Amit Beka
Best Practices for Machine Learning Systems: An Industrial Framework for Analysis and Optimization
Jun 09, 2023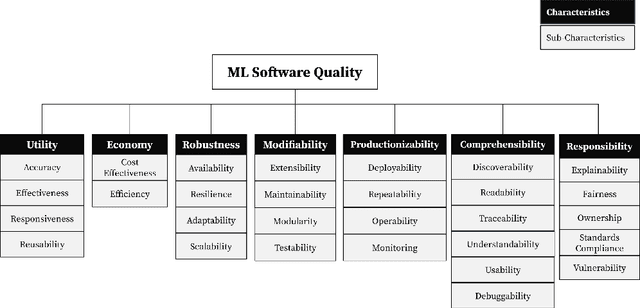

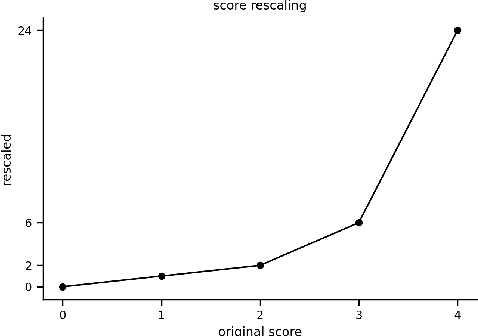
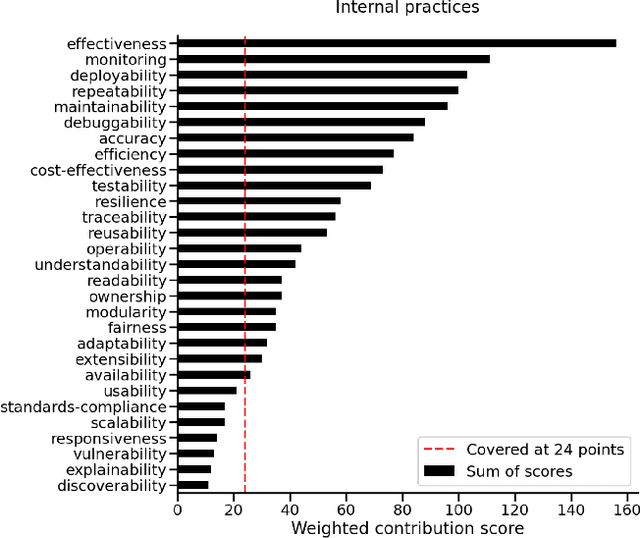
Abstract:In the last few years, the Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence community has developed an increasing interest in Software Engineering (SE) for ML Systems leading to a proliferation of best practices, rules, and guidelines aiming at improving the quality of the software of ML Systems. However, understanding their impact on the overall quality has received less attention. Practices are usually presented in a prescriptive manner, without an explicit connection to their overall contribution to software quality. Based on the observation that different practices influence different aspects of software-quality and that one single quality aspect might be addressed by several practices we propose a framework to analyse sets of best practices with focus on quality impact and prioritization of their implementation. We first introduce a hierarchical Software Quality Model (SQM) specifically tailored for ML Systems. Relying on expert knowledge, the connection between individual practices and software quality aspects is explicitly elicited for a large set of well-established practices. Applying set-function optimization techniques we can answer questions such as what is the set of practices that maximizes SQM coverage, what are the most important ones, which practices should be implemented in order to improve specific quality aspects, among others. We illustrate the usage of our framework by analyzing well-known sets of practices.
With One Voice: Composing a Travel Voice Assistant from Re-purposed Models
Aug 04, 2021
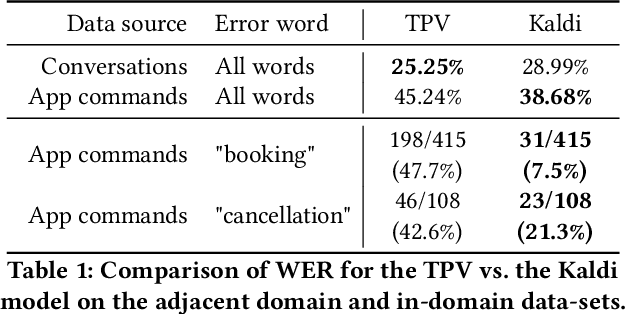
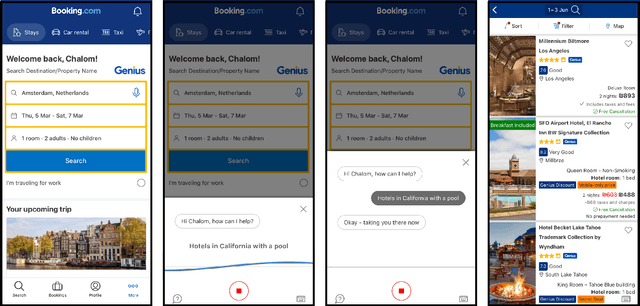
Abstract:Voice assistants provide users a new way of interacting with digital products, allowing them to retrieve information and complete tasks with an increased sense of control and flexibility. Such products are comprised of several machine learning models, like Speech-to-Text transcription, Named Entity Recognition and Resolution, and Text Classification. Building a voice assistant from scratch takes the prolonged efforts of several teams constructing numerous models and orchestrating between components. Alternatives such as using third-party vendors or re-purposing existing models may be considered to shorten time-to-market and development costs. However, each option has its benefits and drawbacks. We present key insights from building a voice search assistant for Booking.com search and recommendation system. Our paper compares the achieved performance and development efforts in dedicated tailor-made solutions against existing re-purposed models. We share and discuss our data-driven decisions about implementation trade-offs and their estimated outcomes in hindsight, showing that a fully functional machine learning product can be built from existing models.
* 2nd International Workshop on Industrial Recommendation Systems @ KDD 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge