Alvaro L. Fazenda
Sampling Strategies based on Wisdom of Crowds for Amazon Deforestation Detection
Aug 22, 2024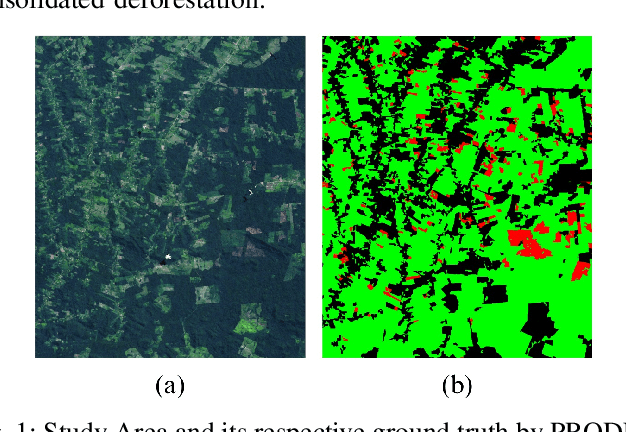
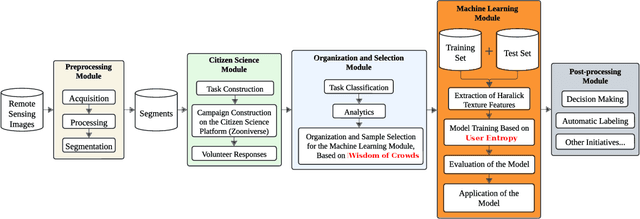
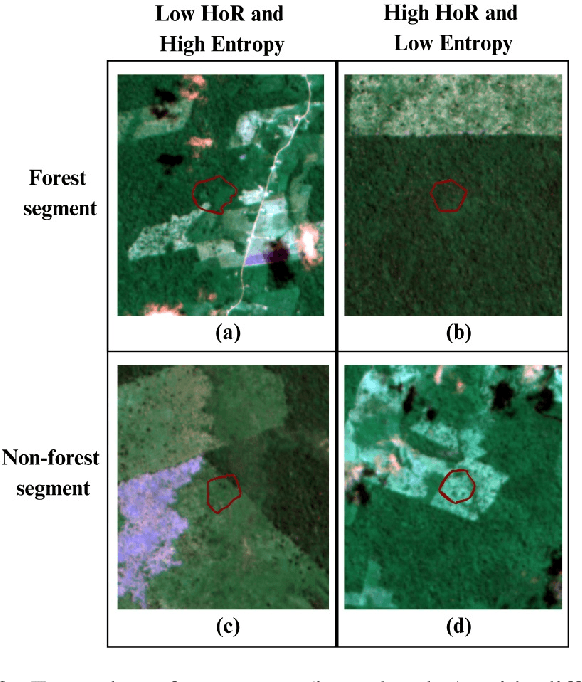
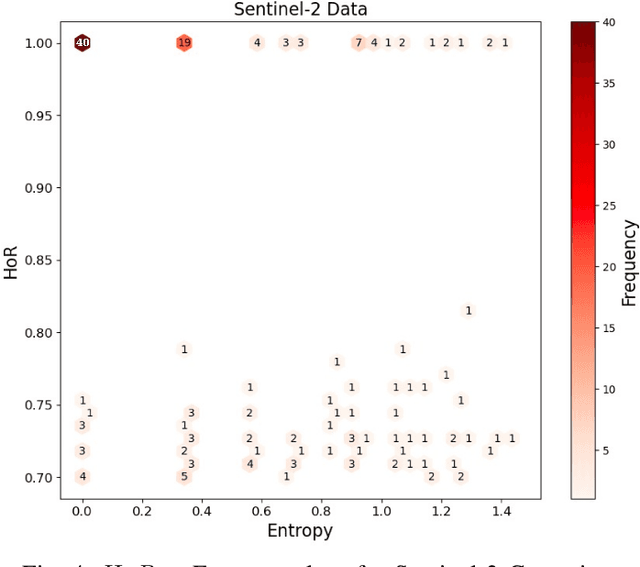
Abstract:Conserving tropical forests is highly relevant socially and ecologically because of their critical role in the global ecosystem. However, the ongoing deforestation and degradation affect millions of hectares each year, necessitating government or private initiatives to ensure effective forest monitoring. In April 2019, a project based on Citizen Science and Machine Learning models called ForestEyes (FE) was launched with the aim of providing supplementary data to assist experts from government and non-profit organizations in their deforestation monitoring efforts. Recent research has shown that labeling FE project volunteers/citizen scientists helps tailor machine learning models. In this sense, we adopt the FE project to create different sampling strategies based on the wisdom of crowds to select the most suitable samples from the training set to learn an SVM technique and obtain better classification results in deforestation detection tasks. In our experiments, we can show that our strategy based on user entropy-increasing achieved the best classification results in the deforestation detection task when compared with the random sampling strategies, as well as, reducing the convergence time of the SVM technique.
Femural Head Autosegmentation for 3D Radiotherapy Planning: Preliminary Results
Dec 11, 2018



Abstract:Contouring of organs at risk is an important but time consuming part of radiotherapy treatment planning. Several authors proposed methods for automatic delineation but the clinical experts eye remains the gold standard method. In this paper, we present a totally visual software for automated delineation of the femural head. The software was successfully characterized in pelvic CT Scan of prostate patients (n=11). The automatic delineation was compared with manual and approved delineation through blind test evaluated by a panel of seniors radiation oncologists (n=9). Clinical experts evaluated that no any contouring correction were need in 77.8% and 67.8% of manual and automatic delineation respectively. Our results show that the software is robust, the automated delineation was reproducible in all patient, and its performance was similar to manually delineation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge