Alexander Yalunin
Predicting COVID-19 and pneumonia complications from admission texts
May 05, 2023Abstract:In this paper we present a novel approach to risk assessment for patients hospitalized with pneumonia or COVID-19 based on their admission reports. We applied a Longformer neural network to admission reports and other textual data available shortly after admission to compute risk scores for the patients. We used patient data of multiple European hospitals to demonstrate that our approach outperforms the Transformer baselines. Our experiments show that the proposed model generalises across institutions and diagnoses. Also, our method has several other advantages described in the paper.
RuBioRoBERTa: a pre-trained biomedical language model for Russian language biomedical text mining
Apr 08, 2022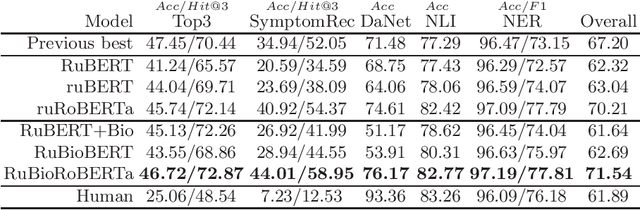
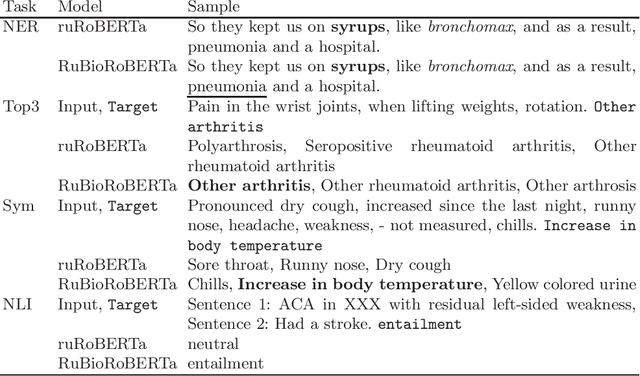
Abstract:This paper presents several BERT-based models for Russian language biomedical text mining (RuBioBERT, RuBioRoBERTa). The models are pre-trained on a corpus of freely available texts in the Russian biomedical domain. With this pre-training, our models demonstrate state-of-the-art results on RuMedBench - Russian medical language understanding benchmark that covers a diverse set of tasks, including text classification, question answering, natural language inference, and named entity recognition.
Abstractive summarization of hospitalisation histories with transformer networks
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:In this paper we present a novel approach to abstractive summarization of patient hospitalisation histories. We applied an encoder-decoder framework with Longformer neural network as an encoder and BERT as a decoder. Our experiments show improved quality on some summarization tasks compared with pointer-generator networks. We also conducted a study with experienced physicians evaluating the results of our model in comparison with PGN baseline and human-generated abstracts, which showed the effectiveness of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge