Alfan Farizki Wicaksono
Pengembangan Model untuk Mendeteksi Kerusakan pada Terumbu Karang dengan Klasifikasi Citra
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:The abundant biodiversity of coral reefs in Indonesian waters is a valuable asset that needs to be preserved. Rapid climate change and uncontrolled human activities have led to the degradation of coral reef ecosystems, including coral bleaching, which is a critical indicator of coral health conditions. Therefore, this research aims to develop an accurate classification model to distinguish between healthy corals and corals experiencing bleaching. This study utilizes a specialized dataset consisting of 923 images collected from Flickr using the Flickr API. The dataset comprises two distinct classes: healthy corals (438 images) and bleached corals (485 images). These images have been resized to a maximum of 300 pixels in width or height, whichever is larger, to maintain consistent sizes across the dataset. The method employed in this research involves the use of machine learning models, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNN), to recognize and differentiate visual patterns associated with healthy and bleached corals. In this context, the dataset can be used to train and test various classification models to achieve optimal results. By leveraging the ResNet model, it was found that a from-scratch ResNet model can outperform pretrained models in terms of precision and accuracy. The success in developing accurate classification models will greatly benefit researchers and marine biologists in gaining a better understanding of coral reef health. These models can also be employed to monitor changes in the coral reef environment, thereby making a significant contribution to conservation and ecosystem restoration efforts that have far-reaching impacts on life.
Multi-Task Active Learning for Neural Semantic Role Labeling on Low Resource Conversational Corpus
Jun 05, 2018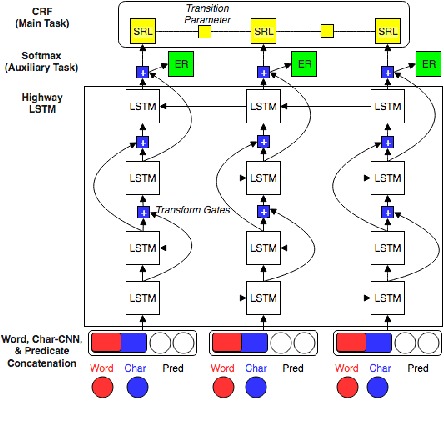
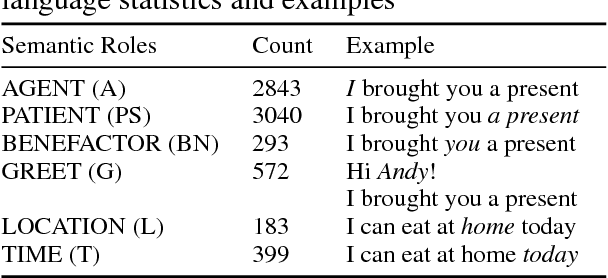
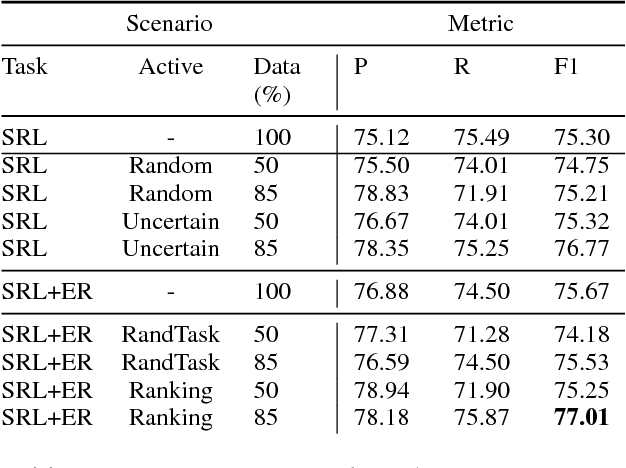
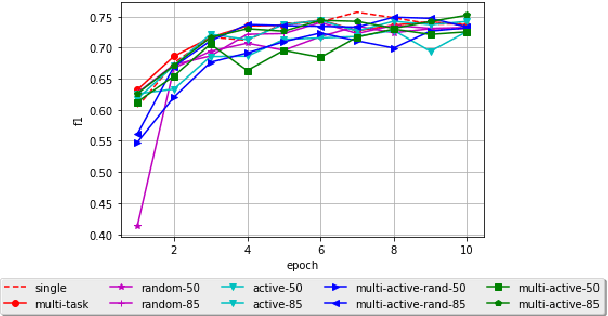
Abstract:Most Semantic Role Labeling (SRL) approaches are supervised methods which require a significant amount of annotated corpus, and the annotation requires linguistic expertise. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Task Active Learning framework for Semantic Role Labeling with Entity Recognition (ER) as the auxiliary task to alleviate the need for extensive data and use additional information from ER to help SRL. We evaluate our approach on Indonesian conversational dataset. Our experiments show that multi-task active learning can outperform single-task active learning method and standard multi-task learning. According to our results, active learning is more efficient by using 12% less of training data compared to passive learning in both single-task and multi-task setting. We also introduce a new dataset for SRL in Indonesian conversational domain to encourage further research in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge