Alex Szorkovszky
Central pattern generators evolved for real-time adaptation
Oct 14, 2022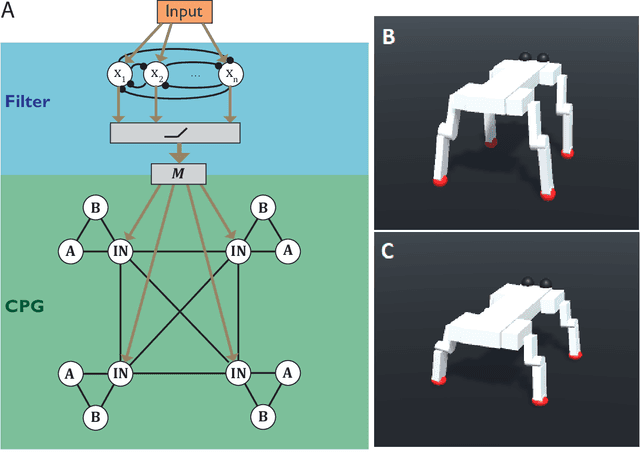
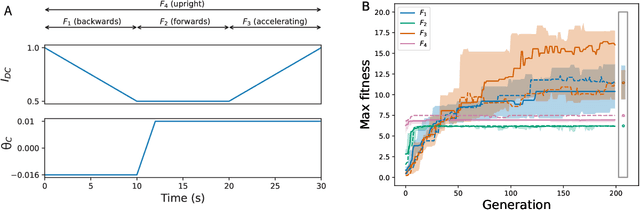
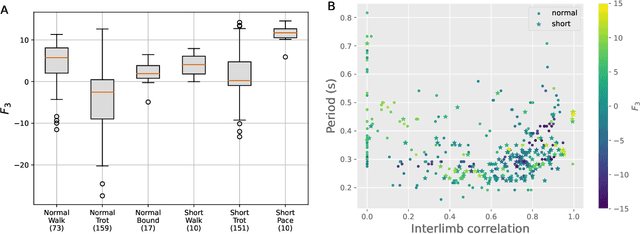
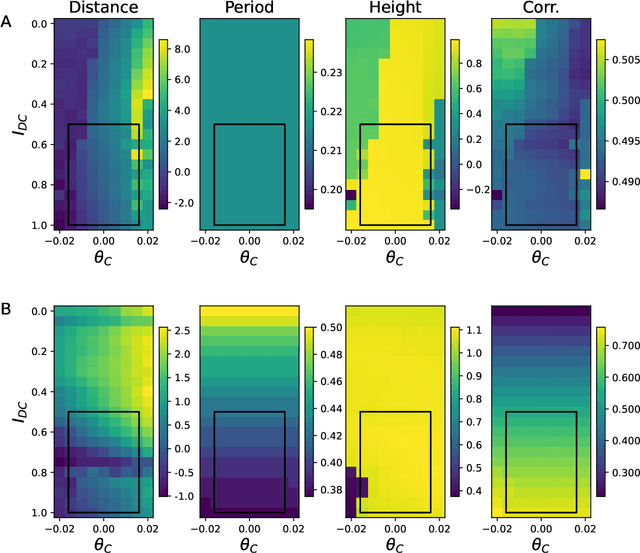
Abstract:For a robot to be both autonomous and collaborative requires the ability to adapt its movement to a variety of external stimuli, whether these come from humans or other robots. Typically, legged robots have oscillation periods explicitly defined as a control parameter, limiting the adaptability of walking gaits. Here we demonstrate a virtual quadruped robot employing a bio-inspired central pattern generator (CPG) that can spontaneously synchronize its movement to a range of rhythmic stimuli. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms were used to optimize the variation of movement speed and direction as a function of the brain stem drive and the center of mass control respectively. This was followed by optimization of an additional layer of neurons that filters fluctuating inputs. As a result, a range of CPGs were able to adjust their gait pattern and/or frequency to match the input period. We show how this can be used to facilitate coordinated movement despite differences in morphology, as well as to learn new movement patterns.
Rapid rhythmic entrainment in bio-inspired central pattern generators
Jun 03, 2022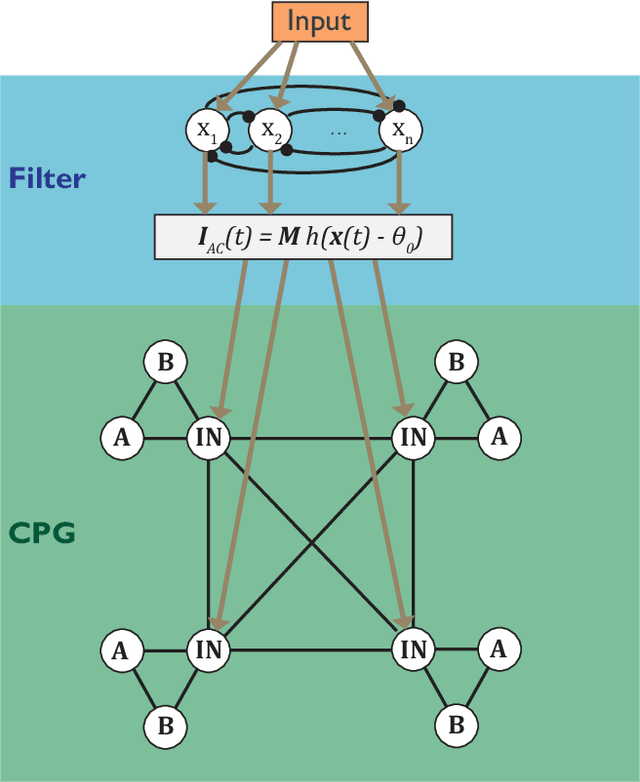
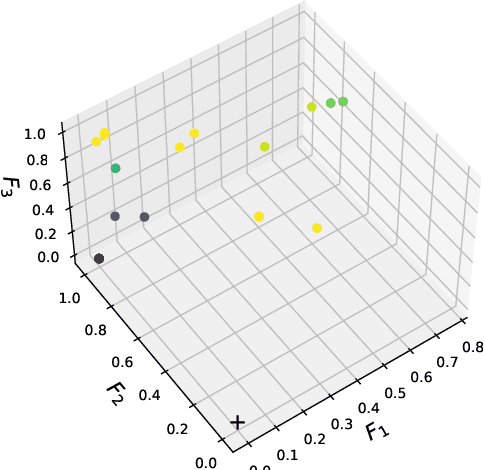
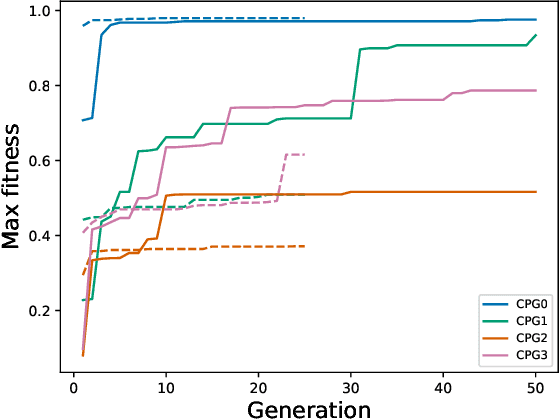
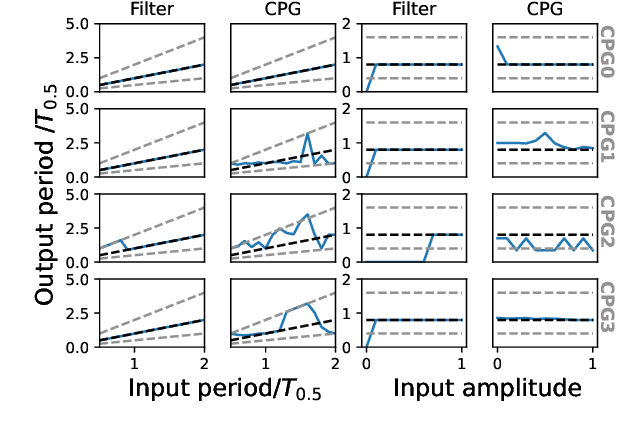
Abstract:Entrainment of movement to a periodic stimulus is a characteristic intelligent behaviour in humans and an important goal for adaptive robotics. We demonstrate a quadruped central pattern generator (CPG), consisting of modified Matsuoka neurons, that spontaneously adjusts its period of oscillation to that of a periodic input signal. This is done by simple forcing, with the aid of a filtering network as well as a neural model with tonic input-dependent oscillation period. We first use the NSGA3 algorithm to evolve the CPG parameters, using separate fitness functions for period tunability, limb homogeneity and gait stability. Four CPGs, maximizing different weighted averages of the fitness functions, are then selected from the Pareto front and each is used as a basis for optimizing a filter network. Different numbers of neurons are tested for each filter network. We find that period tunability in particular facilitates robust entrainment, that bounding gaits entrain more easily than walking gaits, and that more neurons in the filter network are beneficial for pre-processing input signals. The system that we present can be used in conjunction with sensory feedback to allow low-level adaptive and robust behaviour in walking robots.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge