Alex Drlica-Wagner
Opportunities in AI/ML for the Rubin LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The Vera C. Rubin Observatory's Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) will produce unprecedented volumes of heterogeneous astronomical data (images, catalogs, and alerts) that challenge traditional analysis pipelines. The LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration (DESC) aims to derive robust constraints on dark energy and dark matter from these data, requiring methods that are statistically powerful, scalable, and operationally reliable. Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) are already embedded across DESC science workflows, from photometric redshifts and transient classification to weak lensing inference and cosmological simulations. Yet their utility for precision cosmology hinges on trustworthy uncertainty quantification, robustness to covariate shift and model misspecification, and reproducible integration within scientific pipelines. This white paper surveys the current landscape of AI/ML across DESC's primary cosmological probes and cross-cutting analyses, revealing that the same core methodologies and fundamental challenges recur across disparate science cases. Since progress on these cross-cutting challenges would benefit multiple probes simultaneously, we identify key methodological research priorities, including Bayesian inference at scale, physics-informed methods, validation frameworks, and active learning for discovery. With an eye on emerging techniques, we also explore the potential of the latest foundation model methodologies and LLM-driven agentic AI systems to reshape DESC workflows, provided their deployment is coupled with rigorous evaluation and governance. Finally, we discuss critical software, computing, data infrastructure, and human capital requirements for the successful deployment of these new methodologies, and consider associated risks and opportunities for broader coordination with external actors.
Inferring Structural Parameters of Low-Surface-Brightness-Galaxies with Uncertainty Quantification using Bayesian Neural Networks
Jul 07, 2022

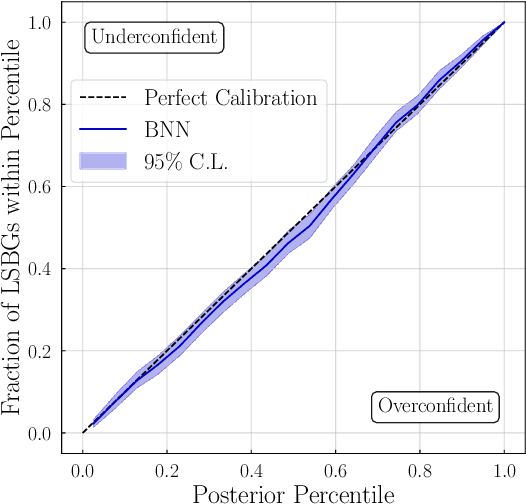

Abstract:Measuring the structural parameters (size, total brightness, light concentration, etc.) of galaxies is a significant first step towards a quantitative description of different galaxy populations. In this work, we demonstrate that a Bayesian Neural Network (BNN) can be used for the inference, with uncertainty quantification, of such morphological parameters from simulated low-surface-brightness galaxy images. Compared to traditional profile-fitting methods, we show that the uncertainties obtained using BNNs are comparable in magnitude, well-calibrated, and the point estimates of the parameters are closer to the true values. Our method is also significantly faster, which is very important with the advent of the era of large galaxy surveys and big data in astrophysics.
DeepShadows: Separating Low Surface Brightness Galaxies from Artifacts using Deep Learning
Nov 24, 2020



Abstract:Searches for low-surface-brightness galaxies (LSBGs) in galaxy surveys are plagued by the presence of a large number of artifacts (e.g., objects blended in the diffuse light from stars and galaxies, Galactic cirrus, star-forming regions in the arms of spiral galaxies, etc.) that have to be rejected through time consuming visual inspection. In future surveys, which are expected to collect hundreds of petabytes of data and detect billions of objects, such an approach will not be feasible. We investigate the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for the problem of separating LSBGs from artifacts in survey images. We take advantage of the fact that, for the first time, we have available a large number of labeled LSBGs and artifacts from the Dark Energy Survey, that we use to train, validate, and test a CNN model. That model, which we call DeepShadows, achieves a test accuracy of $92.0 \%$, a significant improvement relative to feature-based machine learning models. We also study the ability to use transfer learning to adapt this model to classify objects from the deeper Hyper-Suprime-Cam survey, and we show that after the model is retrained on a very small sample from the new survey, it can reach an accuracy of $87.6\%$. These results demonstrate that CNNs offer a very promising path in the quest to study the low-surface-brightness universe.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge