Altan Cakir
Exploring the Influence of Dimensionality Reduction on Anomaly Detection Performance in Multivariate Time Series
Mar 07, 2024
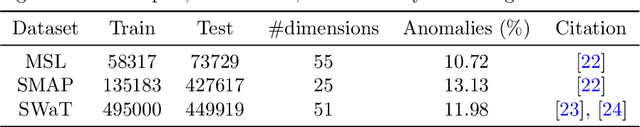


Abstract:This paper presents an extensive empirical study on the integration of dimensionality reduction techniques with advanced unsupervised time series anomaly detection models, focusing on the MUTANT and Anomaly-Transformer models. The study involves a comprehensive evaluation across three different datasets: MSL, SMAP, and SWaT. Each dataset poses unique challenges, allowing for a robust assessment of the models' capabilities in varied contexts. The dimensionality reduction techniques examined include PCA, UMAP, Random Projection, and t-SNE, each offering distinct advantages in simplifying high-dimensional data. Our findings reveal that dimensionality reduction not only aids in reducing computational complexity but also significantly enhances anomaly detection performance in certain scenarios. Moreover, a remarkable reduction in training times was observed, with reductions by approximately 300\% and 650\% when dimensionality was halved and minimized to the lowest dimensions, respectively. This efficiency gain underscores the dual benefit of dimensionality reduction in both performance enhancement and operational efficiency. The MUTANT model exhibits notable adaptability, especially with UMAP reduction, while the Anomaly-Transformer demonstrates versatility across various reduction techniques. These insights provide a deeper understanding of the synergistic effects of dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection, contributing valuable perspectives to the field of time series analysis. The study underscores the importance of selecting appropriate dimensionality reduction strategies based on specific model requirements and dataset characteristics, paving the way for more efficient, accurate, and scalable solutions in anomaly detection.
Modified Query Expansion Through Generative Adversarial Networks for Information Extraction in E-Commerce
Dec 30, 2022



Abstract:This work addresses an alternative approach for query expansion (QE) using a generative adversarial network (GAN) to enhance the effectiveness of information search in e-commerce. We propose a modified QE conditional GAN (mQE-CGAN) framework, which resolves keywords by expanding the query with a synthetically generated query that proposes semantic information from text input. We train a sequence-to-sequence transformer model as the generator to produce keywords and use a recurrent neural network model as the discriminator to classify an adversarial output with the generator. With the modified CGAN framework, various forms of semantic insights gathered from the query document corpus are introduced to the generation process. We leverage these insights as conditions for the generator model and discuss their effectiveness for the query expansion task. Our experiments demonstrate that the utilization of condition structures within the mQE-CGAN framework can increase the semantic similarity between generated sequences and reference documents up to nearly 10% compared to baseline models
Twitter Referral Behaviours on News Consumption with Ensemble Clustering of Click-Stream Data in Turkish Media
Feb 04, 2022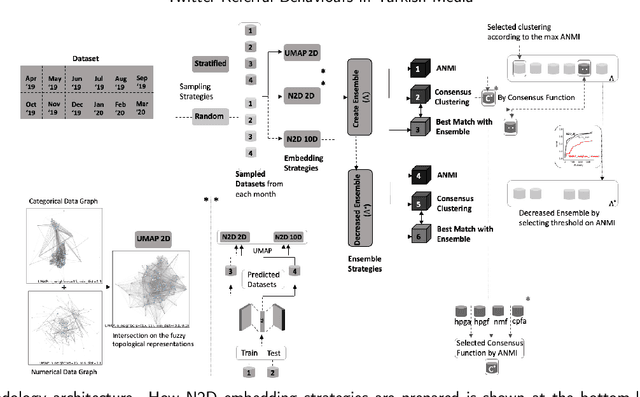
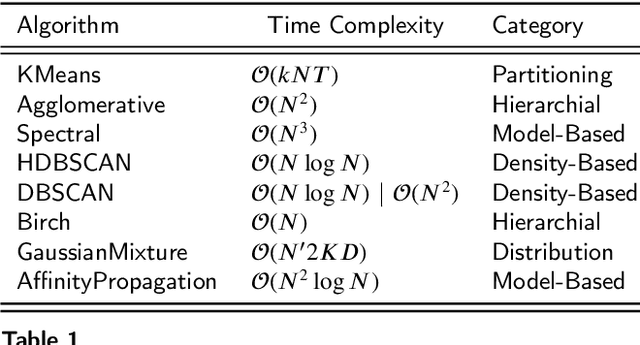
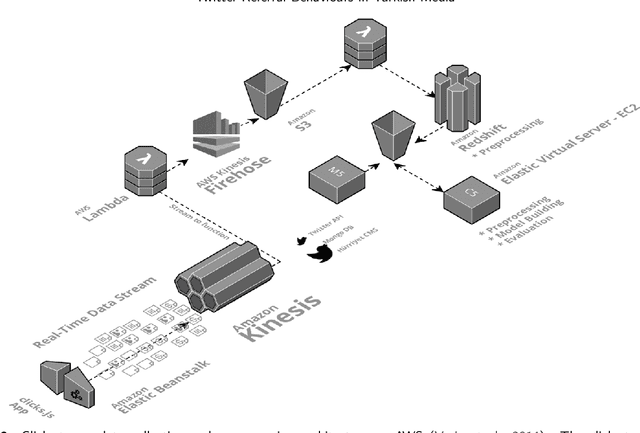
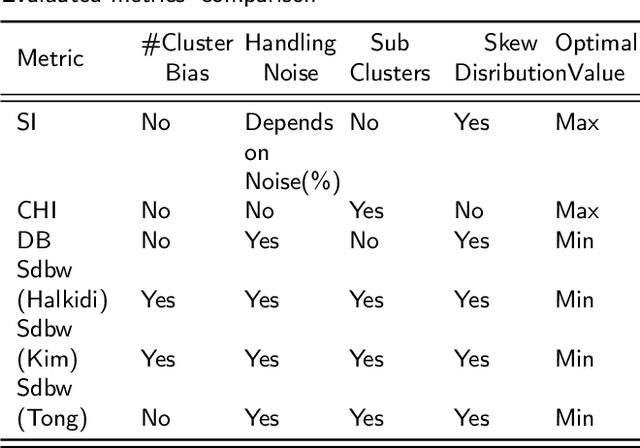
Abstract:Click-stream data, which comes with a massive volume generated by the human activities on the websites, has become a prominent feature to identify readers' characteristics by the newsrooms after the digitization of the news outlets. It is essential to have elastic architectures to process the streaming data, particularly for unprecedented traffic, enabling conducting more comprehensive analyses such as recommending mostly related articles to the readers. Although the nature of click-stream data has a similar logic within the websites, it has inherent limitations to recognize human behaviors when looking from a broad perspective, which brings the need of limiting the problem in niche areas. This study investigates the anonymized readers' click activities in the organizations' websites to identify news consumption patterns following referrals from Twitter, who incidentally reach but propensity is mainly the routed news content. The investigation is widened to a broad perspective by linking the log data with news content to enrich the insights rather than sticking into the web journey. The methodologies on ensemble cluster analysis with mixed-type embedding strategies are applied and compared to find similar reader groups and interests independent from time. Our results demonstrate that the quality of clustering mixed-type data set approaches to optimal internal validation scores when embedded by Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) and using consensus function as a key to access the most applicable hyper parameter configurations in the given ensemble rather than using consensus function results directly. Evaluation of the resulting clusters highlights specific clusters repeatedly present in the samples, which provide insights to the news organizations and overcome the degradation of the modeling behaviors due to the change in the interest over time.
An Evaluation of Recent Neural Sequence Tagging Models in Turkish Named Entity Recognition
May 18, 2020



Abstract:Named entity recognition (NER) is an extensively studied task that extracts and classifies named entities in a text. NER is crucial not only in downstream language processing applications such as relation extraction and question answering but also in large scale big data operations such as real-time analysis of online digital media content. Recent research efforts on Turkish, a less studied language with morphologically rich nature, have demonstrated the effectiveness of neural architectures on well-formed texts and yielded state-of-the art results by formulating the task as a sequence tagging problem. In this work, we empirically investigate the use of recent neural architectures (Bidirectional long short-term memory and Transformer-based networks) proposed for Turkish NER tagging in the same setting. Our results demonstrate that transformer-based networks which can model long-range context overcome the limitations of BiLSTM networks where different input features at the character, subword, and word levels are utilized. We also propose a transformer-based network with a conditional random field (CRF) layer that leads to the state-of-the-art result (95.95\% f-measure) on a common dataset. Our study contributes to the literature that quantifies the impact of transfer learning on processing morphologically rich languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge