Aleksandr Efimtcev
CNN-based fully automatic wrist cartilage volume quantification in MR Image
Jun 22, 2022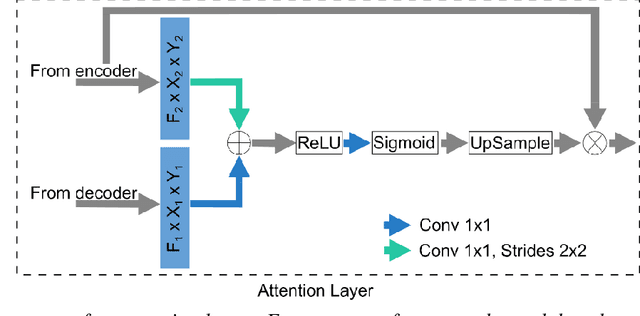
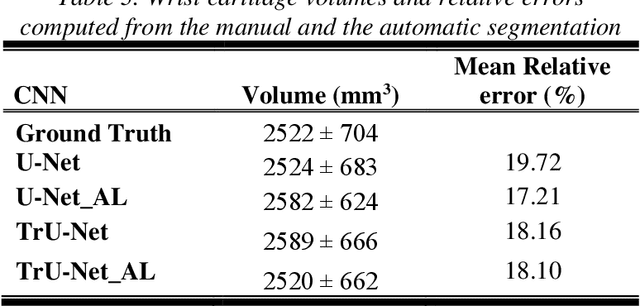
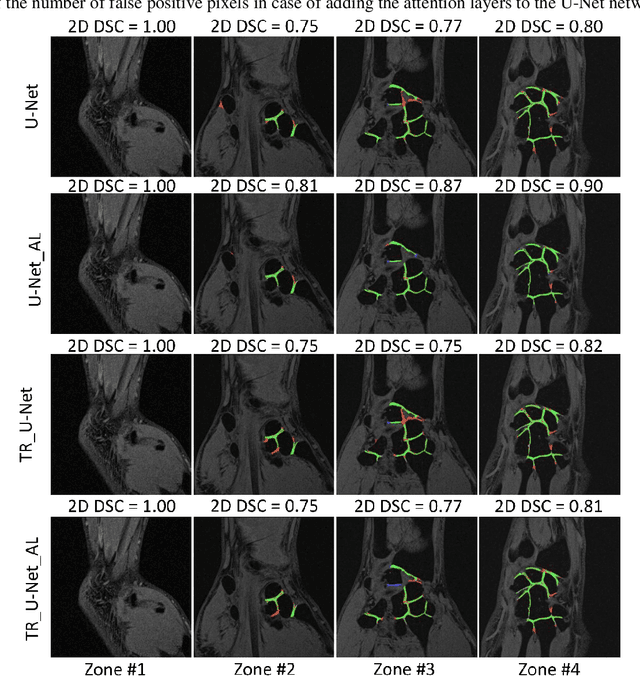
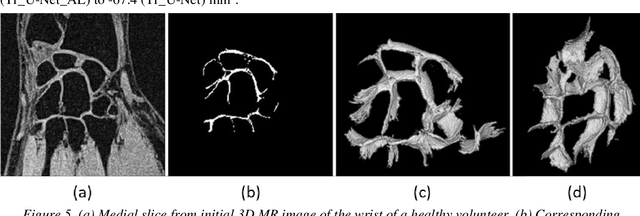
Abstract:Detection of cartilage loss is crucial for the diagnosis of osteo- and rheumatoid arthritis. A large number of automatic segmentation tools have been reported so far for cartilage assessment in magnetic resonance images of large joints. As compared to knee or hip, wrist cartilage has a more complex structure so that automatic tools developed for large joints are not expected to be operational for wrist cartilage segmentation. In that respect, a fully automatic wrist cartilage segmentation method would be of high clinical interest. We assessed the performance of four optimized variants of the U-Net architecture with truncation of its depth and addition of attention layers (U-Net_AL). The corresponding results were compared to those from a patch-based convolutional neural network (CNN) we previously designed. The segmentation quality was assessed on the basis of a comparative analysis with manual segmentation using several morphological (2D DSC, 3D DSC, precision) and a volumetric metrics. The four networks outperformed the patch-based CNN in terms of segmentation homogeneity and quality. The median 3D DSC value computed with the U-Net_AL (0.817) was significantly larger than the corresponding DSC values computed with the other networks. In addition, the U-Net_AL CNN provided the lowest mean volume error (17%) and the highest Pearson correlation coefficient (0.765) with respect to the ground truth. Of interest, the reproducibility computed from using U-Net_AL was larger than the reproducibility of the manual segmentation. U-net convolutional neural network with additional attention layers provides the best wrist cartilage segmentation performance. In order to be used in clinical conditions, the trained network can be fine-tuned on a dataset representing a group of specific patients. The error of cartilage volume measurement should be assessed independently using a non-MRI method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge