Andrew Morris
Zero-Shot Distracted Driver Detection via Vision Language Models with Double Decoupling
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Distracted driving is a major cause of traffic collisions, calling for robust and scalable detection methods. Vision-language models (VLMs) enable strong zero-shot image classification, but existing VLM-based distracted driver detectors often underperform in real-world conditions. We identify subject-specific appearance variations (e.g., clothing, age, and gender) as a key bottleneck: VLMs entangle these factors with behavior cues, leading to decisions driven by who the driver is rather than what the driver is doing. To address this, we propose a subject decoupling framework that extracts a driver appearance embedding and removes its influence from the image embedding prior to zero-shot classification, thereby emphasizing distraction-relevant evidence. We further orthogonalize text embeddings via metric projection onto Stiefel manifold to improve separability while staying close to the original semantics. Experiments demonstrate consistent gains over prior baselines, indicating the promise of our approach for practical road-safety applications.
FireBERT: Hardening BERT-based classifiers against adversarial attack
Aug 10, 2020Abstract:We present FireBERT, a set of three proof-of-concept NLP classifiers hardened against TextFooler-style word-perturbation by producing diverse alternatives to original samples. In one approach, we co-tune BERT against the training data and synthetic adversarial samples. In a second approach, we generate the synthetic samples at evaluation time through substitution of words and perturbation of embedding vectors. The diversified evaluation results are then combined by voting. A third approach replaces evaluation-time word substitution with perturbation of embedding vectors. We evaluate FireBERT for MNLI and IMDB Movie Review datasets, in the original and on adversarial examples generated by TextFooler. We also test whether TextFooler is less successful in creating new adversarial samples when manipulating FireBERT, compared to working on unhardened classifiers. We show that it is possible to improve the accuracy of BERT-based models in the face of adversarial attacks without significantly reducing the accuracy for regular benchmark samples. We present co-tuning with a synthetic data generator as a highly effective method to protect against 95% of pre-manufactured adversarial samples while maintaining 98% of original benchmark performance. We also demonstrate evaluation-time perturbation as a promising direction for further research, restoring accuracy up to 75% of benchmark performance for pre-made adversarials, and up to 65% (from a baseline of 75% orig. / 12% attack) under active attack by TextFooler.
Automated and Network Structure Preserving Segmentation of Optical Coherence Tomography Angiograms
Dec 20, 2019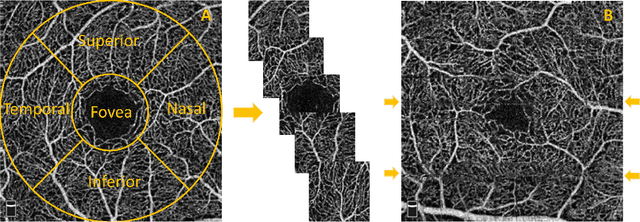
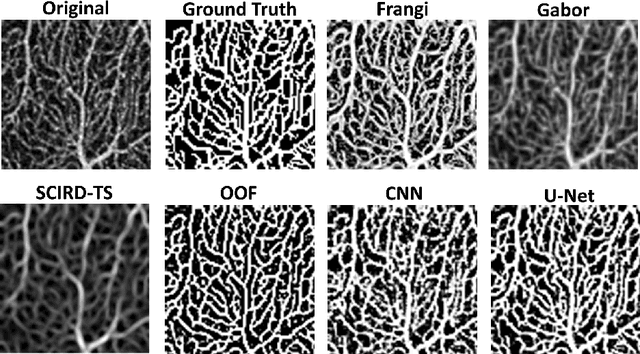

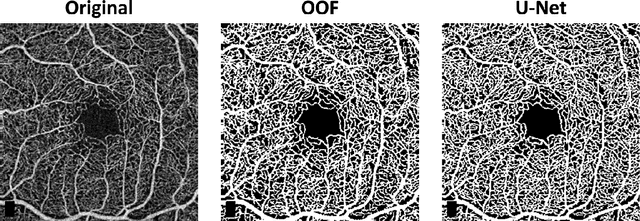
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a novel non-invasive imaging modality for the visualisation of microvasculature in vivo. OCTA has encountered broad adoption in retinal research. OCTA potential in the assessment of pathological conditions and the reproducibility of studies relies on the quality of the image analysis. However, automated segmentation of parafoveal OCTA images is still an open problem in the field. In this study, we generate the first open dataset of retinal parafoveal OCTA images with associated ground truth manual segmentations. Furthermore, we establish a standard for OCTA image segmentation by surveying a broad range of state-of-the-art vessel enhancement and binarisation procedures. We provide the most comprehensive comparison of these methods under a unified framework to date. Our results show that, for the set of images considered, the U-Net machine learning (ML) architecture achieves the best performance with a Dice similarity coefficient of 0.89. For applications where manually segmented data is not available to retrain this ML approach, our findings suggest that optimal oriented flux is the best handcrafted filter enhancement method for OCTA images from those considered. Furthermore, we report on the importance of preserving network connectivity in the segmentation to enable vascular network phenotyping. We introduce a new metric for network connectivity evaluations in segmented angiograms and report an accuracy of up to 0.94 in preserving the morphological structure of the network in our segmentations. Finally, we release our data and source code to support standardisation efforts in OCTA image segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge