent Approach for Task-Oriented Dialog Systems
Nov 01, 2024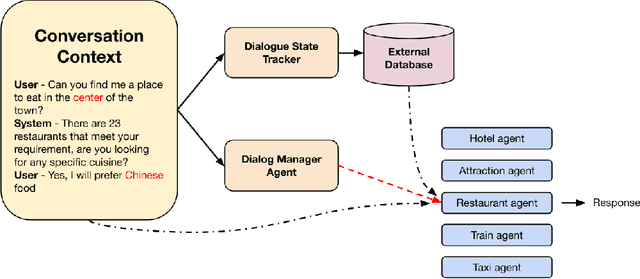
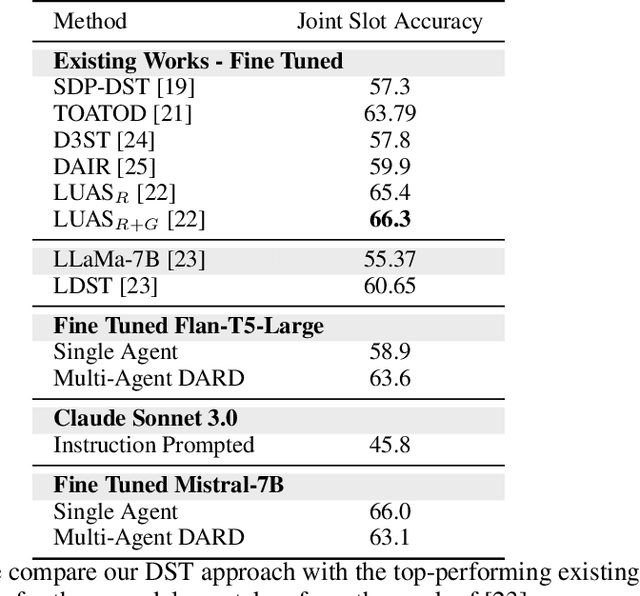
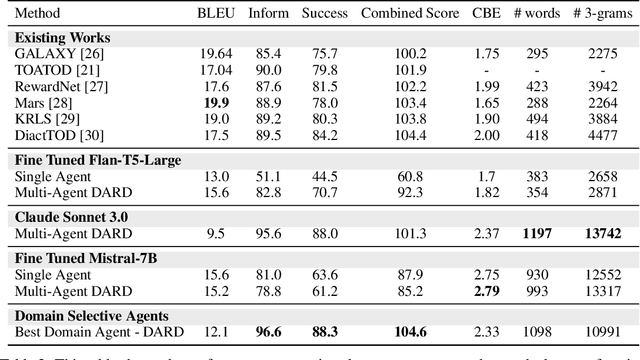

Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue systems are essential for applications ranging from customer service to personal assistants and are widely used across various industries. However, developing effective multi-domain systems remains a significant challenge due to the complexity of handling diverse user intents, entity types, and domain-specific knowledge across several domains. In this work, we propose DARD (Domain Assigned Response Delegation), a multi-agent conversational system capable of successfully handling multi-domain dialogs. DARD leverages domain-specific agents, orchestrated by a central dialog manager agent. Our extensive experiments compare and utilize various agent modeling approaches, combining the strengths of smaller fine-tuned models (Flan-T5-large & Mistral-7B) with their larger counterparts, Large Language Models (LLMs) (Claude Sonnet 3.0). We provide insights into the strengths and limitations of each approach, highlighting the benefits of our multi-agent framework in terms of flexibility and composability. We evaluate DARD using the well-established MultiWOZ benchmark, achieving state-of-the-art performance by improving the dialogue inform rate by 6.6% and the success rate by 4.1% over the best-performing existing approaches. Additionally, we discuss various annotator discrepancies and issues within the MultiWOZ dataset and its evaluation system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge