Andras Fulop
Computational Doob's $h$-transforms for Online Filtering of Discretely Observed Diffusions
Jun 07, 2022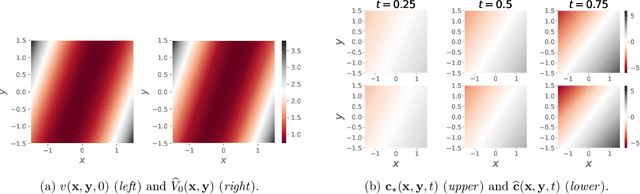


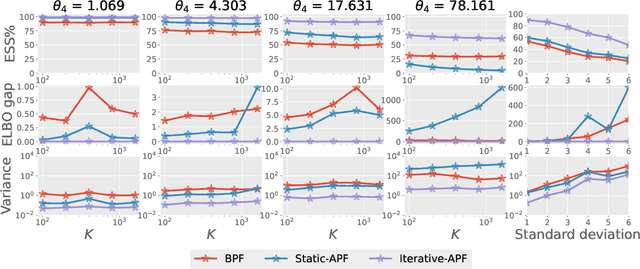
Abstract:This paper is concerned with online filtering of discretely observed nonlinear diffusion processes. Our approach is based on the fully adapted auxiliary particle filter, which involves Doob's $h$-transforms that are typically intractable. We propose a computational framework to approximate these $h$-transforms by solving the underlying backward Kolmogorov equations using nonlinear Feynman-Kac formulas and neural networks. The methodology allows one to train a locally optimal particle filter prior to the data-assimilation procedure. Numerical experiments illustrate that the proposed approach can be orders of magnitude more efficient than the bootstrap particle filter in the regime of highly informative observations, when the observations are extreme under the model, and if the state dimension is large.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge