Amjad Rehman
Recent Developments in Detection of Central Serous Retinopathy through Imaging and Artificial Intelligence Techniques A Review
Dec 26, 2020



Abstract:The Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR) is a major significant disease responsible for causing blindness and vision loss among numerous people across the globe. This disease is also known as the Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSC) occurs due to the accumulation of watery fluids behind the retina. The detection of CSR at an early stage allows taking preventive measures to avert any impairment to the human eye. Traditionally, several manual detection methods were developed for observing CSR, but they were proven to be inaccurate, unreliable, and time-consuming. Consequently, the research community embarked on seeking automated solutions for CSR detection. With the advent of modern technology in the 21st century, Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques are immensely popular in numerous research fields including the automated CSR detection. This paper offers a comprehensive review of various advanced technologies and researches, contributing to the automated CSR detection in this scenario. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and limitations of many classical imaging methods ranging from Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and the Fundus imaging, to more recent approaches like AI based Machine/Deep Learning techniques. Study primary objective is to analyze and compare many Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms that have efficiently achieved automated CSR detection using OCT imaging. Furthermore, it describes various retinal datasets and strategies proposed for CSR assessment and accuracy. Finally, it is concluded that the most recent Deep Learning (DL) classifiers are performing accurate, fast, and reliable detection of CSR.
Neural Computing for Online Arabic Handwriting Character Recognition using Hard Stroke Features Mining
May 02, 2020



Abstract:Online Arabic cursive character recognition is still a big challenge due to the existing complexities including Arabic cursive script styles, writing speed, writer mood and so forth. Due to these unavoidable constraints, the accuracy of online Arabic character's recognition is still low and retain space for improvement. In this research, an enhanced method of detecting the desired critical points from vertical and horizontal direction-length of handwriting stroke features of online Arabic script recognition is proposed. Each extracted stroke feature divides every isolated character into some meaningful pattern known as tokens. A minimum feature set is extracted from these tokens for classification of characters using a multilayer perceptron with a back-propagation learning algorithm and modified sigmoid function-based activation function. In this work, two milestones are achieved; firstly, attain a fixed number of tokens, secondly, minimize the number of the most repetitive tokens. For experiments, handwritten Arabic characters are selected from the OHASD benchmark dataset to test and evaluate the proposed method. The proposed method achieves an average accuracy of 98.6% comparable in state of art character recognition techniques.
* 16 pages
An Ensemble of Neural Networks for Non-Linear Segmentation of Overlapped Cursive Script
Apr 07, 2019



Abstract:Precise character segmentation is the only solution towards higher Optical Character Recognition (OCR) accuracy. In cursive script, overlapped characters are serious issue in the process of character segmentations as characters are deprived from their discriminative parts using conventional linear segmentation strategy. Hence, non-linear segmentation is an utmost need to avoid loss of characters parts and to enhance character/script recognition accuracy. This paper presents an improved approach for non-linear segmentation of the overlapped characters in handwritten roman script. The proposed technique is composed of a sequence of heuristic rules based on geometrical features of characters to locate possible non-linear character boundaries in a cursive script word. However, to enhance efficiency, heuristic approach is integrated with trained ensemble neural network validation strategy for verification of character boundaries. Accordingly, correct boundaries are retained and incorrect are removed based on ensemble neural networks vote. Finally, based on verified valid segmentation points, characters are segmented non-linearly. For fair comparison CEDAR benchmark database is experimented. The experimental results are much better than conventional linear character segmentation techniques reported in the state of art. Ensemble neural network play vital role to enhance character segmentation accuracy as compared to individual neural networks.
Cursive Multilingual Characters Recognition Based on Hard Geometric Features
Apr 07, 2019



Abstract:The cursive nature of multilingual characters segmentation and recognition of Arabic, Persian, Urdu languages have attracted researchers from academia and industry. However, despite several decades of research, still multilingual characters classification accuracy is not up to the mark. This paper presents an automated approach for multilingual characters segmentation and recognition. The proposed methodology explores character based on their geometric features. However, due to uncertainty and without dictionary support few characters are over-divided. To expand the productivity of the proposed methodology a BPN is prepared with countless division focuses for cursive multilingual characters. Prepared BPN separates off base portioned indicates effectively with rapid upgrade character acknowledgment precision. For reasonable examination, only benchmark dataset is utilized.
Improved Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) Approach for Online Signature Verification
Mar 26, 2019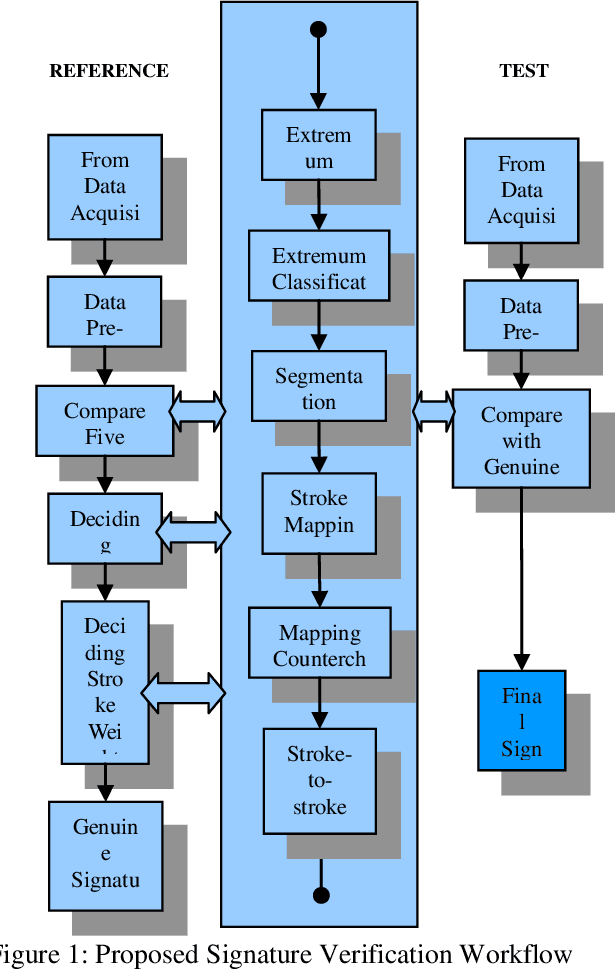

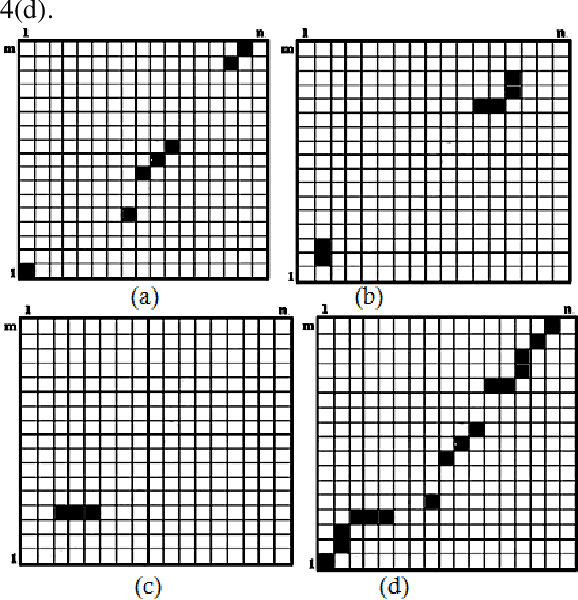
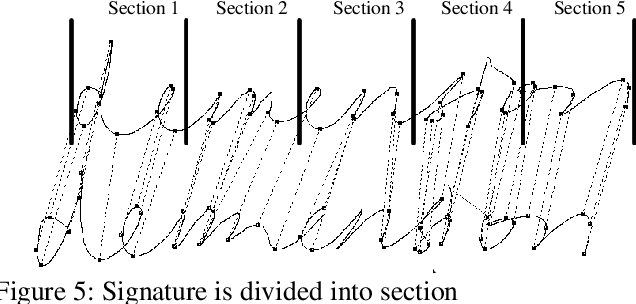
Abstract:Online signature verification is the process of verifying time series signature data which is generally obtained from the tablet-based device. Unlike offline signature images, the online signature image data consists of points that are arranged in a sequence of time. The aim of this research is to develop an improved approach to map the strokes in both test and reference signatures. Current methods make use of the Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm and its variant to segment them before comparing each of its data dimension. This paper presents a modified DTW algorithm with the proposed Lost Box Recovery Algorithm aims to improve the mapping performance for online signature verification
Cursive Overlapped Character Segmentation: An Enhanced Approach
Mar 23, 2019



Abstract:Segmentation of highly slanted and horizontally overlapped characters is a challenging research area that is still fresh. Several techniques are reported in the state of art, but produce low accuracy for the highly slanted characters segmentation and cause overall low handwriting recognition precision. Accordingly, this paper presents a simple yet effective approach for character segmentation of such difficult slanted cursive words without using any slant correction technique. Rather a new concept of core-zone is introduced for segmenting such difficult slanted handwritten words. However, due to the inherent nature of cursive words, few characters are over-segmented and therefore, a threshold is selected heuristically to overcome this problem. For fair comparison, difficult words are extracted from the IAM benchmark database. Experiments thus performed exhibit promising result and high speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge