Alistair Francis
Major TOM: Expandable Datasets for Earth Observation
Feb 19, 2024


Abstract:Deep learning models are increasingly data-hungry, requiring significant resources to collect and compile the datasets needed to train them, with Earth Observation (EO) models being no exception. However, the landscape of datasets in EO is relatively atomised, with interoperability made difficult by diverse formats and data structures. If ever larger datasets are to be built, and duplication of effort minimised, then a shared framework that allows users to combine and access multiple datasets is needed. Here, Major TOM (Terrestrial Observation Metaset) is proposed as this extensible framework. Primarily, it consists of a geographical indexing system based on a set of grid points and a metadata structure that allows multiple datasets with different sources to be merged. Besides the specification of Major TOM as a framework, this work also presents a large, open-access dataset, MajorTOM-Core, which covers the vast majority of the Earth's land surface. This dataset provides the community with both an immediately useful resource, as well as acting as a template for future additions to the Major TOM ecosystem. Access: https://huggingface.co/Major-TOM
From LAION-5B to LAION-EO: Filtering Billions of Images Using Anchor Datasets for Satellite Image Extraction
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:Large datasets, such as LAION-5B, contain a diverse distribution of images shared online. However, extraction of domain-specific subsets of large image corpora is challenging. The extraction approach based on an anchor dataset, combined with further filtering, is proposed here and demonstrated for the domain of satellite imagery. This results in the release of LAION-EO, a dataset sourced from the web containing pairs of text and satellite images in high (pixel-wise) resolution. The paper outlines the acquisition procedure as well as some of the features of the dataset.
SEnSeI: A Deep Learning Module for Creating Sensor Independent Cloud Masks
Nov 16, 2021
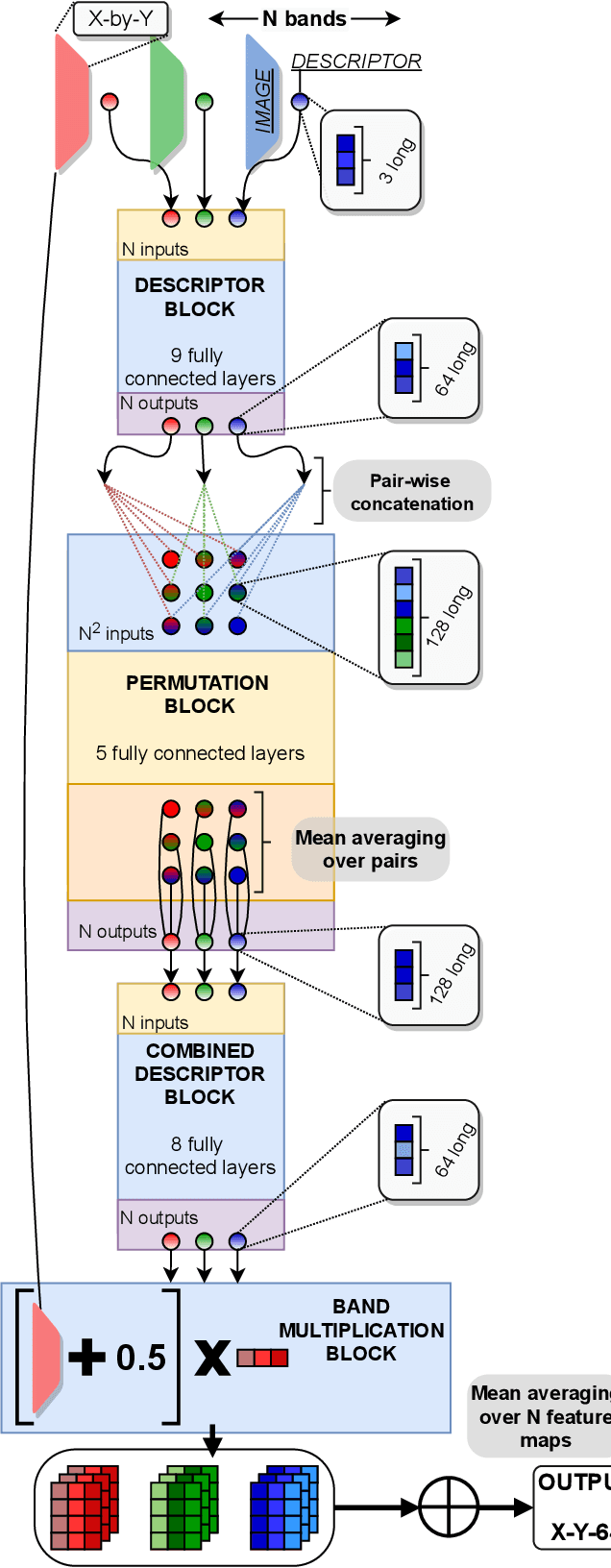
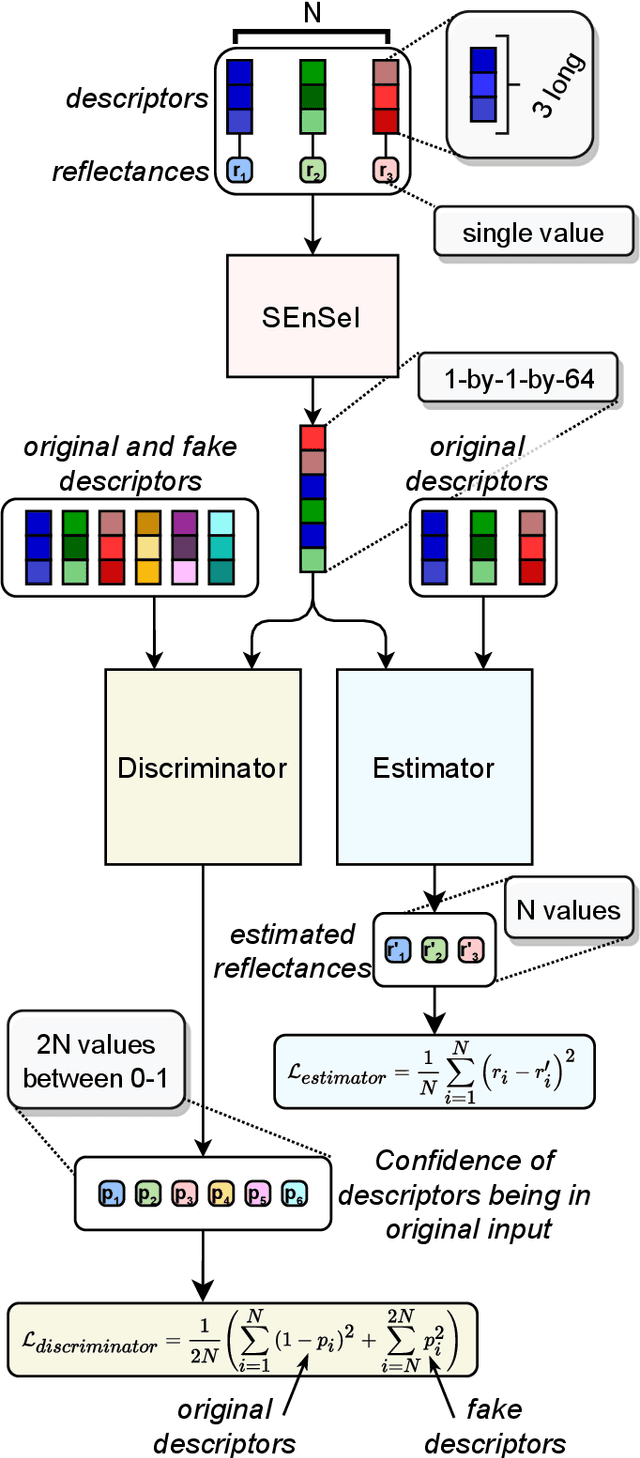
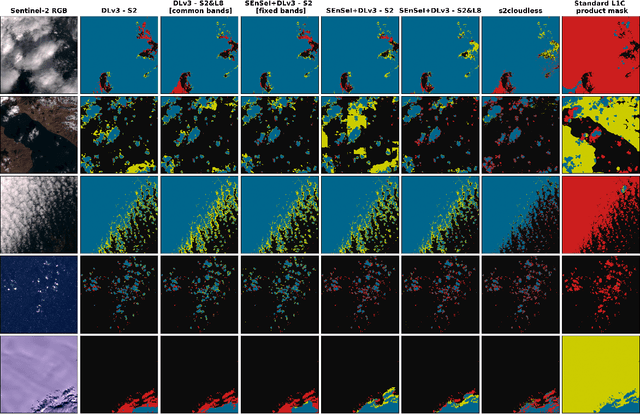
Abstract:We introduce a novel neural network architecture -- Spectral ENcoder for SEnsor Independence (SEnSeI) -- by which several multispectral instruments, each with different combinations of spectral bands, can be used to train a generalised deep learning model. We focus on the problem of cloud masking, using several pre-existing datasets, and a new, freely available dataset for Sentinel-2. Our model is shown to achieve state-of-the-art performance on the satellites it was trained on (Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8), and is able to extrapolate to sensors it has not seen during training such as Landsat 7, Per\'uSat-1, and Sentinel-3 SLSTR. Model performance is shown to improve when multiple satellites are used in training, approaching or surpassing the performance of specialised, single-sensor models. This work is motivated by the fact that the remote sensing community has access to data taken with a hugely variety of sensors. This has inevitably led to labelling efforts being undertaken separately for different sensors, which limits the performance of deep learning models, given their need for huge training sets to perform optimally. Sensor independence can enable deep learning models to utilise multiple datasets for training simultaneously, boosting performance and making them much more widely applicable. This may lead to deep learning approaches being used more frequently for on-board applications and in ground segment data processing, which generally require models to be ready at launch or soon afterwards.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge