Ali Pour Yazdanpanah
ODE-based Deep Network for MRI Reconstruction
Dec 27, 2019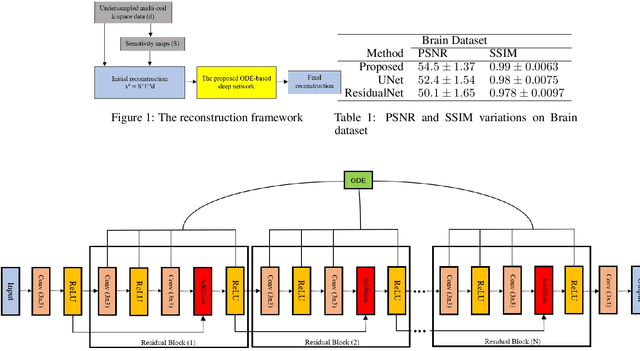
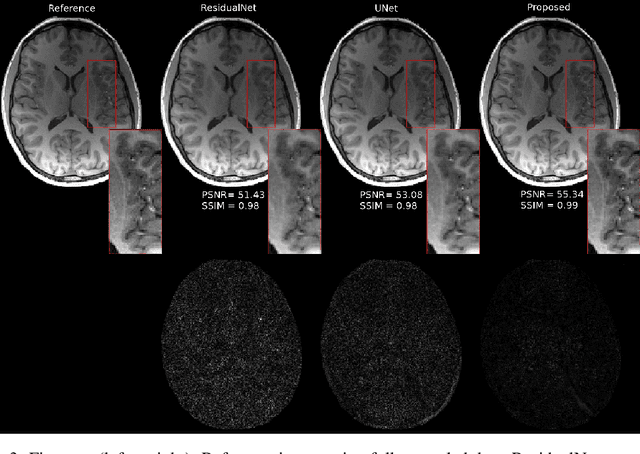
Abstract:Fast data acquisition in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is vastly in demand and scan time directly depends on the number of acquired k-space samples. The data-driven methods based on deep neural networks have resulted in promising improvements, compared to the conventional methods, in image reconstruction algorithms. The connection between deep neural network and Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) has been observed and studied recently. The studies show that different residual networks can be interpreted as Euler discretization of an ODE. In this paper, we propose an ODE-based deep network for MRI reconstruction to enable the rapid acquisition of MR images with improved image quality. Our results with undersampled data demonstrate that our method can deliver higher quality images in comparison to the reconstruction methods based on the standard UNet network and Residual network.
Deep Plug-and-Play Prior for Parallel MRI Reconstruction
Sep 06, 2019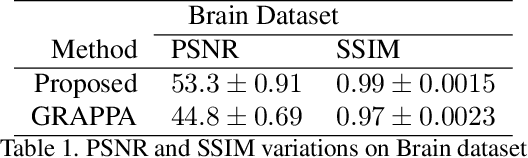
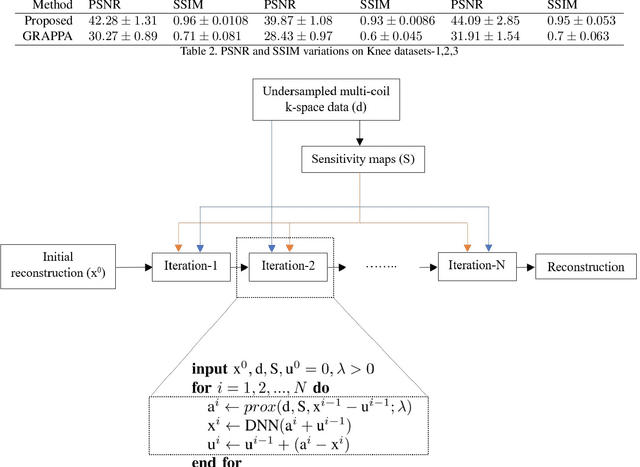
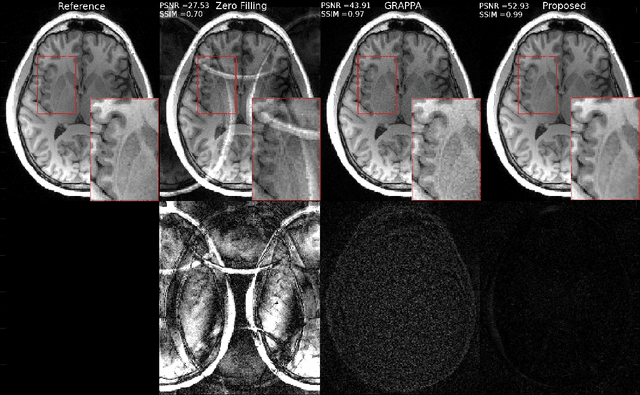
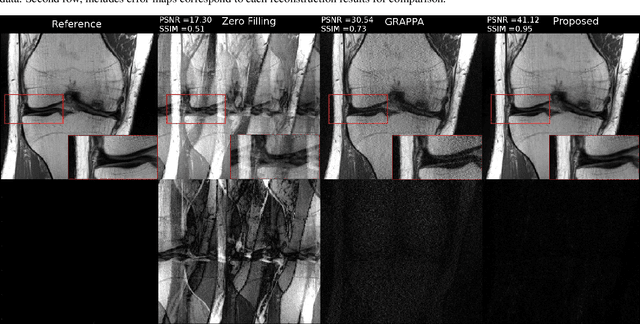
Abstract:Fast data acquisition in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is vastly in demand and scan time directly depends on the number of acquired k-space samples. Conventional MRI reconstruction methods for fast MRI acquisition mostly relied on different regularizers which represent analytical models of sparsity. However, recent data-driven methods based on deep learning has resulted in promising improvements in image reconstruction algorithms. In this paper, we propose a deep plug-and-play prior framework for parallel MRI reconstruction problems which utilize a deep neural network (DNN) as an advanced denoiser within an iterative method. This, in turn, enables rapid acquisition of MR images with improved image quality. The proposed method was compared with the reconstructions using the clinical gold standard GRAPPA method. Our results with undersampled data demonstrate that our method can deliver considerably higher quality images at high acceleration factors in comparison to clinical gold standard method for MRI reconstructions. Our proposed reconstruction enables an increase in acceleration factor, and a reduction in acquisition time while maintaining high image quality.
Non-Learning based Deep Parallel MRI Reconstruction (NLDpMRI)
Oct 23, 2018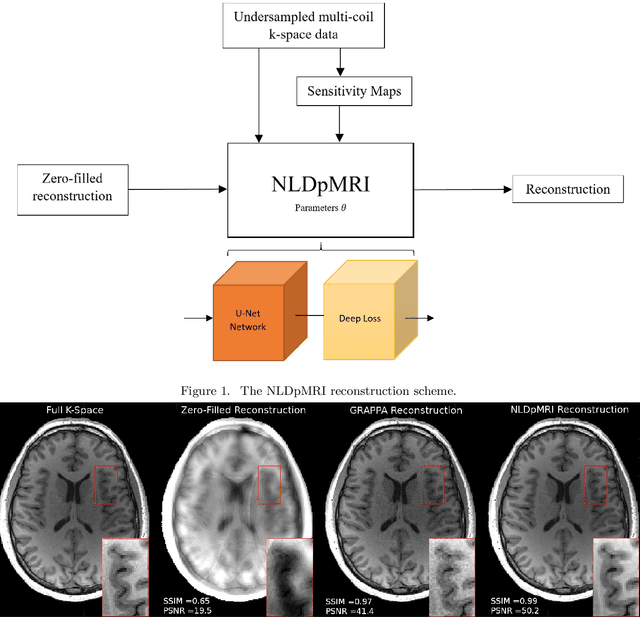
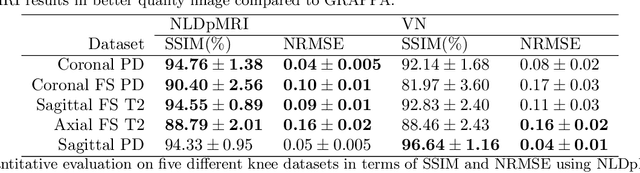
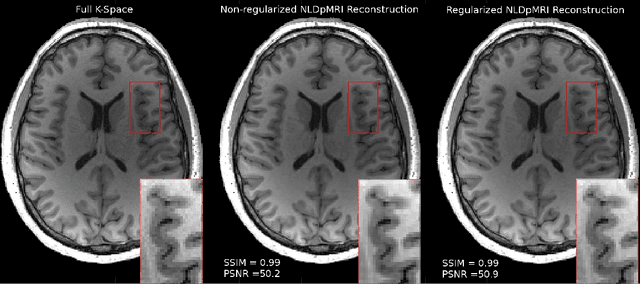
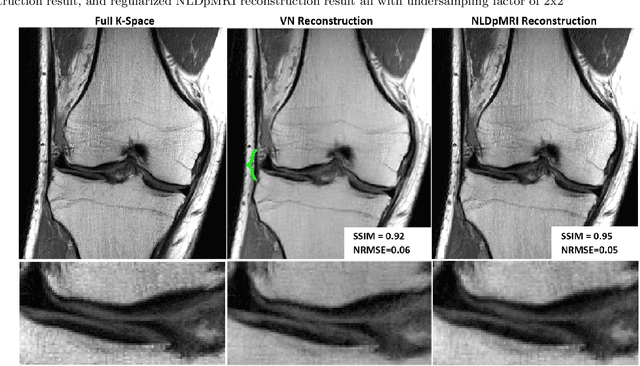
Abstract:Fast data acquisition in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is vastly in demand and scan time directly depends on the number of acquired k-space samples. The most common issues in any deep learning-based MRI reconstruction approaches are generalizability and transferability. For different MRI scanner configurations using these approaches, the network must be trained from scratch every time with new training dataset, acquired under new configurations, to be able to provide good reconstruction performance. Here, we propose a new parallel imaging method based on deep neural networks called NLDpMRI to reduce any structured aliasing ambiguities related to the different k-space undersampling patterns for accelerated data acquisition. Two loss functions including non-regularized and regularized are proposed for parallel MRI reconstruction using deep network optimization and we reconstruct MR images by optimizing the proposed loss functions over the network parameters. Unlike any deep learning-based MRI reconstruction approaches, our method doesn't include any training step that the network learns from a large number of training samples and it only needs the single undersampled multi-coil k-space data for reconstruction. Also, the proposed method can handle k-space data with different undersampling patterns, and different number of coils. Unlike most deep learning-based MRI reconstruction methods, our method operates on real-world acquisitions with the complex data format, not on simulated data, real-valued data, or data with added simulated-phase. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms the current state-of-the-art GRAPPA reconstruction method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge