Angelos Angelopoulos
Advancing Intra-operative Precision: Dynamic Data-Driven Non-Rigid Registration for Enhanced Brain Tumor Resection in Image-Guided Neurosurgery
Aug 31, 2023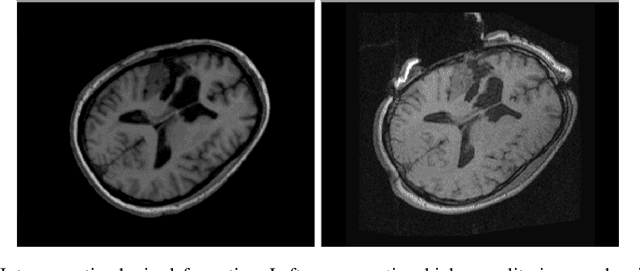
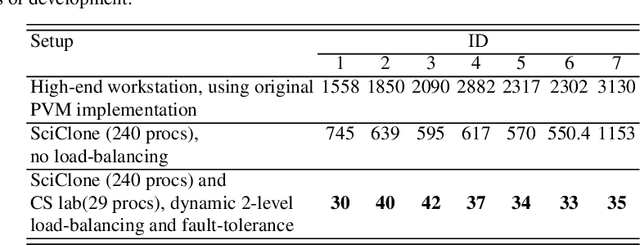
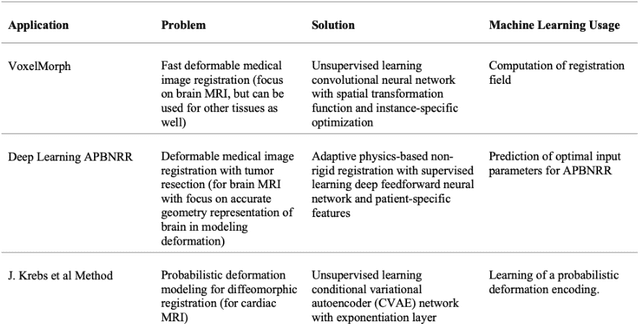
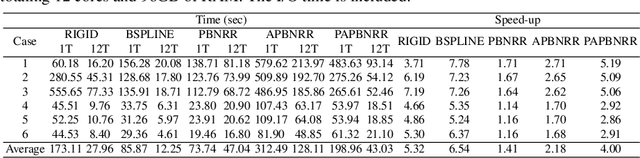
Abstract:During neurosurgery, medical images of the brain are used to locate tumors and critical structures, but brain tissue shifts make pre-operative images unreliable for accurate removal of tumors. Intra-operative imaging can track these deformations but is not a substitute for pre-operative data. To address this, we use Dynamic Data-Driven Non-Rigid Registration (NRR), a complex and time-consuming image processing operation that adjusts the pre-operative image data to account for intra-operative brain shift. Our review explores a specific NRR method for registering brain MRI during image-guided neurosurgery and examines various strategies for improving the accuracy and speed of the NRR method. We demonstrate that our implementation enables NRR results to be delivered within clinical time constraints while leveraging Distributed Computing and Machine Learning to enhance registration accuracy by identifying optimal parameters for the NRR method. Additionally, we highlight challenges associated with its use in the operating room.
Using Artificial Intelligence for Particle Track Identification in CLAS12 Detector
Aug 28, 2020



Abstract:In this article we describe the development of machine learning models to assist the CLAS12 tracking algorithm by identifying the best track candidates from combinatorial track candidates from the hits in drift chambers. Several types of machine learning models were tested, including: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) and Extremely Randomized Trees (ERT). The final implementation was based on an MLP network and provided an accuracy $>99\%$. The implementation of AI assisted tracking into the CLAS12 reconstruction workflow and provided a 6 times code speedup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge