Alex B. Kiefer
EcoNet: Multiagent Planning and Control Of Household Energy Resources Using Active Inference
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Advances in automated systems afford new opportunities for intelligent management of energy at household, local area, and utility scales. Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) can play a role by optimizing the schedule and use of household energy devices and resources. One challenge is that the goals of a household can be complex and conflicting. For example, a household might wish to reduce energy costs and grid-associated greenhouse gas emissions, yet keep room temperatures comfortable. Another challenge is that an intelligent HEMS agent must make decisions under uncertainty. An agent must plan actions into the future, but weather and solar generation forecasts, for example, provide inherently uncertain estimates of future conditions. This paper introduces EcoNet, a Bayesian approach to household and neighborhood energy management that is based on active inference. The aim is to improve energy management and coordination, while accommodating uncertainties and taking into account potentially conditional and conflicting goals and preferences. Simulation results are presented and discussed.
Free Energy in a Circumplex Model of Emotion
Jul 02, 2024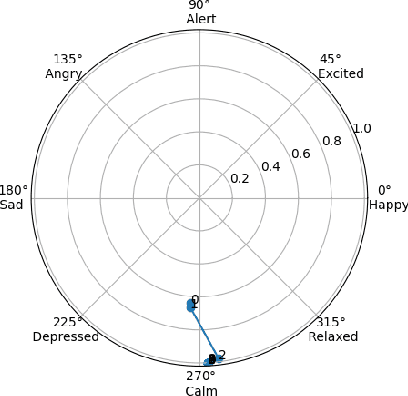
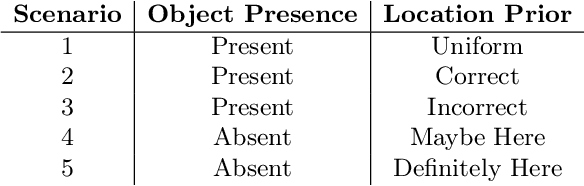

Abstract:Previous active inference accounts of emotion translate fluctuations in free energy to a sense of emotion, mainly focusing on valence. However, in affective science, emotions are often represented as multi-dimensional. In this paper, we propose to adopt a Circumplex Model of emotion by mapping emotions into a two-dimensional spectrum of valence and arousal. We show how one can derive a valence and arousal signal from an agent's expected free energy, relating arousal to the entropy of posterior beliefs and valence to utility less expected utility. Under this formulation, we simulate artificial agents engaged in a search task. We show that the manipulation of priors and object presence results in commonsense variability in emotional states.
Efficient search of active inference policy spaces using k-means
Sep 07, 2022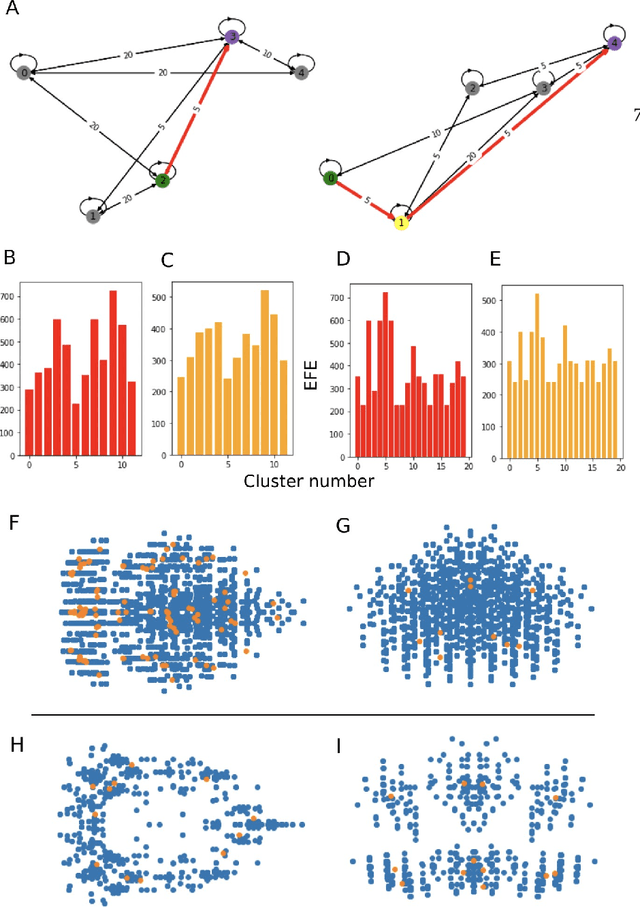
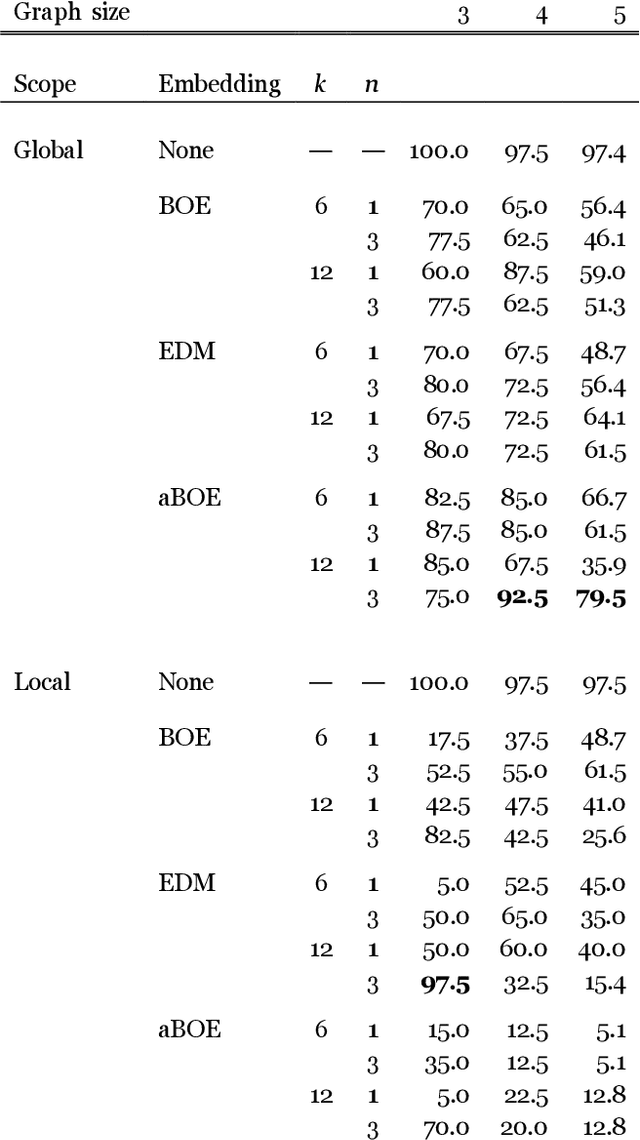
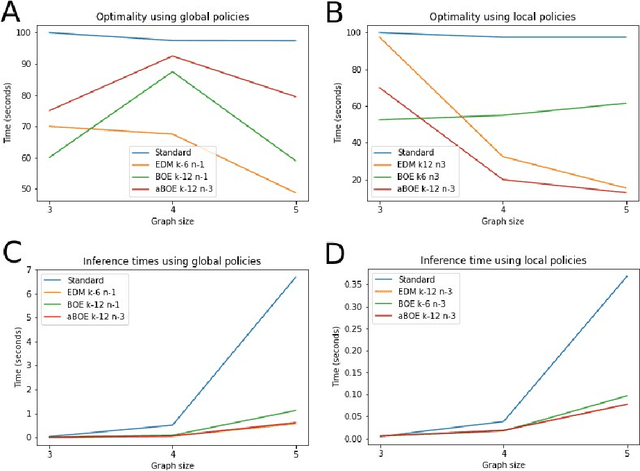
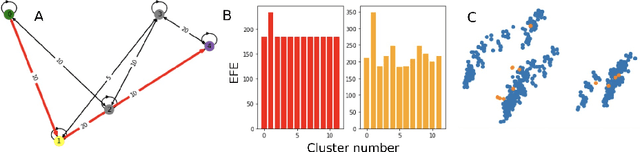
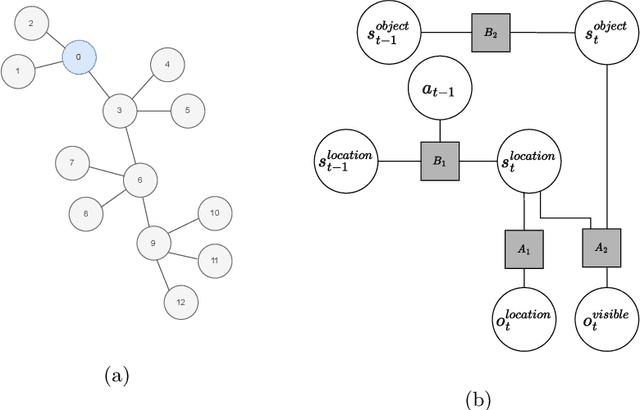
Abstract:We develop an approach to policy selection in active inference that allows us to efficiently search large policy spaces by mapping each policy to its embedding in a vector space. We sample the expected free energy of representative points in the space, then perform a more thorough policy search around the most promising point in this initial sample. We consider various approaches to creating the policy embedding space, and propose using k-means clustering to select representative points. We apply our technique to a goal-oriented graph-traversal problem, for which naive policy selection is intractable for even moderately large graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge