Amanda Fernández-Fontelo
Classification ensembles for multivariate functional data with application to mouse movements in web surveys
May 26, 2022


Abstract:We propose new ensemble models for multivariate functional data classification as combinations of semi-metric-based weak learners. Our models extend current semi-metric-type methods from the univariate to the multivariate case, propose new semi-metrics to compute distances between functions, and consider more flexible options for combining weak learners using stacked generalisation methods. We apply these ensemble models to identify respondents' difficulty with survey questions, with the aim to improve survey data quality. As predictors of difficulty, we use mouse movement trajectories from the respondents' interaction with a web survey, in which several questions were manipulated to create two scenarios with different levels of difficulty.
Predicting respondent difficulty in web surveys: A machine-learning approach based on mouse movement features
Nov 05, 2020
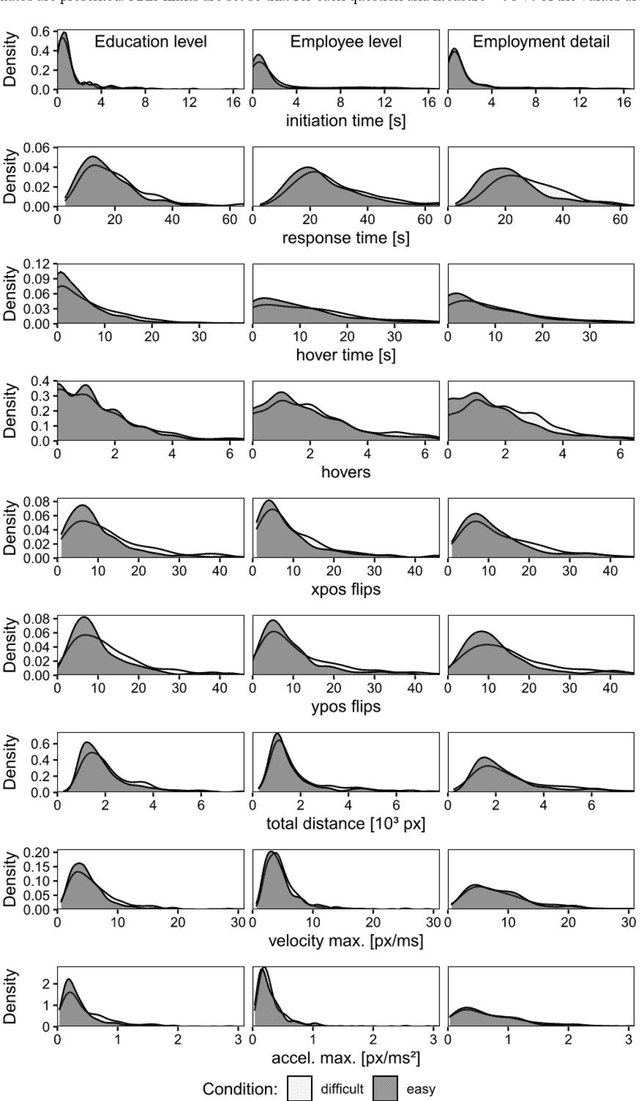
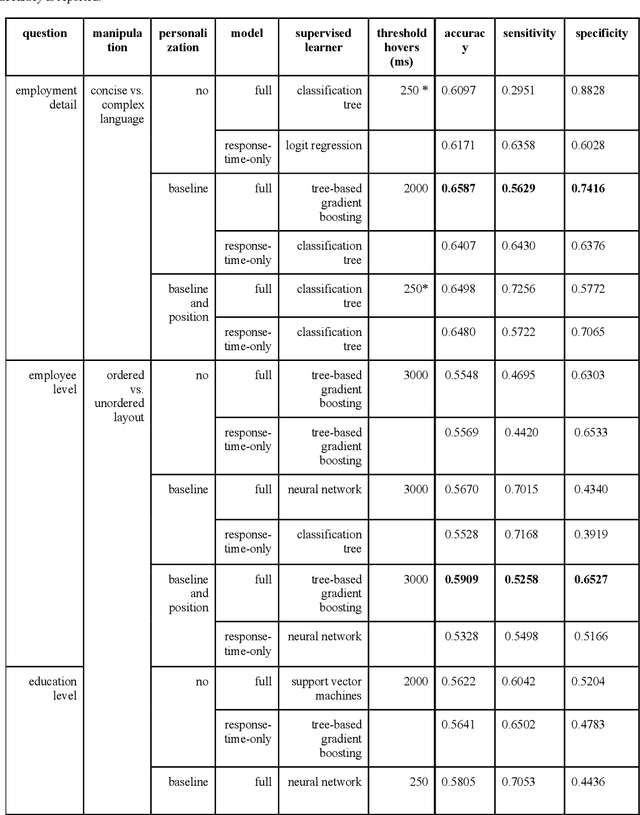
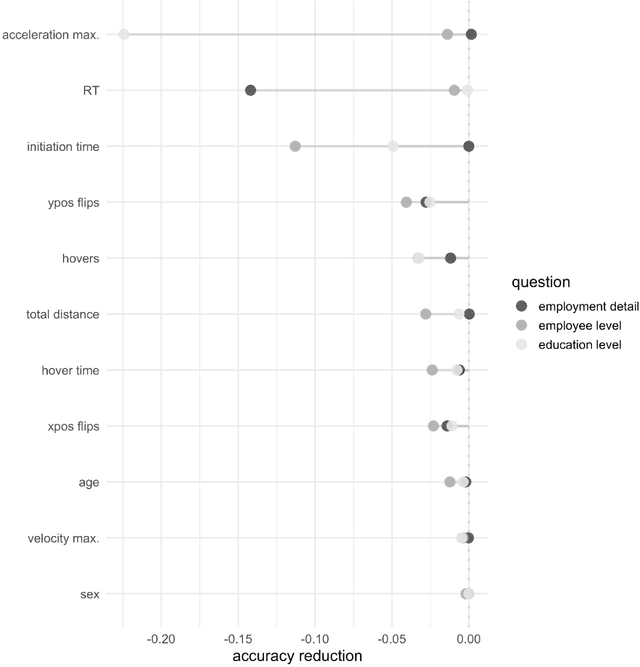
Abstract:A central goal of survey research is to collect robust and reliable data from respondents. However, despite researchers' best efforts in designing questionnaires, respondents may experience difficulty understanding questions' intent and therefore may struggle to respond appropriately. If it were possible to detect such difficulty, this knowledge could be used to inform real-time interventions through responsive questionnaire design, or to indicate and correct measurement error after the fact. Previous research in the context of web surveys has used paradata, specifically response times, to detect difficulties and to help improve user experience and data quality. However, richer data sources are now available, in the form of the movements respondents make with the mouse, as an additional and far more detailed indicator for the respondent-survey interaction. This paper uses machine learning techniques to explore the predictive value of mouse-tracking data with regard to respondents' difficulty. We use data from a survey on respondents' employment history and demographic information, in which we experimentally manipulate the difficulty of several questions. Using features derived from the cursor movements, we predict whether respondents answered the easy or difficult version of a question, using and comparing several state-of-the-art supervised learning methods. In addition, we develop a personalization method that adjusts for respondents' baseline mouse behavior and evaluate its performance. For all three manipulated survey questions, we find that including the full set of mouse movement features improved prediction performance over response-time-only models in nested cross-validation. Accounting for individual differences in mouse movements led to further improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge