Alexander Grünberger
Machine learning in bioprocess development: From promise to practice
Oct 04, 2022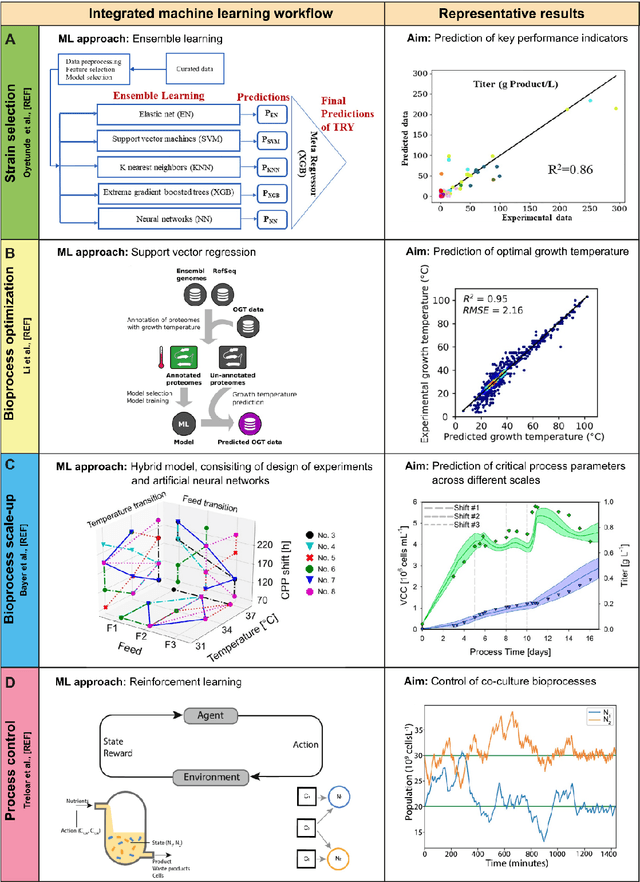
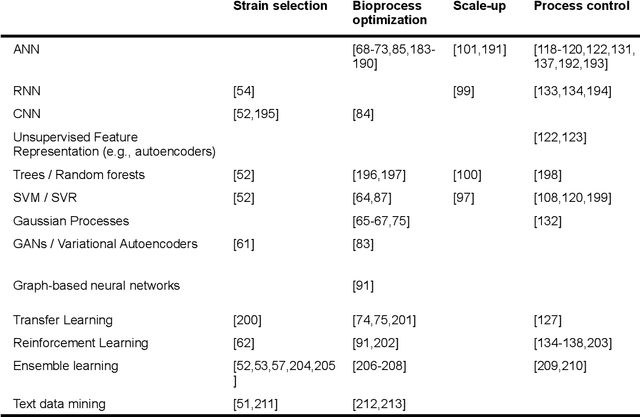
Abstract:Fostered by novel analytical techniques, digitalization and automation, modern bioprocess development provides high amounts of heterogeneous experimental data, containing valuable process information. In this context, data-driven methods like machine learning (ML) approaches have a high potential to rationally explore large design spaces while exploiting experimental facilities most efficiently. The aim of this review is to demonstrate how ML methods have been applied so far in bioprocess development, especially in strain engineering and selection, bioprocess optimization, scale-up, monitoring and control of bioprocesses. For each topic, we will highlight successful application cases, current challenges and point out domains that can potentially benefit from technology transfer and further progress in the field of ML.
Towards an Automatic Analysis of CHO-K1 Suspension Growth in Microfluidic Single-cell Cultivation
Oct 20, 2020



Abstract:Motivation: Innovative microfluidic systems carry the promise to greatly facilitate spatio-temporal analysis of single cells under well-defined environmental conditions, allowing novel insights into population heterogeneity and opening new opportunities for fundamental and applied biotechnology. Microfluidics experiments, however, are accompanied by vast amounts of data, such as time series of microscopic images, for which manual evaluation is infeasible due to the sheer number of samples. While classical image processing technologies do not lead to satisfactory results in this domain, modern deep learning technologies such as convolutional networks can be sufficiently versatile for diverse tasks, including automatic cell tracking and counting as well as the extraction of critical parameters, such as growth rate. However, for successful training, current supervised deep learning requires label information, such as the number or positions of cells for each image in a series; obtaining these annotations is very costly in this setting. Results: We propose a novel Machine Learning architecture together with a specialized training procedure, which allows us to infuse a deep neural network with human-powered abstraction on the level of data, leading to a high-performing regression model that requires only a very small amount of labeled data. Specifically, we train a generative model simultaneously on natural and synthetic data, so that it learns a shared representation, from which a target variable, such as the cell count, can be reliably estimated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge