Alessio Fiorentino
DaRLing: A Datalog rewriter for OWL 2 RL ontological reasoning under SPARQL queries
Aug 05, 2020Abstract:The W3C Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a powerful knowledge representation formalism at the basis of many semantic-centric applications. Since its unrestricted usage makes reasoning undecidable already in case of very simple tasks, expressive yet decidable fragments have been identified. Among them, we focus on OWL 2 RL, which offers a rich variety of semantic constructors, apart from supporting all RDFS datatypes. Although popular Web resources - such as DBpedia - fall in OWL 2 RL, only a few systems have been designed and implemented for this fragment. None of them, however, fully satisfy all the following desiderata: (i) being freely available and regularly maintained; (ii) supporting query answering and SPARQL queries; (iii) properly applying the sameAs property without adopting the unique name assumption; (iv) dealing with concrete datatypes. To fill the gap, we present DaRLing, a freely available Datalog rewriter for OWL 2 RL ontological reasoning under SPARQL queries. In particular, we describe its architecture, the rewriting strategies it implements, and the result of an experimental evaluation that demonstrates its practical applicability. This paper is under consideration in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
Precomputing Datalog evaluation plans in large-scale scenarios
Jul 29, 2019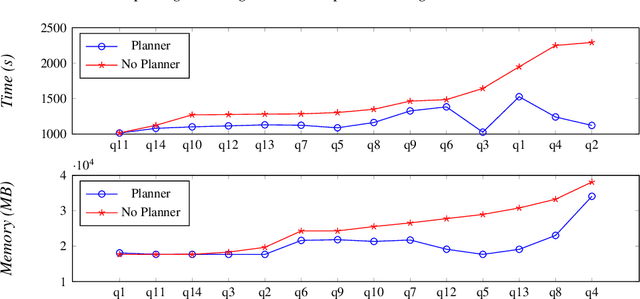
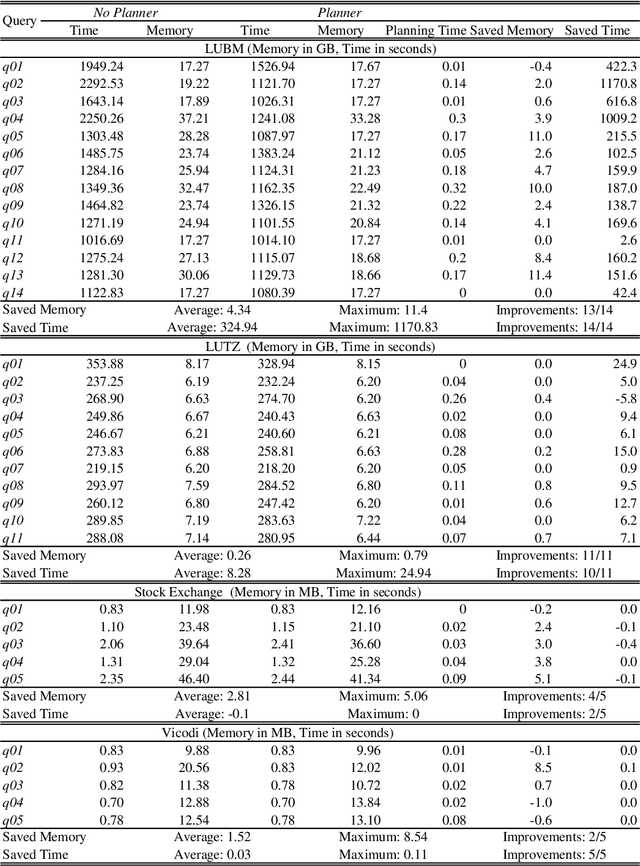
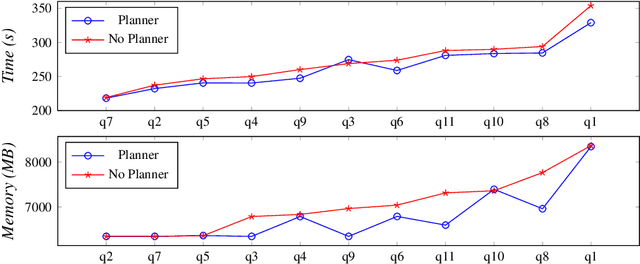
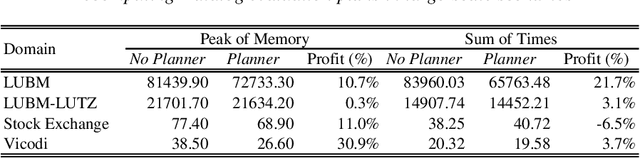
Abstract:With the more and more growing demand for semantic Web services over large databases, an efficient evaluation of Datalog queries is arousing a renewed interest among researchers and industry experts. In this scenario, to reduce memory consumption and possibly optimize execution times, the paper proposes novel techniques to determine an optimal indexing schema for the underlying database together with suitable body-orderings for the Datalog rules. The new approach is compared with the standard execution plans implemented in DLV over widely used ontological benchmarks. The results confirm that the memory usage can be significantly reduced without paying any cost in efficiency. This paper is under consideration in Theory and Practice of Logic Programming (TPLP).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge