Amin Karamlou
Quantum Natural Language Generation on Near-Term Devices
Nov 01, 2022Abstract:The emergence of noisy medium-scale quantum devices has led to proof-of-concept applications for quantum computing in various domains. Examples include Natural Language Processing (NLP) where sentence classification experiments have been carried out, as well as procedural generation, where tasks such as geopolitical map creation, and image manipulation have been performed. We explore applications at the intersection of these two areas by designing a hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for sentence generation. Our algorithm is based on the well-known simulated annealing technique for combinatorial optimisation. An implementation is provided and used to demonstrate successful sentence generation on both simulated and real quantum hardware. A variant of our algorithm can also be used for music generation. This paper aims to be self-contained, introducing all the necessary background on NLP and quantum computing along the way.
Complexity Results and Algorithms for Bipolar Argumentation
Mar 05, 2019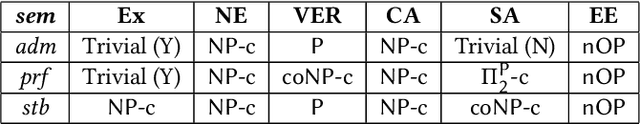
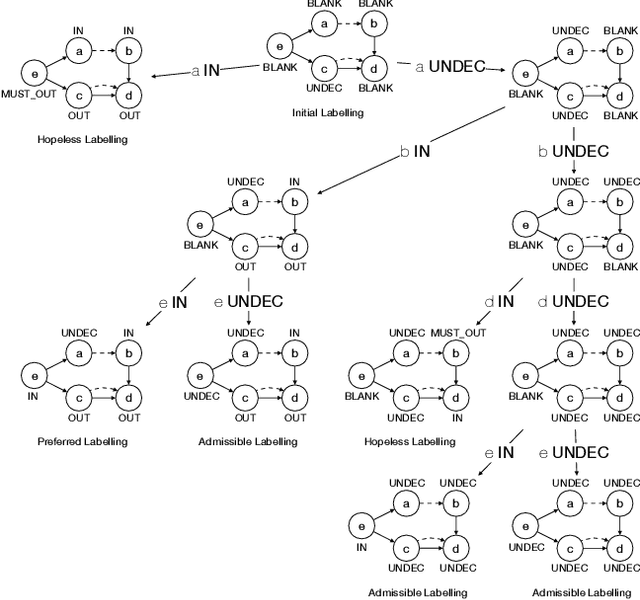
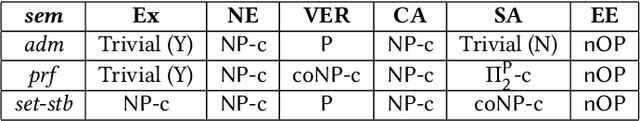
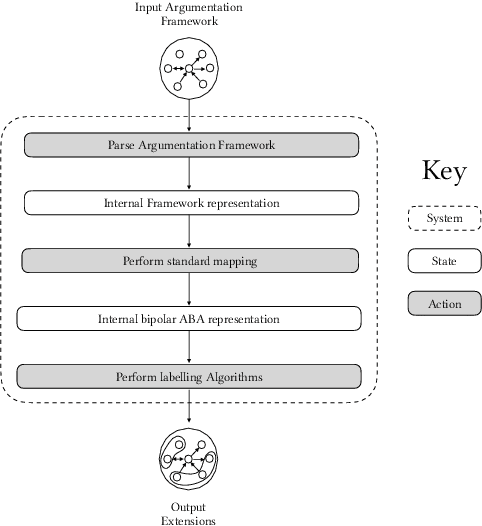
Abstract:Bipolar Argumentation Frameworks (BAFs) admit several interpretations of the support relation and diverging definitions of semantics. Recently, several classes of BAFs have been captured as instances of bipolar Assumption-Based Argumentation, a class of Assumption-Based Argumentation (ABA). In this paper, we establish the complexity of bipolar ABA, and consequently of several classes of BAFs. In addition to the standard five complexity problems, we analyse the rarely-addressed extension enumeration problem too. We also advance backtracking-driven algorithms for enumerating extensions of bipolar ABA frameworks, and consequently of BAFs under several interpretations. We prove soundness and completeness of our algorithms, describe their implementation and provide a scalability evaluation. We thus contribute to the study of the as yet uninvestigated complexity problems of (variously interpreted) BAFs as well as of bipolar ABA, and provide the lacking implementations thereof.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge