Andre Teixeira Lopes
Deep Learning Based Large-Scale Automatic Satellite Crosswalk Classification
Jul 05, 2017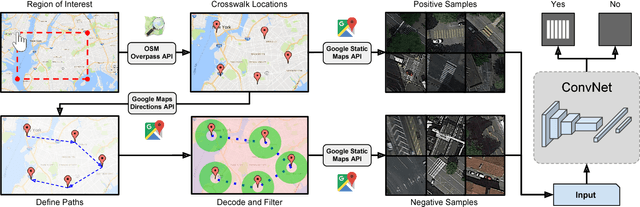
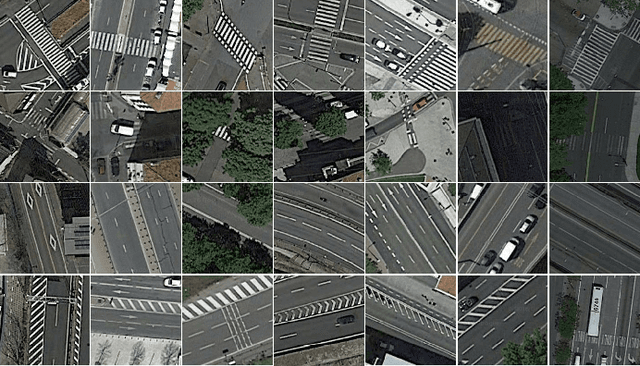
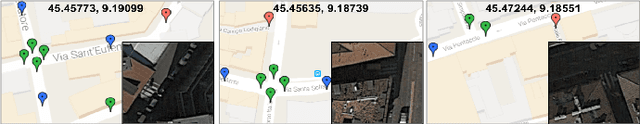
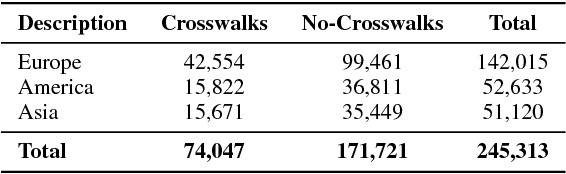
Abstract:High-resolution satellite imagery have been increasingly used on remote sensing classification problems. One of the main factors is the availability of this kind of data. Even though, very little effort has been placed on the zebra crossing classification problem. In this letter, crowdsourcing systems are exploited in order to enable the automatic acquisition and annotation of a large-scale satellite imagery database for crosswalks related tasks. Then, this dataset is used to train deep-learning-based models in order to accurately classify satellite images that contains or not zebra crossings. A novel dataset with more than 240,000 images from 3 continents, 9 countries and more than 20 cities was used in the experiments. Experimental results showed that freely available crowdsourcing data can be used to accurately (97.11%) train robust models to perform crosswalk classification on a global scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge