Anik Khan
CIDMP: Completely Interpretable Detection of Malaria Parasite in Red Blood Cells using Lower-dimensional Feature Space
Jul 05, 2020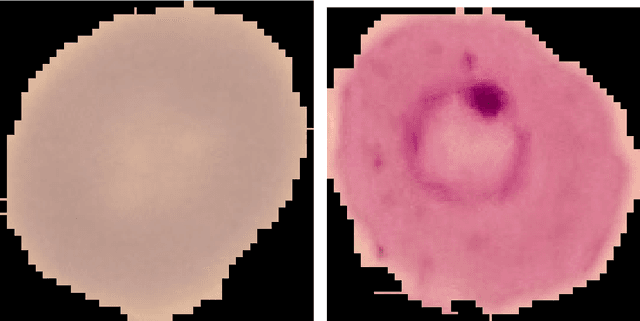
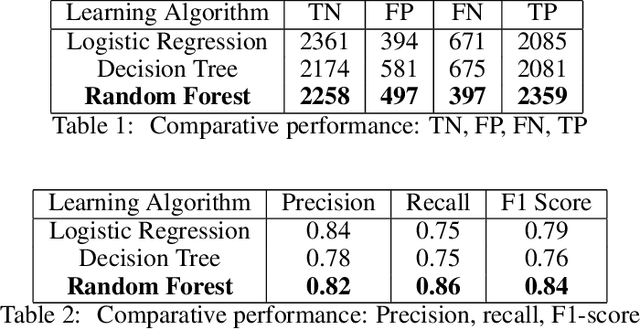
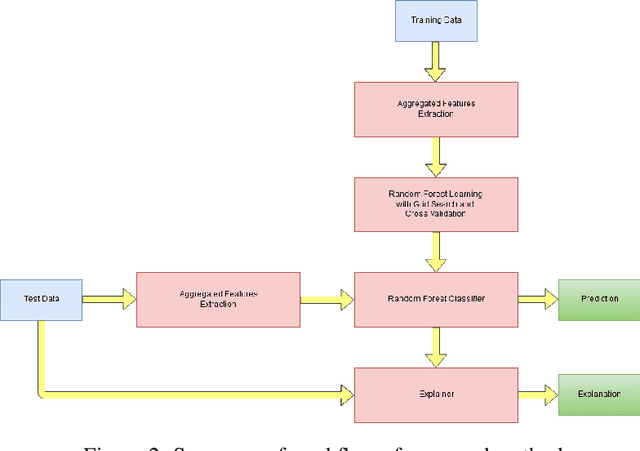
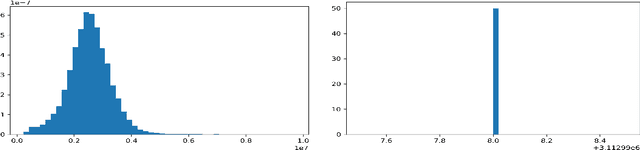
Abstract:Predicting if red blood cells (RBC) are infected with the malaria parasite is an important problem in Pathology. Recently, supervised machine learning approaches have been used for this problem, and they have had reasonable success. In particular, state-of-the-art methods such as Convolutional Neural Networks automatically extract increasingly complex feature hierarchies from the image pixels. While such generalized automatic feature extraction methods have significantly reduced the burden of feature engineering in many domains, for niche tasks such as the one we consider in this paper, they result in two major problems. First, they use a very large number of features (that may or may not be relevant) and therefore training such models is computationally expensive. Further, more importantly, the large feature-space makes it very hard to interpret which features are truly important for predictions. Thus, a criticism of such methods is that learning algorithms pose opaque black boxes to its users, in this case, medical experts. The recommendation of such algorithms can be understood easily, but the reason for their recommendation is not clear. This is the problem of non-interpretability of the model, and the best-performing algorithms are usually the least interpretable. To address these issues, in this paper, we propose an approach to extract a very small number of aggregated features that are easy to interpret and compute, and empirically show that we obtain high prediction accuracy even with a significantly reduced feature-space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge