Alexander Reiterer
SemanticBridge - A Dataset for 3D Semantic Segmentation of Bridges and Domain Gap Analysis
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel dataset that has been specifically designed for 3D semantic segmentation of bridges and the domain gap analysis caused by varying sensors. This addresses a critical need in the field of infrastructure inspection and maintenance, which is essential for modern society. The dataset comprises high-resolution 3D scans of a diverse range of bridge structures from various countries, with detailed semantic labels provided for each. Our initial objective is to facilitate accurate and automated segmentation of bridge components, thereby advancing the structural health monitoring practice. To evaluate the effectiveness of existing 3D deep learning models on this novel dataset, we conduct a comprehensive analysis of three distinct state-of-the-art architectures. Furthermore, we present data acquired through diverse sensors to quantify the domain gap resulting from sensor variations. Our findings indicate that all architectures demonstrate robust performance on the specified task. However, the domain gap can potentially lead to a decline in the performance of up to 11.4% mIoU.
Smart(Sampling)Augment: Optimal and Efficient Data Augmentation for Semantic Segmentation
Oct 31, 2021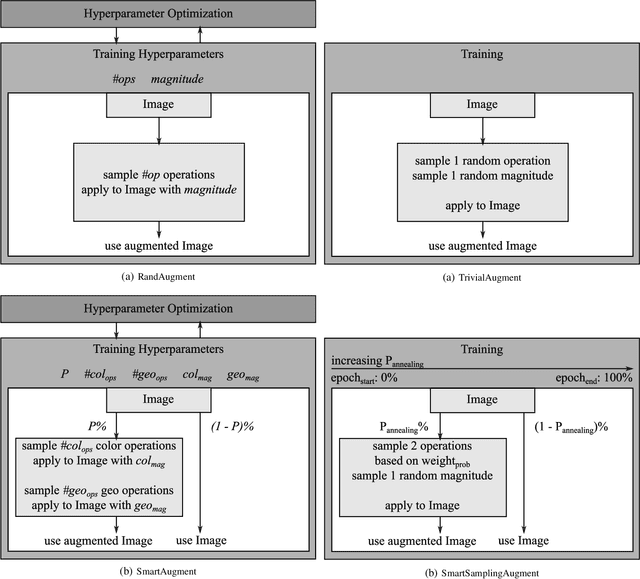
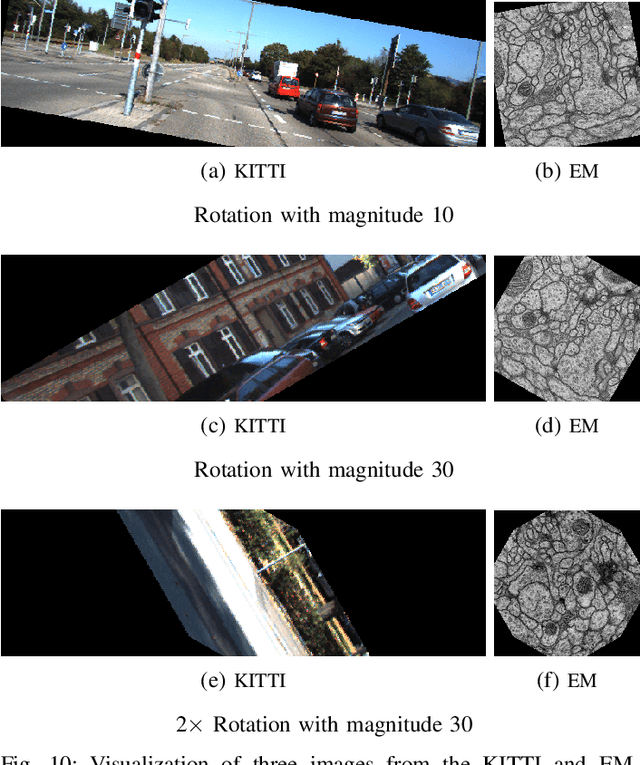

Abstract:Data augmentation methods enrich datasets with augmented data to improve the performance of neural networks. Recently, automated data augmentation methods have emerged, which automatically design augmentation strategies. Existing work focuses on image classification and object detection, whereas we provide the first study on semantic image segmentation and introduce two new approaches: \textit{SmartAugment} and \textit{SmartSamplingAugment}. SmartAugment uses Bayesian Optimization to search over a rich space of augmentation strategies and achieves a new state-of-the-art performance in all semantic segmentation tasks we consider. SmartSamplingAugment, a simple parameter-free approach with a fixed augmentation strategy competes in performance with the existing resource-intensive approaches and outperforms cheap state-of-the-art data augmentation methods. Further, we analyze the impact, interaction, and importance of data augmentation hyperparameters and perform ablation studies, which confirm our design choices behind SmartAugment and SmartSamplingAugment. Lastly, we will provide our source code for reproducibility and to facilitate further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge