Amy Widdicombe
Gradient-Based Interpretability Methods and Binarized Neural Networks
Jun 23, 2021


Abstract:Binarized Neural Networks (BNNs) have the potential to revolutionize the way that deep learning is carried out in edge computing platforms. However, the effectiveness of interpretability methods on these networks has not been assessed. In this paper, we compare the performance of several widely used saliency map-based interpretabilty techniques (Gradient, SmoothGrad and GradCAM), when applied to Binarized or Full Precision Neural Networks (FPNNs). We found that the basic Gradient method produces very similar-looking maps for both types of network. However, SmoothGrad produces significantly noisier maps for BNNs. GradCAM also produces saliency maps which differ between network types, with some of the BNNs having seemingly nonsensical explanations. We comment on possible reasons for these differences in explanations and present it as an example of why interpretability techniques should be tested on a wider range of network types.
NeuroMask: Explaining Predictions of Deep Neural Networks through Mask Learning
Aug 05, 2019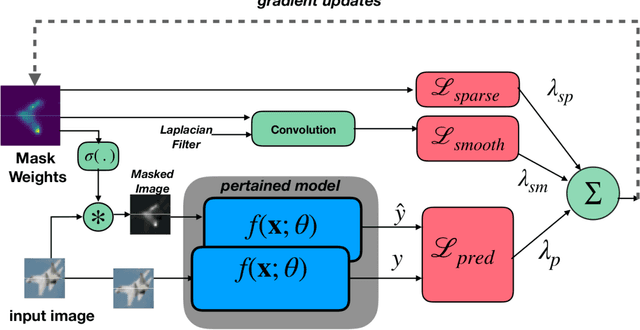


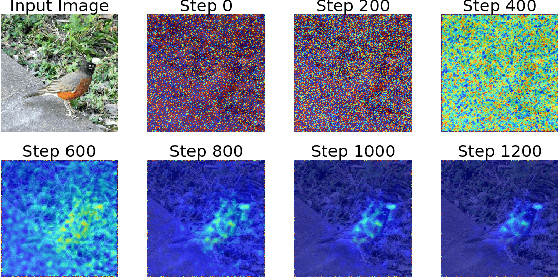
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) deliver state-of-the-art performance in many image recognition and understanding applications. However, despite their outstanding performance, these models are black-boxes and it is hard to understand how they make their decisions. Over the past few years, researchers have studied the problem of providing explanations of why DNNs predicted their results. However, existing techniques are either obtrusive, requiring changes in model training, or suffer from low output quality. In this paper, we present a novel method, NeuroMask, for generating an interpretable explanation of classification model results. When applied to image classification models, NeuroMask identifies the image parts that are most important to classifier results by applying a mask that hides/reveals different parts of the image, before feeding it back into the model. The mask values are tuned by minimizing a properly designed cost function that preserves the classification result and encourages producing an interpretable mask. Experiments using state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Networks for image recognition on different datasets (CIFAR-10 and ImageNet) show that NeuroMask successfully localizes the parts of the input image which are most relevant to the DNN decision. By showing a visual quality comparison between NeuroMask explanations and those of other methods, we find NeuroMask to be both accurate and interpretable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge