Amal Alqahtani
StressRoBERTa: Cross-Condition Transfer Learning from Depression, Anxiety, and PTSD to Stress Detection
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The prevalence of chronic stress represents a significant public health concern, with social media platforms like Twitter serving as important venues for individuals to share their experiences. This paper introduces StressRoBERTa, a cross-condition transfer learning approach for automatic detection of self-reported chronic stress in English tweets. The investigation examines whether continual training on clinically related conditions (depression, anxiety, PTSD), disorders with high comorbidity with chronic stress, improves stress detection compared to general language models and broad mental health models. RoBERTa is continually trained on the Stress-SMHD corpus (108M words from users with self-reported diagnoses of depression, anxiety, and PTSD) and fine-tuned on the SMM4H 2022 Task 8 dataset. StressRoBERTa achieves 82% F1-score, outperforming the best shared task system (79% F1) by 3 percentage points. The results demonstrate that focused cross-condition transfer from stress-related disorders (+1% F1 over vanilla RoBERTa) provides stronger representations than general mental health training. Evaluation on Dreaddit (81% F1) further demonstrates transfer from clinical mental health contexts to situational stress discussions.
A Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Schizophrenia Language
Jan 25, 2022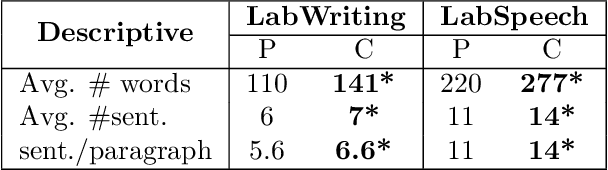
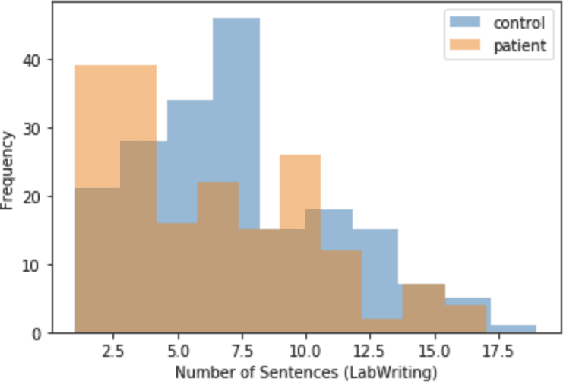
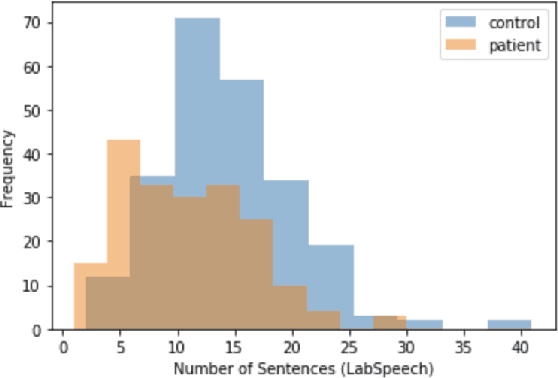
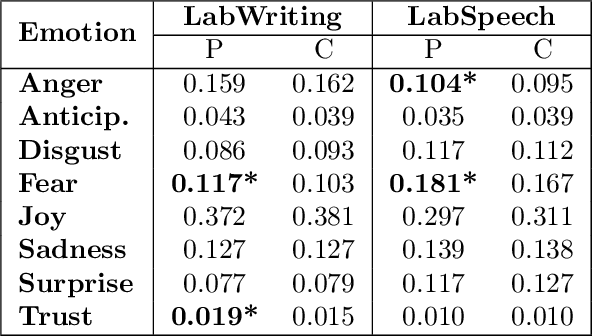
Abstract:Schizophrenia is one of the most disabling mental health conditions to live with. Approximately one percent of the population has schizophrenia which makes it fairly common, and it affects many people and their families. Patients with schizophrenia suffer different symptoms: formal thought disorder (FTD), delusions, and emotional flatness. In this paper, we quantitatively and qualitatively analyze the language of patients with schizophrenia measuring various linguistic features in two modalities: speech and written text. We examine the following features: coherence and cohesion of thoughts, emotions, specificity, level of committed belief (LCB), and personality traits. Our results show that patients with schizophrenia score high in fear and neuroticism compared to healthy controls. In addition, they are more committed to their beliefs, and their writing lacks details. They score lower in most of the linguistic features of cohesion with significant p-values.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge