Amy Chi
Wrist-Squeezing Force Feedback Improves Accuracy and Speed in Robotic Surgery Training
May 13, 2022


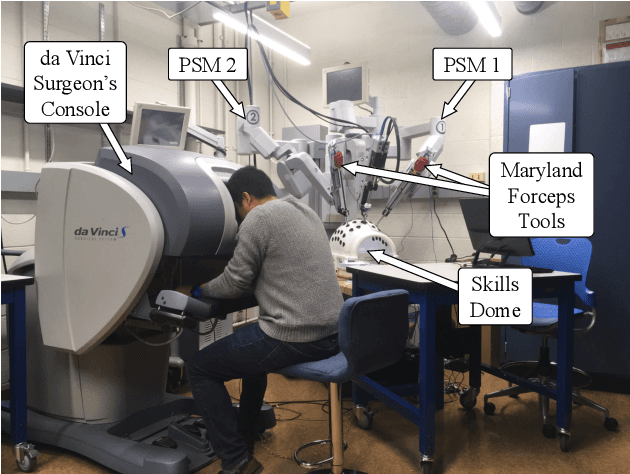
Abstract:Current robotic minimally invasive surgery (RMIS) platforms provide surgeons with no haptic feedback of the robot's physical interactions. This limitation forces surgeons to rely heavily on visual feedback and can make it challenging for surgical trainees to manipulate tissue gently. Prior research has demonstrated that haptic feedback can increase task accuracy in RMIS training. However, it remains unclear whether these improvements represent a fundamental improvement in skill, or if they simply stem from re-prioritizing accuracy over task completion time. In this study, we provide haptic feedback of the force applied by the surgical instruments using custom wrist-squeezing devices. We hypothesize that individuals receiving haptic feedback will increase accuracy (produce less force) while increasing their task completion time, compared to a control group receiving no haptic feedback. To test this hypothesis, N=21 novice participants were asked to repeatedly complete a ring rollercoaster surgical training task as quickly as possible. Results show that participants receiving haptic feedback apply significantly less force (0.67 N) than the control group, and they complete the task no faster or slower than the control group after twelve repetitions. Furthermore, participants in the feedback group decreased their task completion times significantly faster (7.68%) than participants in the control group (5.26%). This form of haptic feedback, therefore, has the potential to help trainees improve their technical accuracy without compromising speed.
Preliminary investigation into how limb choice affects kinesthetic perception
Jul 22, 2021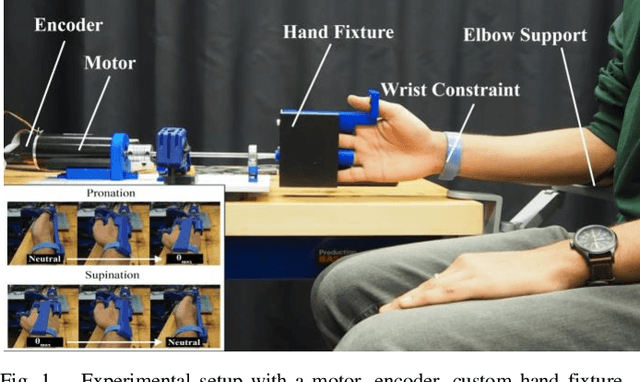

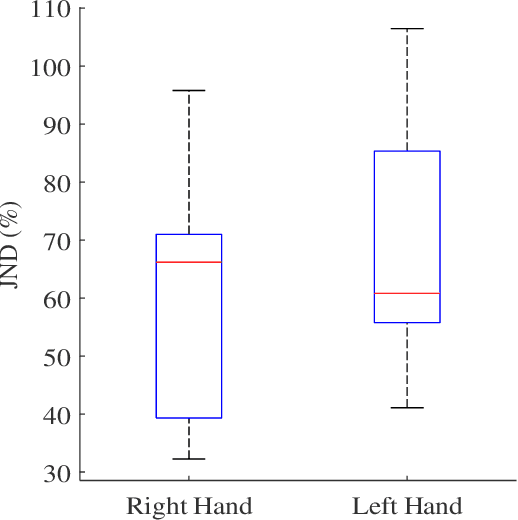

Abstract:We have a limited understanding of how we integrate haptic information in real-time from our upper limbs to perform complex bimanual tasks, an ability that humans routinely employ to perform tasks of varying levels of difficulty. In order to understand how information from both limbs is used to create a unified percept, it is important to study both the limbs separately first. Prevalent theories highlighting the role of central nervous system (CNS) in accounting for internal body dynamics seem to suggest that both upper limbs should be equally sensitive to external stimuli. However, there is empirical proof demonstrating a perceptual difference in our upper limbs for tasks like shape discrimination, prompting the need to study effects of limb choice on kinesthetic perception. In this manuscript, we start evaluating Just Noticeable Difference (JND) for stiffness for both forearms separately. Early results validate the need for a more thorough investigation of limb choice on kinesthetic perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge